4088
3D Deep Learning Segmentation of White Matter Hyperintensity on 3T and 7T Brain MRI Scans1University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, United States, 2Temple University, Philadelphia, PA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: High-Field MRI, Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence
White matter lesions (WMLs), commonly found as hyperintensities (WMHs) on T2-weighted FLAIR MR brain images, are associated with neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. In the present study, we adapted a 3D U-Net deep learning method to automatedly segment the WMHs on 3T and 7T MRI T2w FLAIR brain images. Using 3D U-Net, the accuracy of WMH segmentation is 98.8% for 3T data, while it drops to 90.3% for 7T data. However, after incorporating histogram matching in the preprocessing, the accuracy of WMHs segmentation significantly improves to 97.5% for 7T data.Introduction
White matter hyperintensities (WMHs) is associated with vascular dementia [1], Alzheimer’s disease [1], and late-onset late-life depression (LLD) [2]. We and others have previously developed conventional semi-automated or automated segmentation methods for quantifying and localizing WMHs [3][7]. Recently a number of deep learning-based segmentation methods have been proposed [4][8]. All these methods focus primarily on the segmentation of WMHs using 3T MRI data. With growing research and clinical applications of ultra-high field 7T MRI, and with the lack of WMH segmentation method on 7T data, in this study we aim to develop a 3D U-NET deep learning method to segment WMHs on 3T and 7T MRI images.Methods
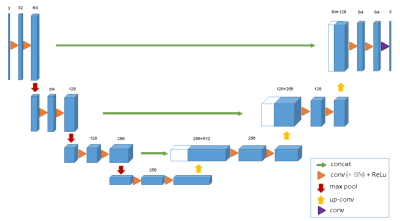
3T and 7T dataset: 3T data include T2w FLAIR images on 160 elderly adults (age average 76.3, 55 males and 105 females). WMH on 3T data were segmented using an automated pipeline previously developed in our lab [3][7], and the resulted WMH masks were visually inspected to ensure accurate segmentation and were used as the ground truth for training/testing the 3D U-Net. WMHs on 7T data were hand traced data include T2w FLAIR images on 49 elderly adults (age: average 68.4, 14 males and 35 females) and these manually traced WMH masks served as the ground truth for 7T data.Neural Network Architecture: To segment WMHs on 3T and 7T MRI scans, we use a 3D U-Net [5] which is a 3D convolutional neural network that applied on semantic segmentation (Figure 1). 3D U-Net is a state-of-the-art neural network which is based on the encoder-decoder structure [5]. We adapted the following configuration: using 3*3 kernel convolution as convolutional layer and after each conv layer we insert a 3D batch normalization and a max pooling layer with 2*2 kernel. The activation function that we use is rectified linear unit (ReLU) which is same with the standard U-Net. In the decoder part, instead of 3D up-sampling, we use 3D transpose convolution with 2*2 kernel. This is because the transpose convolution provides more learnable parameters and can perform higher performance compared with up-sampling. The optimizer that we use is Adam optimizer and the learning rate is 1e-3 for both 3T and 7T images. Since 3D U-Net requires very large graphic memory, we can only set the batch size to 1. After 10 epochs of training, we test our model with unseen data and compare the prediction result with the ground truth.
The Nyul algorithm for intensity standardization: For the 7T scans preprocessing, we used the Nyul normalizer [6] for matching the intensity histogram of 7T T2w FLAIR images with 3T T2w FLAIR images. Specifically, the Nyul algorithm uses a non-uniform piece-wise trapezoidal Riemann approximation. Visually, after histogram matching preprocessing, the 7T images look brighter and less noise compared to the original 7T scans.
