3818
Preliminary exploration of the influence of B0 drift caused by the change of examination orientations on renal APT images
Wei Zhang1, Xia Wang1, Ruirui Ma1, Na Zhao1, Gang Tian1, Chanjuan Yu1, Min Jia1, Xiuzheng Yue2, and Yuedong Han1
1Department of Radiology, Xi'an GaoXin Hospital, Xi'an, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
1Department of Radiology, Xi'an GaoXin Hospital, Xi'an, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Kidney, CEST & MT
Amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw) is a promising molecular imaging technique that has been employed in clinics for the detection and grading of tumors. APT value is easily influenced by B0 inhomogeneity causing image artifacts; This variation becomes more complex in abdominal motion organs than that in the brain. This study focused on the effect of variation in B0 field drift with different examination orientations on renal APT image quality. The results showed when head-first and foot-first scanning were used on 3D-APT imaging of normal kidneys, the change of B0 drift on the quality of renal APT image should be noticed.Introduction
Amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw) MRI is a promising molecular imaging technique that has been employed in clinics for the detection and grading of tumors. APT values are easily influenced by B0 inhomogeneity causing artifacts[1], and related studies have made effective progress in the brain [2]. However, the magnetic field environment of abdominal organs is more complex than that in the brain due to movement, intestinal gas magnetic sensitivity artifact, and other factors; and few relevant studies have been reported. Our previous research found that the image quality of renal 3D-APTw imaging was effectively improved by intermittent breath-hold (IBH) [3]. Meanwhile, we also found that the pseudo-color colors of B0 map images differed between head-first and foot-first examination orientations during renal 3D-APTw imaging. Whether the fluctuation of B0 drift caused by this difference affects the quality of renal APT image still needs to be explored.Method
Nineteen healthy adult volunteers (6 males and 13 females, age range 22-40 years) were prospectively included in April-May 2022. All MR images were obtained on a 3.0 T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare) using a 32-channel phased-array abdominal coil. MR images included axial mDixon-T1WI and 3D-APTw sequences with examination orientations of head-first and foot-first (Table 1). A B0 map was embedded in the 3D-APTw imaging and created from three different TEs (TE = ±0.4ms) using a three-point Dixon method [3]. Three slices centered on the bilateral kidney hilum were then scanned on axial APTw imagings with IBH mode. The MR images were uploaded to the workstation of IntelliSpace Portal (Version 8, Philips Healthcare) for post-processing to obtain APTw and B0 map images of bilateral kidneys. Two senior attending physicians used a 5-point Likert scale (1=poor, 5=good) to assess the score of the bilateral renal APT images. The large region of interest (ROI) was used to measure B0 values, and APT values with head-first and foot-first, respectively, and ROI was first placed on the B0 map, then copied to the APTw images. Using SPSS 25.0 software, paired samples t-test and Wilcoxon signed-rank test were used to analyze the differences in renal B0 values and APT values at head-first and foot-first. Spearman correlation analysis was used to analyze the relationship between the B0 and APT values (|r| < 0.4 low linear correlation).Result
Analysis of the data under IBH respiratory mode in 19 subjects showed APT values were significantly higher in the head-first than that in the foot-first in bilateral kidneys; B0 values were significantly higher in the head-first than that in the foot-first in the left kidney, and there was not a statistically significant change in B0 values in the right kidney (Table 2). Correlation analysis showed a low negative correlation between B0 values and APT values in bilateral kidneys (rL = - 0.268, P= 0.004; rR = - 0.390, P< 0.001) (Fig. 1). Additionally, the B0 values of the left kidney were significantly lower than the right kidney in both head-first and foot-first (P < 0.001), in contrast, the left kidney APT values were significantly higher than the right kidney (P < 0.001) (Fig. 2).Discussion
The results of this study showed that the normal kidney APT values showed a low negative correlation with the B0 values during head-first and foot-first; there were significant differences in B0 values and APT values between the left and right kidneys regardless of head-first or foot-first. The results of this study showed that there was a relationship between the stability of APTw imaging of the normal kidneys and the B0 drift after head-first and foot-first changing positions. However, there are many and complex factors affecting B0 field uniformity, and this study only controlled for the interference of respiratory motion, and the other factors need to be further investigated.Conclusions
The effect of changes in the B0 drift caused by changing examination position (head first and foot first) on the quality of renal 3D-APTw should be noticed.Acknowledgements
we sincerely thank the participants in this study.References
[1] Chen Y, Dang X, Zhao B, et al. B0 Correction for 3T Amide Proton Transfer (APT) MRI Using a Simplified Two-Pool Lorentzian Model of Symmetric Water and Asymmetric Solutes.TOMOGRAPHY, 2022, 8(4):1974-1986.
[2] Togao O, Keupp J, Hiwatashi A, et al. Amide proton transfer imaging of brain tumors using a self-corrected 3D fast spin-echo Dixon method: comparison with separate B0 correction. magn Reson Med, 2017, 77:2272-2279
[3] Xia Wang, Yu Jiang, Zeliu Du, et al. Exploring the reproducibility of APT imaging technology in healthy adult kidneys based on breathing patterns Proc. Iintl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 30(2022)
Figures
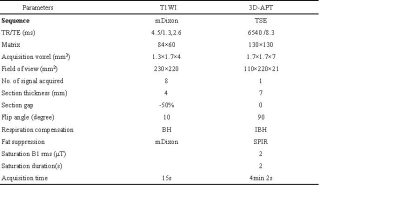
Table 1. MRI pulse sequences and parameters(BH: breath-hold; IBH: intermittent breath-hold ).
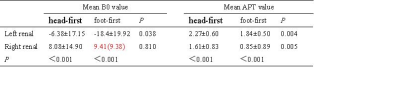
Table 2. Comparative analysis of B0 and APT values between head first and foot first (n=19).
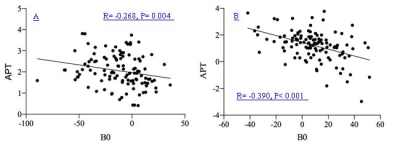
Fig.1 Scatter plot displayed the left renal (Fig. A) and right renal (Fig. B) of correlation between APT and B0 values in head first and foot first.
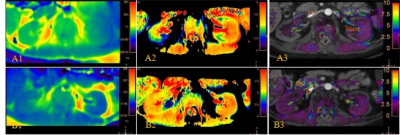
Fig.2 A1~A3 foot first MR images, the right perirenal was warm color in B0 pseudo-color map (A1), and APT signal intensity of right kidney was low in pseudo-color images of APT (A2) and APTw image fused with T1WI (A3). When changed head first (B1~B3), the right perirenal was cool color in the pseudo-colored B0 map (B1), and bilateral kidneys pseudo-color images of APT no significant difference (B2, B3).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/3818