3966
Black Blood Cardiac Diffusion Imaging using Second Order Motion Compensation and Double Inversion Recovery
Yishi Wang1, Zhen Zhang2, Rui Wang2, Xiuzheng Yue1, Fang Wang2, Rongrong Zhu2, and Ruoshui Ha2
1Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, 2Medical Imaging Center, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan, China
1Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, 2Medical Imaging Center, People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Pulse Sequence Design, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, Cardiac Diffusion, Black Blood, Motion Compensation
Second-order motion-compensated diffusion imaging is a robust solution for cardiac diffusion imaging but prone to bright blood signals due to motion compensation itself. In this work, we incorporated black blood module into second-order motion-compensated sequence to achieve cardiac diffusion imaging with blood signal suppressed.Introduction
As an emerging motion compensation technique, a second-order motion-compensated spin echo (M2-SE) sequence can be used to reduce the signal loss for cardiac diffusion imaging [1]. However, the signal of the flowing blood is also compensated to induce a bright blood signal in the acquired diffusion images. Double inversion recovery (DIR) is a common scheme to obtain black blood images of the heart such as in T2 weighted images. This study aimed to combine M2-SE and DIR to achieve robust black blood cardiac diffusion imaging.Methods
The combination of DIR and M2-SE was implemented on the Philips MR platform. The sequence was tested on two healthy volunteers on two different 3T scanners (Ingenia CX and Ingenia Elition X, Best, the Netherlands). The sequence diagram was shown in Figure 1. All diffusion weighted images were acquired in the short-axis plane using two schemes on each scanner. One used M2-SE combined with DIR and the other used M2-SE only. The sequence was performed with an ECG trigger and breath hold. The inversion delay of DIR was calculated automatically according to the heart rate and the repetition time was set to 2 heartbeats. The ECG trigger delay was set to mid-systole according to a previous study. The detailed scan parameters are shown in Table 1.Results
Figure 2 showed the images of the first volunteer. There was a hyperintensity blood signal in the b=0 image using M2-SE only, while the signal contamination from the blood pool was well suppressed in the images of all three b values when DIR was combined with M2-SE. Figure 3 showed the images of b=400 s/mm2 of the second volunteer. There was an obvious residual blood pool signal in the image from M2-SE while the blood signal was well suppressed in M2-SE with DIR.Discussion and conclusion
M2-SE is an effective method for cardiac diffusion imaging as an alternative to stimulated echo method. However, the motion-compensated diffusion encoding gradient also compensated the blood flow signal which may hamper the observation of real changes in the myocardium. We incorporated DIR for blood signal suppression into M2-SE to achieve black blood cardiac DWI and showed its feasibility on two different 3T scanners. Further study should be performed to evaluate its clinical value with a larger cohort.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Stoeck, et.al. Second-order motion-compensated spin echo diffusion tensor imaging of the human heart. MRM, 2016.Figures
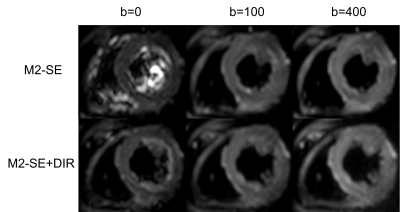
Figure 1. The images of the first volunteer
acquired on Elition 3T scanner. The scanner was equipped with a gradient system
which has a maximum amplitude of 45 mT/m and a maximum slew rate of 220 mT/(m*ms).
The blood signal in the b0 image was well suppressed using DIR+M2-SE compared
to M2-SE only.
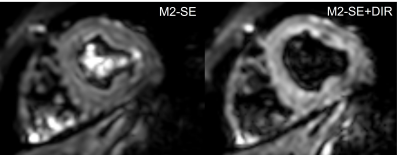
Figure 2. The images of the second
volunteer acquired on CX 3T scanner. The scanner was equipped with a gradient
system which has a maximum amplitude of 80 mT/m and a maximum slew rate of 100
mT/(m*ms). The blood signal in the b=400 image was well suppressed using DIR+M2-SE
compared to M2-SE only.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/3966