Results
For the 3T WMH segmentation, the training accuracy was 98.8% and testing accuracy was 98%. Using the same network architecture, the training accuracy for 7T data is 95.2%, for testing data is 90.3%. After applying histogram matching in the preprocessing, the segmentation accuracy of 7T data is comparable to 3T data, increasing to 97.5%.Discussion and Conclusion
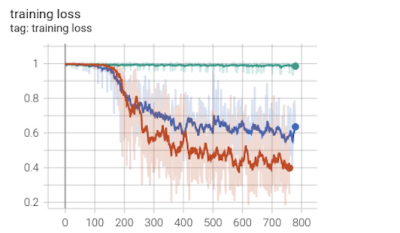
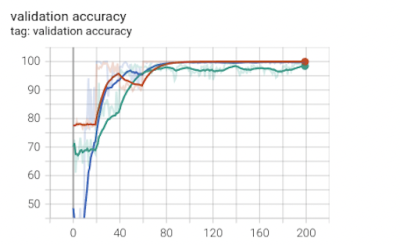
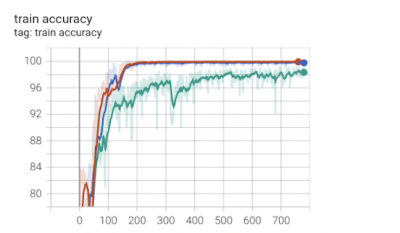
In this work, we use 3D U-Net to segment WMHs on 3T and 7T T2w-FLAIR data. We found out that after preprocessing of 7T images for histogram matching and intensity standardization, the segmentation accuracy enormously improved. Specifically, Figures 2-4 show that for the 7T 3D U-Net model the training loss, validation accuracy, training accuracy, and testing accuracy consistently improved for 7T data with intensity histogram matching versus those without.Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the University of Pittsburgh Center for Research Computing through the resources provided and the NIH funding: R01 AG067018, RF1 AG025516, R01 AG063525, R01 MH111265, and R56 AG074467.
References
[1] Alber J, Alladi S, Bae HJ, Barton DA, Beckett LA, Bell JM, Berman SE, Biessels GJ, Black SE, Bos I, Bowman GL, Brai E, Brickman AM, Callahan BL, Corriveau RA, Fossati S, Gottesman RF, Gustafson DR, Hachinski V, Hayden KM, Helman AM, Hughes TM, Isaacs JD, Jefferson AL, Johnson SC, Kapasi A, Kern S, Kwon JC, Kukolja J, Lee A, Lockhart SN, Murray A, Osborn KE, Power MC, Price BR, Rhodius-Meester HFM, Rondeau JA, Rosen AC, Rosene DL, Schneider JA, Scholtzova H, Shaaban CE, Silva NCBS, Snyder HM, Swardfager W, Troen AM, van Veluw SJ, Vemuri P, Wallin A, Wellington C, Wilcock DM, Xie SX, Hainsworth AH. White matter hyperintensities in vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID): Knowledge gaps and opportunities. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2019 Apr 9;5:107-117. doi: 10.1016/j.trci.2019.02.001. PMID: 31011621; PMCID: PMC6461571.
[2] Wu, M., Aizenstein, HJ., (2017). The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry: The Multi-Faceted Relationship between White Matter Lesions and Late-Life Depression.
[3] Ding, T., Cohen, AD., O’Connor, EE., Karim, HT., Crainiceanu, A., Muschelli, J., Lopez, O., WE Klunk, WE., Aizenstein, HJ, Krafty, R., Crainiceanu, CM., Tudorascu, DL. (2020), NeuroImaging: Clinical, An improved algorithm of white matter hyperintensity detection in elderly adults.
[4] Park, G., Hong J., Duffy, BA., Lee, JM., Kim, H., White matter hyperintensities segmentation using the ensemble U-Net with multi-scale highlighting foregrounds. 2021 May, NeuroImage Volume 237, 15 August 2021, 118140.
[5] Özgün Ç., Ahmed A., Soeren S. L., Thomas B., Olaf R., (2016). Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition: 3D U-Net: Learning Dense Volumetrci Segmentation from Sparse Annotation.
[6] Jesse K., Graham W. T., April K., (2017). Journal of Computational Vision and Imaging Systems: Equivalence of histogram equalization, histogram matching and the Nyul algorithm for intensity standardization in MRI.
[7] Wu, M., Rosano C., Butters, M., Whyte, E., Nable, M., Crooks, R., Meltzer, CC., Reynolds III, CF., Aizenstein HJ., (2006), Psychiatry Research: NeuroImaging, A full automated method for quantifying and localizing white matter hyperintensities on MR images.
[8] Zhao, X., Sicilia, A., Minhas, DS., O’Connor, EE., Aizenstein, HJ., Klunk, WE., Tudorascu, DL., Hwang, SJ., (2021), 2021 IEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Robus white matter hyperintensity segmentation on unseen domain.
Figures