3986
Accelerated 3D free-breathing MRCP using Relaxation-Enhanced MAgnetization-prepared radial stack-of-STARs (REMASTAR) and Compressed SENSE1Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 2Division of Radiology, Miyazaki University Hospital, Miyazaki, Japan, 3Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Miyazaki, Miyazaki, Japan, 4Department of Radiology, Kumamoto Chuo Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan
Synopsis
Keywords: Pancreas, Pancreas, MRCP
3D TSE RT is commonly used to MRCP imaging. But the image qualities of them are unstable especially in patients with irregular respiratory motion and tachypnea. A T2-prepared pulse is often used to emphasize long T2 component such as CSF, bile, and pancreatic duct. A 3D VANE has been applied in abdominal imaging as a useful free-breathing technique. We attempted to combine bTFE based on 3D VANE with magnetization T2prep pulses (3D REMASTAR) for MRCP instead of, otherwise in addition to 3D TSE RT. We have demonstrated the feasibility of 3D REMASTAR MRCP particularly in subject with unstable respiratory motion.INTRODUCTION
Respiratory-triggered 3D heavily T2 TSE (3D TSE RT) is commonly used to MRCP imaging, but the image quality (IQ) of 3D TSE RT are unstable especially in patients with irregular respiration and/or tachypnea1. Recently, clinical usefulness of breath-hold 3D MRCP using either compressed SENSE or GRASE has been reported2,3. However, the IQ of those techniques are significantly degraded in patient with failed breath-holding. A balanced turbo field-echo (bTFE) based MRCP is also helpful sequence in addition to conventional MRCP for assessment of the pancreaticobiliary duct system4,5. T2-prepared (T2prep) pulse is often used to suppress signal from static tissues, such as muscles, nerves and organs, and to enhance blood-to-tissue contrast based on their difference in relaxation times in non-contrast MRA technique6. Namely, it can be extended to emphasize long T2 component, such as bile and pancreatic duct. Furthermore, 3D pseudo golden angle radial stack-of-stars (3D VANE) allows free-breathing acquisition for abdominal imaging and combining navigator echo is helpful to improve the IQ7. We attempted to combine bTFE 3D VANE with T2prep pulses called Relaxation-Enhanced MAgnetization prepared radial stack-of-STARs (3D REMASTAR) for free-breathing MRCP. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the feasibility of 3D REMASTAR for free-breathing MRCP imaging.METHODS
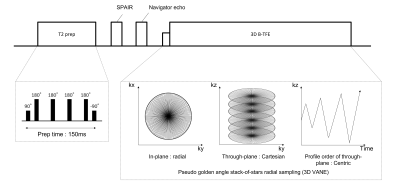
Six subjects underwent MRCP using 3D TSE RT and 3D REMASTAR on 3.0T scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare). The subjects obtained informed consent and approved by institutional review board. Imaging parameter for 3D REMASTAR was shown in Tabel 1 and sequence diagram was shown in Fig. 1. The technical implementation is following.Enabling high contrast of bile and pancreatic duct: A long T2prep pulse consisting of four adiabatic refocusing pulses is applied to emphasize T2 contrast of long T2 component, such as bile and pancreatic duct. SPAIR pulse combines with centric profile order in kz-direction is used to attenuate fat signal uniformly. In addition, shot interval time of 1000ms is applied to increase the contrast of bile and pancreatic duct while suppressing fat signals efficiently. To increase the effect of both pre-pulses, transient-state signal is filled at the center of k-space with no startup echoes.
Reducing artefacts: Since bTFE theoretically provides high SNR, a low flip angle such as 35 degree was used to shorten TE/TR to prevent banding artefact due to B0 inhomogeneity especially in 3.0T. To reduce artefact due to eddy current, all Z phase encodings for a given Y phase encoding are measured in subsequent shots with a golden-angle manner. Furthermore, utilizing compressed SENSE reconstruction framework is helpful for reducing the noise artefacts.
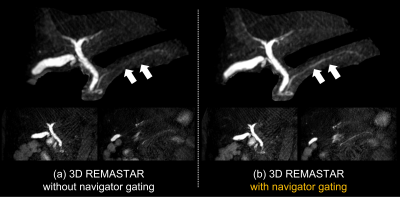
Additional motion robustness techniques: For more robustness against respiratory motion, we combine 3D VANE with navigator gating techniques. The data only accepted when the position of the diaphragm falls within a gating window, it promises to improve the IQ.
RESULTS & DISCUSSION
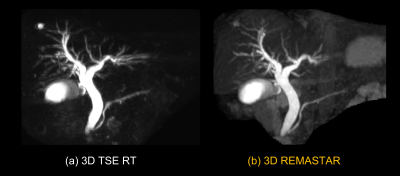
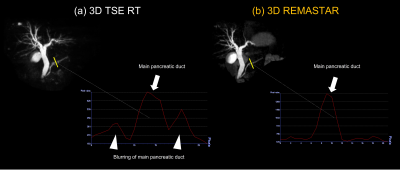
Fig. 2 shows a comparison of MRCP images of 3D REMASTAR and 3D TSE RT and Fig. 3 shows signal profile curves of main pancreatic duct (MPD) on those images. Visualization of MPD and bile duct on 3D REMASTAR were clearly sharper than those on 3D TSE RT. It suggested our proposed 3D REMASTAR was less sensitive to unstable respiratory motion. In subjects without dilated MPD, the visualization of MPD on 3D REMASTAR was lower due to the high background pancreatic signal than 3D TSE RT. Fig. 4 shows the comparison of 3D REMASTAR with/without navigator gating. 3D REMASTAR with navigator gating was improved IQ than without it.CONCLUSION
We have demonstrated the feasibility of 3D REMASTAR MRCP particularly in subject with unstable respiratory motion. Adding, or even replacing 3D REMASTAR sequence to conventional 3D TSE MRCP may be helpful to improve the diagnostic performance for evaluation of pancreaticobiliary duct system.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. T. Nakaura, et al. Usefulness of the SPACE pulse sequence at 1.5T MR cholangiography: Comparison of image quality and image acquisition time with conventional 3D-TSE sequence. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 38 (5) (2013) 1014–1019
2. M. Yoshida, et al. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography with GRASE sequence at 3.0T: does it improve image quality and acquisition time as compared with 3D TSE? Eur Radiol. 2018 Jun;28(6):2436-2443.
3. M. He, et al. Comparison and Evaluation of the Efficacy of Compressed SENSE (CS) and Gradientand Spin-Echo (GRASE) in Breath-Hold (BH) Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Mar;51(3):824-832.
4. Y. Noda, et al, Improved diagnosis of common bile duct stone with single-shot balanced turbo field-echo sequence in MRCP. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017 Apr;42(4):1183-1188.
5. F. C. Hasse, et al, Balanced steady‑state free precession MRCP is a robust alternative to respiration‑navigated 3D turbo‑spin‑echo MRCP. BMC Med Imaging. 2021 Jan 11;21(1):10
6. M. Yoneyama, et al. Free-breathing non-contrast-enhanced flow-independent MR angiography using magnetization-prepared 3D non-balanced dual-echo Dixon method: A feasibility study at 3 Tesla. Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Aug 16;63:137-146.
7. K. Kajita, et al, Thin-slice Free-breathing Pseudo-golden-angle Radial Stack-of-stars with Gating and Tracking T1-weighted Acquisition: An Efficient Gadoxetic Acid-enhanced Hepatobiliary-phase Imaging Alternative for Patients with Unstable Breath Holding. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2019 Jan 10;18(1):4-11.
Figures