3845
Intravascular Shifted fMRI Contrast for Visual Stimulations at 3 Tesla Using DANTE-Prepared Dual-Echo EPI1Functional MRI Facility, National Institute of Mental Health, Bethesda, MD, United States, 2Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, United States, 3Section on Functional Imaging Methods, National Institute of Mental Health, Bethesda, MD, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: fMRI, fMRI (task based), Intravascular fMRI contrast, extravascular fMRI contrast
By using dual-echo DANTE-EPI for functional visual stimulation studies, the contrast of fractions of intravascular signal to total signal change can be generated. We show an intravascular shifted (IVS) contrast can provide simultaneous visualization of intra-extra vascular contrast under different frequencies of visual stimulations at 3T.Introduction
The blood-oxygenation-level dependent (BOLD) effect consists of intravascular and extravascular components, both of which can arise from small and large blood vessels as well as from the capillary bed. It is desirable to develop a fMRI contrast that can visually and quantifiably differentiate both of intravascular and extravascular components.Vascular space occupancy (VASO) fMRI1 is a non-BOLD technique that relies on nulling of the arterial, arteriolar and capillary blood signal with dark blood pulse module such as inversion recovery (IR) or “delay alternating with nutation for tailored excitation” (DANTE) preparation pulses2. Based on the opposing effects of intravascular and BOLD signal changes in the microvasculature while dark blood pulse modules were applied, we successfully demonstrated that prepared dual-echo EPI (DANTE-dEPI) may be used for quantification of CBV changes3.
In this work, using functional images from DANTE-dEPI, the pixel-wised contrast of fractions of intravascular to total signal changes can be generated. We show that the averaged fractions of intravascular signal change (∆S0/S0)intra in the total BOLD signal (∆S/S)tot is determined to be 34.5%, (or extravascular change 65.5% at TE=30ms under 3 Tesla). In addition, we show this fraction is independent of applied visual stimulation frequencies and individual subjects. Finally, using the constant fraction 34.5% of intravascular to total BOLD as a reference fraction, we demonstrate an intravascular shifted (IVS) contrast can provide visually differentiable of intra-extra vascular contrast simultaneously under different frequencies of visual stimulations.
Methods:
1. Fraction of intravascular change to total signal changeWhen assuming the blood signal is fully suppressed at the ideal case, from the perspective of the vascular components.$$\left(\frac{\Delta S}{S}\right)_{tot} =\left(\frac{\Delta S_0}{S_0}\right)_{intraV}+\left(\frac{\Delta S_{TE_2}}{S_{TE_2}}\right)_{extraV} \left(1\right)$$
$$1=R_{intraV}+R_{extraV} \left(2\right)$$, where the intra-extra vascular components can be normalized by total signal changes; the RintraV=(∆S0/S0)intraV /(∆S/S)tot and RextraV=(∆S0/S0)extraV /(∆S/S)tot. The (∆S0/S0)intraV is intravascular change extrapolated from DANTE images of two echo times; the (∆STE2/STE2)extraV is extravascular signal change equivalent to the BOLD change of DANTE images from second echo time TE=30 ms.
2. Intravascular shifted (IVS) contrast, (analog to the definition of NMR chemical shift)
$$ γ_i = \frac{R_{intraV_i}-R_{ref}}{R_{ref}} \left(3\right)$$
The γi in Eq. 3 represents for shifting distance of individual pixel away from a constant reference of intravascular Rref=0.345. RintraV, i is the fraction of (∆S0/S0)intraV /(∆S/S)tot in the individual pixel. The Rref is equal to 0.345 based on our measurement of averaged intravascular component of RintraV being 34.5% at 3T and, most importantly, this value not varying with different frequencies of visual stimulus and different subjects. We may use averaged RintraV =34.5% as a constant reference, which is similar to the definition of NMR chemical shift.
3. Imaging methods: Dual-echo DANTE-EPI, DANTE-prepared imaging sequence is shown in Fig. 1, indicating both the DANTE preparation module itself (Fig. 1a ), as well as the proposed method for embedding it within a multi-slice single echo or multi-echo EPI sequence (Fig. 1b). Five healthy volunteers (male, age 35-45 years) underwent fMRI scans in Siemens Prisma 3T. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects and the study was carried out with the ethical approval of our institutional review board. Tasks of fMRI, flashing checkerboard 1, 5 and 10Hz, 0.5 minutes ON-OFF blocks were performed. A standard Siemens 32-channel head coil was employed. Common parameters used for single echo and multi echo EPI were as follows: FAEPI=70°, GRAPPA (R=3), resolution 2.1´2.1 mm in-plane (92´92 pixels) with field of view 192 mm, 2 mm slice thickness with 50% gap, bandwidth 2074 Hz/pixel. For imaging of DANTE single echo EPI with echo time TE=9 ms, 38 slices were acquired within 3s TR. For imaging of DANTE multi echo EPI with echo time TE=11 and 29 ms, respectively, 32 slices were acquired. DANTE parameters: Number of pulses = 52; Interpulse delay = 700 us, Flip angle = 7.
