3954
Comparison of uniform-density, variable-density and dual-density spiral samplings for multi-shot diffusion-weighted imaging1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, United States, 3Radiology, C.J. Gorter Center for High-Field MRI, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, Netherlands, 4Philips Research, Hamburg, Germany, 5Center for MR Research and Departments of Radiology, Neurosurgery, and Biomedical Engineering, University of Illinois College of Medicine at Chicago, Chicago, IL, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Data Acquisition, Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Different multi-shot spiral sampling schemes have been developed for high-resolution DWI. However, the performances of these sampling strategies such as variable-density spiral (VDS), dual-density spiral (DDS) and uniform-density spiral (UDS) have not been compared comprehensively. In this study, we compare multi-shot UDS, VDS and DDS in brain DWI in terms of inter-shot phase error correction, overall image quality and SNR performance. Both theoretical analysis and in-vivo results demonstrate that UDS exhibits the best off-resonance performance among the three spiral sampling patterns. Additionally, UDS achieves the highest SNR in diffusion imaging over the VDS and DDS acquisitions.Introduction
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has been widely used in clinical diagnosis and neuroscience research. Various multi-shot spiral samplings have been successfully developed to achieve high-resolution DWI 1-4. For multi-shot DWI, one primary issue is to correct for phase variations among different shots. The phase variations can be measured, either by acquiring extra navigator signals or by computing this information from imaging echoes. According to the ways of acquiring the phase information, corresponding spiral sampling strategies can be divided into three main categories, variable-density spiral (VDS) 5, dual-density spiral (DDS) 6 and uniform-density spiral (UDS) 7. However, to our knowledge, their performances in terms of image quality and efficiency have not been fully compared. Moreover, their off-resonance and SNR performances are unclear and worthy of investigation. In this study, we carried out a comprehensive comparison to investigate the performances of UDS, VDS and DDS for multi-shot diffusion imaging.Methods
1. Spiral trajectories designTo set up a fair comparison, the number of interleaves and the readout durations of these spiral samplings are kept the same. Under-sampling along the radial direction 8 is adopted to increase the radial spacing of DDS and VDS so that their readout durations can be reduced to the same length as UDS.
2. Data acquisition
All experiments were performed on an Ingenia CX 3.0T scanner (Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands) using a 32-channel head coil. The gradient system was operated at a maximum gradient strength of 31 mT/m and with a maximum slew rate of 200 T/m/s.
Experiment 1, 4-shot acquisition: FOV=210×210mm2, resolution=1.28×1.28mm2, matrix=164×164, b value=1000 s/mm2, 12 diffusion directions, TE/TR=55/3000ms, readout duration=26.0ms.
Experiment 2, 6-shot acquisition: FOV=210×210mm2, resolution=0.99×0.99×4.0mm3, acquisition matrix=212×212, b value=1000 s/mm2, 12 diffusion directions, TE/TR=55/3000ms, readout duration=26.0ms. In all experiments, SPIR technique was used to suppress fat signals. In addition, low-resolution field maps acquired using a multi-echo GRE sequence were used for deblurring. The 2D T2-weighted TSE images and T2W-FLAIR images were acquired as anatomical references. The resolution of the anatomical images matches the spiral DWI images of each scan.
3. Image reconstruction and processing
The diffusion images were off-line reconstructed using the POCS-ICE algorithm 9, followed by off-resonance correction. Color-coded FA maps were calculated using FSL toolbox 10. SNR performance of the three spiral samplings was evaluated using a Monte Carlo-based pseudo multiple replica method 11.
Results and Discussion
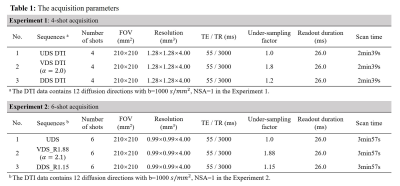
1. Off-resonance performanceFigure 1 show the mean DWI with an in-plane resolution of 0.99×0.99mm2 acquired by 6-shot UDS, VDS and DDS acquisitions, respectively. Six representative slices of the same subject from Experiment 2 are shown. The T2W-FLAIR images are shown in the bottom row as anatomical references. In general, the UDS-, VDS- and DDS-based diffusion images all provide satisfactory anatomic integrity and geometric fidelity in the regions where the B0 inhomogeneity is not so severe. Residual blurring artifacts (yellow dashed circle) can be observed in the deblurred DDS images. There is a slight error in the VDS images (yellow arrow head). UDS exhibits the lowest static B0 off-resonance artifacts. This in vivo results indicate that UDS has better off-resonance performance than DDS and VDS. Thus UDS is suitable for high-efficiency diffusion imaging with long spiral readouts because it is less vulnerable to off-resonance effect.
