3797
Value of Reversed Polarity Gradients and Multiplexed Sensitivity Encoding in improving diffusion weighted imaging quality of uterus1Department of Radiology, Weifang People’s Hospital, Weifang, China, 2MR Research China, GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Artifacts, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, multiplexed sensitivity encoding, reversed polarity gradients
The aim of this study is to investigate the application of multiplexed sensitivity encoding diffusion weighted imaging with reversed polarity gradients in improving the image quality of uterine tumors. 10 patients with uterine lesions in our hospital were enrolled. Conventional SS-EPI DWI, MUSE DWI, and RPG-MUSE DWI sequences were employed. The subjective image quality assessment and objective data measurement of uterine lesions scanned by different DWI sequence was evaluated by three radiologists using double-blind method. The results of this study showed that RPG-MUSE DWI can greatly improve the image quality of the uterus.Introduction
Cervical cancer and endometrial cancer are common malignant tumors in women that seriously endanger patients' health. Timely detection of lesions and accurate assessment of tumor extent are of great importance. It has been documented that diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a useful technique to detect and evaluate uterine tumors1,2. However, single-shot echo-planar imaging (SS-EPI) DWI suffers from artifacts and geometric distortion.Some studies have shown that,reversed polarity gradients (RPG) and multiplexed sensitivity encoding (MUSE) can reduce artifacts and geometric distortion, and gain a high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)3,4,5.
This study compared images of SS-EPI DWI, MUSE DWI, and RPG-MUSE DWI sequences, the aim was to investigate the value of RPG-MUSE DWI in improving the quality of uterine DWI images.
Materials and methods
Subjects10 patients with uterine lesions in our hospital were enrolled(mean age 56 years ranging from 35-75 years), 5 patients with cervical cancer, 4 patients with endometrial cancer and 1 patient with endometrial polyp.
MRI Imaging
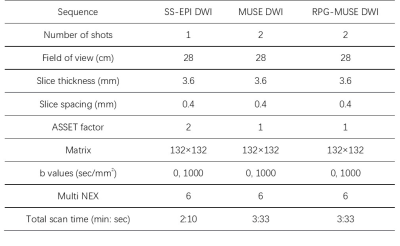
A 3.0-T MR scanner (GE Medical Systems, SIGNATM Architect) with a 30-channel air coil was used for all subjects. Conventional SS-EPI DWI sequence, MUSE DWI, and RPG-MUSE DWI sequences imaging were employed respectively (Table 1).
Data analysis
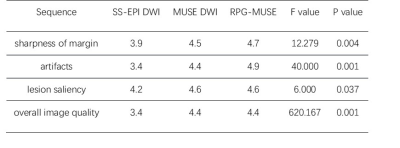
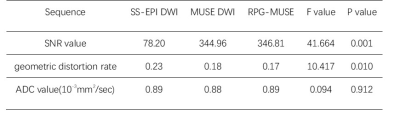
All MRI data were post-processed using vendor-provided software on GE ADW4.7 workstation. The subjective image quality assessment and objective data measurement of uterine lesions scanned by different DWI sequence was double-blind evaluated by three radiologists. The subjective assessment of the sharpness of lesion margin, artifacts, lesion saliency and overall image quality were compared between three types of DWI with a 5-point scale. The objective evaluation was based on the measurement of the tissue signal noise ratio (SNR) value, geometric distortion rate and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 21.0 statistic software was used. Intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) analysis was applied to assess the inter-observer agreement of parameter measurement over three radiologists. An ICC over 0.75 represented a good agreement. Comparison of subjective scores and objective measures of the three sequences by three readers using repeated measures ANOVA. P<0.05 was considered statistically difference.
Results
There was good agreement among three readers (ICC>0.75). The uterus RPG-MUSE DWI achieved significantly better subjective image scores (P < 0.05) (Table 2). The RPG-MUSE DWI achieved lower geometric distortion rate and higher SNR value than MUSE DWI and SS-EPI DWI (P<0.05), there were not significant differences of ADC values of uterine tissue(P>0.05). (Figure1, Table 3)Discussion and Conclusion
In this study, we performed a comparison assessment of conventional SS-EPI DWI, MUSE DWI, and RPG-MUSE DWI sequences in the uterus. Our findings demonstrate, that RPG-MUSE DWI can enhance the image quality of the uterus, and provide accurate imaging evidence for clinical diagnosis and treatment. Further research with bigger cohort of subjects is required.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Mingzhen Chen, Cui Feng, Qiuxia Wang, Jiali Li,Sisi Wu, Daoyu Hu, Baodi Deng, Zhen Li. Comparison of reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and conventional DWI techniques in the assessment of Cervical carcinoma at 3.0T: Image quality and FIGO staging. Eur J Radiol,2021 Apr;137:109557.
2. Nougaret S, Lakhman Y, Vargas HA, Colombo PE, Fujii S, Reinhold C, Sala E. From Staging to Prognostication: Achievements and Challenges of MR Imaging in the Assessment of Endometrial Cancer. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am,2017 Aug;25(3):611-633.
3. Isaac Daimiel Naranjo, Roberto Lo Gullo, Elizabeth A Morris, Toni Larowin, Maggie M Fung, Arnaud Guidon, Katja Pinker, Sunitha B Thakur. High-Spatial-Resolution Multishot Multiplexed Sensitivity-encoding Diffusion-weighted Imaging for Improved Quality of Breast Images and Differentiation of Breast Lesions: A Feasibility Study. Radiol Imaging Cancer,2020 May 29;2(3):e190076.
4. Amaresha Shridhar Konar, Maggie Fung, Ramesh Paudyal, Jung Hun Oh, Yousef Mazaheri, Vaios Hatzoglou, Amita Shukla-Dave. Diffusion-Weighted Echo Planar Imaging using MUltiplexed Sensitivity Encoding and Reverse Polarity Gradient in Head and Neck Cancer: An Initial Study. Tomography,2020 Jun;6(2):231-240.
5. Iain P Bruce, Christopher Petty, Allen W Song. Simultaneous and inherent correction of B0 and eddy-current induced distortions in high-resolution diffusion MRI using reversed polarity gradients and multiplexed sensitivity encoding (RPG-MUSE). Neuroimage,2018 Dec;183:985-993.
Figures