4067
Quiet Lumbar Spine MR Imaging: Preliminary Study with Different Noise Reduction Factors
Jiageng Shen1, Ailian Liu1, Qingwei Song1, Shuheng Zhang2, and Guobin Li2
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Muscle, Spinal Cord
To evaluate the clinical value of quiet T1WI and T2WI sequences in lumbar spine imaging with different noise reduction factors (RFs).Summary of Main Findings
Without degrading image quality and increased patient satisfaction, quiet T1WI and T2WI sequences with RF of 0.6 may be promising in clinical lumbar spine imaging.Materials and methods
Twenty volunteers (5 females and 15 males, average age 50.75±16.29 years) were recruited. All lumbar spine MR images were performed on a 3.0T MR scanner (uMR Omega, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China) using conventional protocol (sagittal T1WI and T2WI without noise reduction, RF = 1.0) and quiet protocol (RF = 0.8, 0.6, 0.4 and 0.2). Sound pressure levels (SPLs) were recorded. Signal to noise ratio (SNR) as well as contrast to noise ratio (CNR) of vertebral body and intervertebral disc were analyzed by two independent observers. Image quality was evaluated on a 4-point scale by the same observers. Kappa test was used to assess the interobserver agreement. Comparisons between the conventional sequences and quiet sequences were assessed by Wilcoxon test.Results
The SPLs of sequences acquired with RF ranged from 1.0 to 0.2 were 99.4, 91.2, 83.4, 82.3, and 79.8 dB on T1WI, and 97.0, 94.0, 83.0, 79.0, and 75.0 dB on T2WI, respectively. Agreement between two observers was good (Kappa: 0.823-0.831). No significant differences were observed for subjective scores, SNR and CNR of vertebral body between RFs (1.0, 0.8 and 0.6) on both T2WI and T1WI sequences. However, there were significant differences in SNR, CNR and qualitative scores between conventional sequences with quiet sequences (RF = 0.4, 0.2) (p<0.01). Additionally, the subjective scores of T1WI and T2WI (RF = 0.4, 0.2) were significantly lower than those of the conventional sequences (p<0.05).Discussion and Conclusions
The SPLs of quiet lumbar spine MR decreased gradually with the increase of RFs. Sound pressure was reduced by 84% and 80% for T1WI and T2WI with RF of 0.6, respectively. The performance of quiet lumbar spine T1WI and T2WI sequences (RF = 0.6) was comparable in comparison with conventional sequences.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]Yang G, Yu S, Dong, H,ect. DAGAN: Deep De-Aliasing Generative Adversarial Networks for Fast Compressed Sensing MRI Reconstruction. IEEE T MED IMAGING. 2018-06-01;37(6):1310-1321.
[2] Hennel, F. Fast spin echo and fast gradient echo MRI with low acoustic noise. J MAGN RESON IMAGING. 2001-06-01;13(6):960-6.
Figures
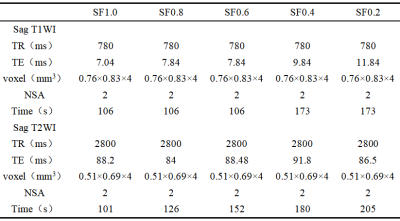
Table 1 Each sequence scan parameter
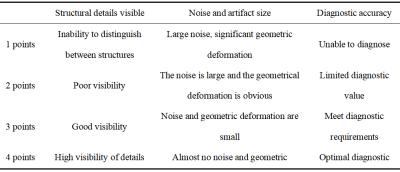
Table 2 Table of subjective scoring criteria
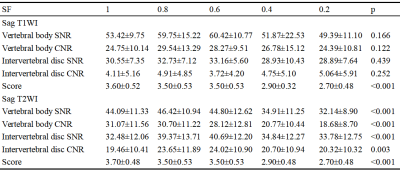
Table 3 Difference comparison of objective evaluation of different SF
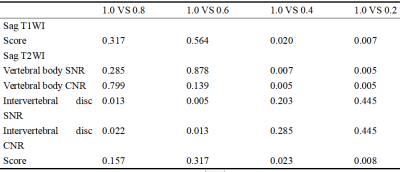
Table 4 Pairwise comparison of objective and subjective scores of different SF (p value)
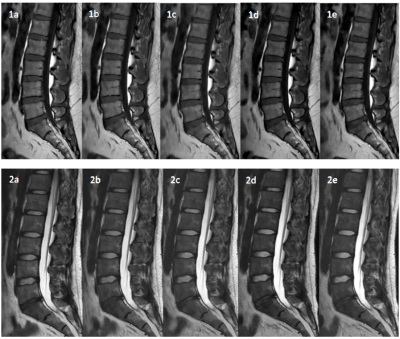
Figures 1a-1e sagittal T1WI-TSE sequences with RFs of 1.0, 0.8, 0.6, 0.4, and 0.2, respectively; 2a-2e are sagittal T2WI-TSE sequences with RFs of 1.0, 0.8, 0.6, 0.4, and 0.2, respectively
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/4067