Results and Discussion:
A linear relationship of averaged fractions (RintraV) of intravascular changes ((∆S0/S0)intraV) to total BOLD signal changes ((∆S/S)tot) was shown in Fig. 2, suggesting that averaged intravascular RintraV =0.345 is a constant independent from stimulation frequencies and subjects. The comparison of intravascular shifted (IVS), or γ contrast with BOLD contrast was shown in Fig. 3. The red and blue pixels in IVS or γ map represent for the intravascular and extravascular components dominated regions, respectively. It can be clearly visualized that under the lower frequencies the activated regions are more extravascular dominated (blue) and intravascular dominated area (red) increases with higher stimulation frequencies. Histograms of one of subjects were shown in Fig. 4, suggesting the shifting of γ values when frequency increases.Conclusion:
By using dual-echo DANTE-EPI for functional visual stimulation studies, the pixel-wised contrast of fractions of intravascular to total signal change can be generated. Due to the constant of averaged fraction 34.5% of intravascular to total BOLD, we show an intravascular shifted (IVS) contrast can provide differentiable intra-extra vascular contrast simultaneously under different frequencies of visual stimulations at 3T.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Mental Health, USA.References
1. H Lu, et al., Functional magnetic resonance imaging based on changes in vascular space occupancyMagnetic Resonance in Medicine 50 (2), 263-274, 2003.
2. L Li, et al., DANTE‐prepared pulse trains: a novel approach to motion‐sensitized and motion‐suppressed quantitative magnetic resonance imaging, Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 68 (5), 2012.
3. L Li, et al., Quantification of cerebral blood volume changes caused by visual stimulation at 3T using DANTE-prepared dual-echo EPI, Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 2022 Apr; 87(4):1846-1862
Figures
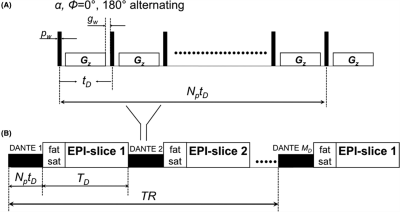
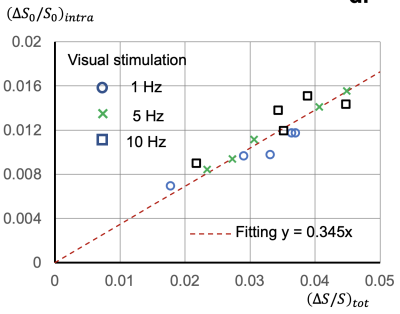
Figure. 2. Averaged fractions of intravascular changes to total signal changes is a constant value of 0.345 at 3T.
Plot of averaged intravascular changes (∆S0/S0)intra changes with total BOLD changes of all five subjects with 1, 5 and 10 Hz frequency stimulations. The fitted slope is 0.345.
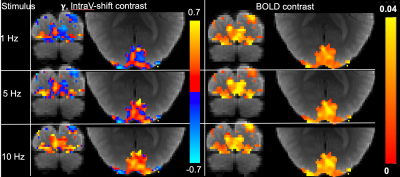
Figure. 3 The comparison of intravascular shifted (IVS), or γ contrast with BOLD contrast
The IVS or γ contrast under different stimulation frequencies were shown in left column. The red pixels represent for the intravascular dominated regions. The blue ones represent for the extravascular dominated regions. Visually, the intravascular regions were significantly increased while higher stimulation frequencies were applied. The corresponding BOLD contrasts were shown in right column, which can show very limited information while the frequencies are increased.
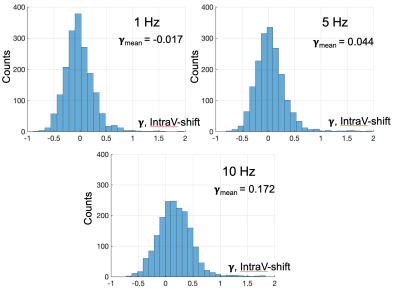
Figure. 4 Quantification of intravascular shifted (IVS), or γ contrast
Histograms of one of subjects were shown. The averaged shifted γ values are -0.017, 0.044 and 0.172 for 1 Hz, 5 Hz and 10 Hz stimulations, respectively.