4117
Reproducibility and image quality of diffusion weighted imaging in volunteers with pancreas using different respiratory schemes
Yigang Pei1, Yu Bai1, Weiyin Vivian Liu2, Wenguang Liu1, and Wenzheng Li1
1Xiangya Hospital of the Central South University, China, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, China, China
1Xiangya Hospital of the Central South University, China, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research China, Beijing, China, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Pancreas, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques
DWI is essential in clinical diagnosis of pancreas. Image quality highly influence ADC measurements. Pancreases in abdomen easily suffers from artifact induced by abdominal and chest respiratory motion. A new diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequence was explored to better delineate pancreas in our previous study (named FOCUS-MUSE DWI). In this study, we compared the clinical utility of FOCUS-MUSE DWI, MUSE DWI, FOCUS DWI and SS DWI using four different breathing schemes (RT, NT, BH and FB) for the repeatability of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) measurements and image quality. Our results suggested that RT‑DWI provided the best ADC reproducibility and image quality among four breathing schemes on 3.0 T MRI, making it as the recommended protocol for clinical DWI of the pancreas.Background and Purpose
DWI is an essential MRI sequence in diagnostic pancreas imaging. It is non-invasive and easy to perform without the need for contrast administration. A new diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequence named FOCUS-MUSE DWI has been developed and used in the pancreatic imaging. The reliability of ADC measurements is essential to the assessment of treatment effect on patients with pancreatic disease. But, DWI is susceptible to intestinal gas, peristalsis, respiratory movement and other factors, Different respiratory compensation techniques such as free-breathing (FB), breath-hold (BH), respiratory-triggering (RT), and navigator-triggering (NT) are used to reduce physiologic motion artifacts, but there is no study systematic comparison of pancreatic imaging quality between FOCUS-MUSE DWI, MUSE DWI, FOCUS DWI and SS DWI with four different breathing schemes. Therefore, the aim of our study is to estimate the reliability of FOCUS-MUSE DWI with MUSE DWI, FOCUS DWI and SS DWI using four different breathing schemes and systematically compare the repeatability of ADC measurements and image quality.Methods
This prospective study was approved by our institutional review board-approved. 24 healthy volunteers (11 males and 13 females, 25 ± 2 years old) underwent pancreatic DWIs (b = 50, 800 s/mm2) on 3.0 T MRI (Signa Premier, GE Healthcare, USA). All volunteers were divided into four groups based on four different breathing schemes (RT, NT, BH and FB) and each group were all scanned with FOCUS-MUSE DWI, MUSE DWI, FOCUS DWI, and SS DWI. The scan parameters were kept the same as much as possible in four DWIs and all DWI sequences were scanned twice with an interval of 10 minutes. ADC were measured with three nonoverlapping approximately 16-mm² circular regions of interest (ROI) in three anatomic locations of pancreas (head, body and tail) 1. Image quality (4-point scale for each of severity of artifacts, sharpness of boundaries, interslice signal homogeneity and overall image quality)2 was also assessed. The sequence with the optimal clinical utility was determined by systematically comparing the ADC repeatability and image quality. Intra-observer and inter-observer repeatability of ADC values were analyzed using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC)3. An ICC over 0.75 represents a good agreement. To visual display for ADC repeatability, the Bland-Altman method was used to compare the 95 % confidence interval (limits of agreement [LOAs]) and the mean difference in ADC values between the first and second DWI scans. Differences were considered significant when P values are less than 0.05.Results