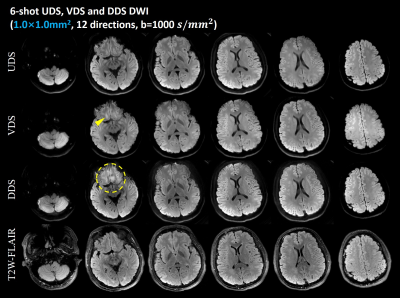
Figure 2 shows the color-coded FA maps obtained by the 6-shot UDS, VDS and DDS samplings from Experiment 2. Seven slices are shown. Multi-shot UDS, VDS and DDS diffusion imaging can provide correct DTI metrics. However, it is obvious that the cFA results of DDS DW images are a little noisy compared to other two counterparts.
2. Inter-shot phase error correction
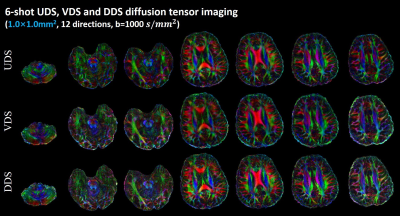
Figure 3 shows the evolutions of estimated phases of 4 shots during the POCS-ICE iterative reconstruction for one set of the in vivo data from Experiment 1. The phase errors of each shot are estimated from the central k-space data, which is densely sampled for VDS and DDS, but under-sampled for UDS. The estimated phases for VDS and DDS after one iteration was very close to the final iteratively updated inter-shot phase. In comparison, more number of iterations are required to reach a stable estimation of shot-to-shot phase errors for UDS than for the other two spirals.
3. SNR performances
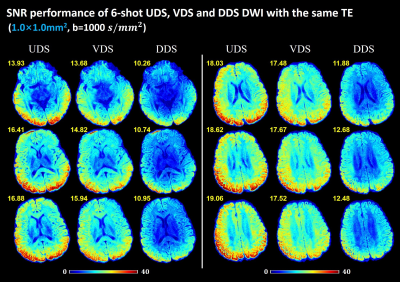
Figure 4 shows the SNR maps of b=1000 s/mm2 diffusion images with in-plane resolution of 0.99mm2 acquired by the three spiral acquisitions from Experiment 2. The SNR maps from six representative slices are shown. The corresponding mean SNR value across the whole brain is marked in the upper left corner of the image. UDS shows the best SNR performance among the three spiral samplings in the diffusion images with the same TE.
Conclusion
This study performed a comprehensive comparison of UDS, VDS and DDS acquisitions for multi-shot diffusion imaging. The results demonstrate that UDS provides superior off-resonance performance and SNR performance over VDS and DDS samplings.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1 Liu C, Bammer R, Kim Dh, Moseley ME. Self-navigated interleaved spiral (SNAILS): application to high-resolution diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med 2004;52:1388–1396.
2 Liu C, Moseley ME, Bammer R. Simultaneous phase correction and SENSE reconstruction for navigated multi-shot DWI with non-cartesian k-space sampling. Magn Reson Med 2005;54:1412–1422.
3 Truong TK, Chen NK, Song AW. Inherent correction of motion-induced phase errors in multishot spiral diffusion-weighted imaging. Magn Reson Med. Oct 2012;68(4):1255-61.
4 Truong TK, Guidon A. High-resolution multishot spiral diffusion tensor imaging with inherent correction of motion-induced phase errors. Magn Reson Med. Feb 2014;71(2):790-6.
5. Kim DH, Adalsteinsson E, Spielman DM. Simple analytic variable density spiral design. Magn Reson Med. Jul 2003;50(1):214-9. 6. Lin W, Börnert P, Huang F, Duensing GR, Reykowski A. Generalized GRAPPA operators for wider spiral bands: rapid self-calibrated parallel reconstruction for variable density spiral MRI. Magn Reson Med. Oct 2011;66(4):1067-78
7. Glover GH. Simple analytic spiral K-space algorithm. Magn Reson Med. Aug 1999;42(2):412-5.
8. Li G, Ye X, Shao X, et al. Four-shot Navigator-free Spiral Acquisition Strategy for High-resolution Diffusion Imaging. In: Proceedings of the 29th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. 2021. p1328.
9. Guo H, Ma X, Zhang Z, Zhang B, Yuan C, Huang F. POCS-enhanced inherent correction of motion-induced phase errors (POCS-ICE) for high-resolution multishot diffusion MRI. Magn Reson Med. Jan 2016;75(1):169-80.
10. Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Smith SM. FSL. Neuroimage 2012;62(2):782-790.
11 Robson PM, Grant AK, Madhuranthakam AJ, Lattanzi R, Sodickson DK, McKenzie CA. Comprehensive quantification of signal-to-noise ratio and g-factor for image-based and k-space-based parallel imaging reconstructions. Magnetic resonance in medicine 2008;60(4):895-907.
Figures