Among the four breathing schemes, RT with FOCUS-MUSE, MUSE, FOCUS and SS DWI all had more reliable intra-observer agreement (intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC): 0.855-0.954 (head), 0.904-0.974 (body), 0.907-0.973 (tail); all P > 0.05) and inter-observer agreement (ICC: 0.940-0.989 (head), 0.921-0.936 (body), 0.884-0.962 (tail); all p > 0.05) than NT, BH, FB. For example, in the ADC measurements between reader 1 and reader 2 with RT, the inter-observer agreement for the pancreatic head (0.989) was higher than RT (0.985), BH (0.945) and FB (0.976, P < 0.05) in FOCUS-MUSE DWI. RT-DWIs had better repeatability of ADC measurement at almost DWI sequences in the three anatomy locations (mean ADC differences: 13.23-42.97 ×10 −6 mm2 /s (head), -1.74 - -58.51 ×10 −6 mm2 /s (body), 4.57-29.99 ×10 −6 mm2 /s (tail)) (Fig 1). Furthermore, DWIs with RT had better image quality than BH and FB (some P < 0.05) and similar image quality with NT (P > 0.05) in terms of severity of artifacts, sharpness of boundaries, interslice signal homogeneity and overall image quality (Fig 2).Discussion and conclusions
Our study showed RT with FOCUS-MUSE, MUSE, FOCUS and SS DWI possessed better reproducibility for ADC values than NT, BH and FB with DWIs on 3.0 T MRI. In our study, DWIs with RT gained a better image quality than BH and FB (some P < 0.05) and had similar image quality to NT (P > 0.05). RT, NT and BH all can reduce the artifacts in DWI protocols, both RT and NT can improve the ADC measurements, image quality, detection of lesions, and BH can reduce scanning time and also improve lesion detection. In our study, four different DWI with RT provide better reproducibility for ADC values and good image quality than other trigger-to-acquisition approaches on 3.0 T MRI, and was recommended for pancreas DWI.Acknowledgements
Not applicable.References
1. Bai Y, Pei Y, Liu WV et.al. MRI: Evaluating the Application of FOCUS-MUSE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the Pancreas in Comparison With FOCUS, MUSE, and Single-Shot DWIs. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022 Aug 27.
2. Tanabe M, Higashi M, Benkert T, et al. Reduced field-of-view diffusionweighted magnetic resonance imaging of the pancreas with tilted excitation plane: A preliminary study. J Magn Reson Imaging 2021;54(3):715-720.
3. Xie S, Masokano IB, Liu W, Long X, Li G, Pei Y, Li W. Comparing the clinical utility of single-shot echo-planar imaging and readout-segmented echo-planar imaging in diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver at 3 tesla. Eur J Radiol. 2021 Feb;135:109472.
Figures
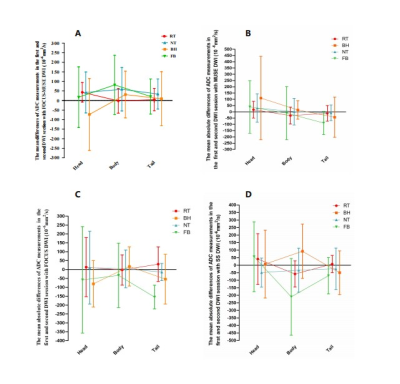
Fig 1. Repeatability of ADC
measurements in head, body and tail of four pancreas DWI sequences with four
different kinds of triggering RT, NT, BH and FB. RT-DWI had the almost lower
bias as it has values closer to the zero point in pancreas head, body and tail,
which suggests that RT-DWI has better ADC measurement repeatability.
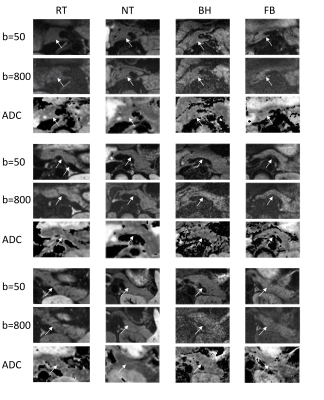
Fig 2. Comparisons of image
quality of RT-, NT-, BH-, and FB - DWI. Diffusion-weighted trace images at two different
b-values (50, 800 s/mm2) with the corresponding ADC maps are
arrayed.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4117