3793
Sub-millimeter Diffusion Tensor Imaging using Single-Shot Spiral Acquisitions with a Large Acceleration Factor1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2MR Clinical Science, Philips Health Technology (China), Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Image Reconstruction, Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Single-shot spiral acquisitions allow shorter TE, thus provide higher SNR compared to EPI acquisitions for DWI. However, spiral acquisitions are sensitive to field inhomogeneity. Parallel imaging techniques can be used to alleviate static B0 off-resonance effects. In this study, single-shot spiral acquisitions with a large acceleration factor of 5 or 6 were used to achieve sub-millimeter diffusion tensor imaging at 3T. The in vivo results demonstrate that the single-shot spiral sampling strategy can be adopted to achieve whole-brain diffusion tensor imaging with an in-plane resolution of 0.77×0.77mm2.Introduction
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a powerful tool for clinical diagnosis and neuroscience studies. Since center-out spiral imaging enables shorter TE acquisition compared to EPI, it has been applied for DWI acquisition 1-7. However, spiral sampling is sensitive to field inhomogeneity and the blurring artifacts induced by field inhomogeneity can degrade the spatial resolution and the image quality. Parallel imaging techniques have been used to shorten spiral readouts, and thus sharp diffusion images can be obtained using single-shot spiral acquisitions. However, increased acceleration factors result in higher g-factor penalty with noise amplification, and then the image quality (low SNR or aliasing artifacts) is degraded. The aim of this work is to study the feasibility of single-shot spiral acquisitions using a large under-sampling factor (5 or 6) and denoising to achieve sub-millimeter diffusion tensor imaging.Methods
1. Data acquisitionUniform-density spiral was used to acquire diffusion data. All spiral diffusion imaging experiments were performed using a Stejskal-Tanner diffusion sequence on a Philips Ingenia CX 3.0T scanner using a 32-channel head coil. The gradient system was operated at a maximum gradient strength of 31 mT/m and a maximum slew rate of 200 T/m/s.
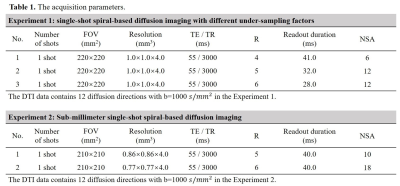
Experiment 1: The feasibility of single-shot spiral acquisitions with a large under-sampling factor. FOV=220×220mm2, resolution=1.0×1.0×4.0mm3, b-value=1000s/mm2, 12 diffusion directions, TE/TR=55/3000ms, 24 axial slices. AQ=41.0, 32.0, and 28.0ms for the single-shot acquisitions with in-plane acceleration factor=4, 5 and 6, respectively.
Experiment 2: Sub-millimeter diffusion imaging using a single-shot spiral acquisition. FOV=210×210mm2, in-plane resolution=0.77×0.77mm2, 24 slices. b-value=1000 s/mm2, 12 diffusion directions, TE/TR=55/3000ms, AQ=40.0ms, acceleration factor=6.
In all experiments, SPIR technique was used to suppress fat signals. In addition, low-resolution field maps acquired using a multi-echo GRE sequence were used for deblurring. Further imaging details can be found in Table 1.
2. Image reconstruction
The single-shot spiral DW images were off-line reconstructed using SPIRiT algorithm 8.
$$argmin\left|\right|Dx-y\left|\right|_{2}^{2} +\lambda\left|\right|(G_{SPIRIT}-I)\left|\right|_{2}^{2}$$
where x is the k-space dataset to be reconstructed, y is the under-sampled k-space data, D is the under-sampling operator, $$$G_{SPIRIT}$$$ is the SPIRiT kernel. In this study, 𝜆=1.0 and the minimization problem was solved using the CG algorithm. CPR method was used for off-resonance correction 9. FA maps were calculated using FSL toolbox 10.
3. Image Denoising
A larger under-sampled factor of 5 or 6 was used in the single-shot spiral acquisition, so the single-shot DW images were noisy. In this work, we tried to use non-local low-rank denoising method to suppress noise 11. The noisy complex-valued diffusion images are denoised after off-resonance correction.
Results and Discussion
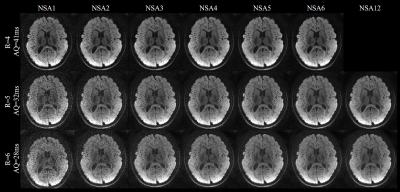
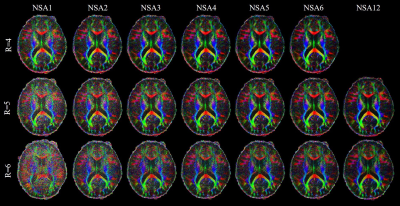
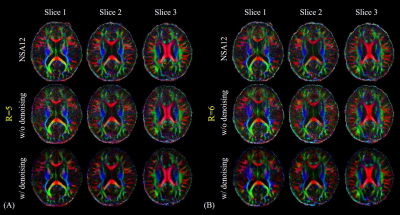
For Experiment 1, Figure 1 shows the DW images acquired by the single-shot spiral acquisitions with the acceleration factor of 4, 5 and 6, respectively. There are no obvious aliasing artifacts in the reconstructed images. This demonstrates that single-shot spiral-based diffusion imaging can be accelerated with a factor up to 6, which is challenging for EPI DWI. However, for R=5 and R=6 reconstruction results, the diffusion images with NSA=1 are noisy. Signal averaging is required to maintain the image SNR.Figure 2 shows the cFA maps of a representative slice. The cFA maps of the diffusion images with and without denoising are shown in the Figure 3. The NSA=2 images for R=5 and NSA=3 images for R=6 are denoised, respectively. The denoising results are visually similar to the NSA=12 reference results. The results show that denoising can improve the image quality distinctly and is useful to suppress the noise in the diffusion images, so the number of signal averages can be reduced.
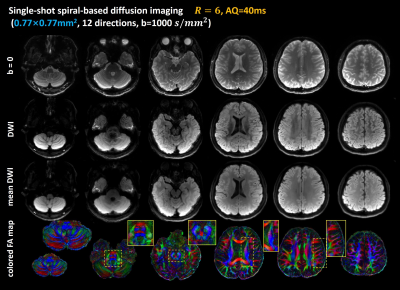
For Experiment 2, Figure 4 shows the single-shot spiral diffusion images with an in-plane resolution of 0.77×0.77mm2. The b=0 images, single DW images, mean DWI and cFA maps of six representative slices are shown. The fine structures of the cerebellum, middle pons, corona radiate and temporal lobes are well rendered and shown in the zoomed-in cFA maps.
Compared to EPI, center-out spiral acquisitions possess shorter TE and thus provide higher SNR. Moreover, spiral sampling offers a favorable g-factor behavior 7. Thus, the single-shot uniform-density spiral acquisition with under-sampling factor of 6 can be well reconstructed and used to achieve sub-millimeter diffusion imaging. For sub-millimeter DWI, the spiral readout duration can be very long (>80ms for 3-shot acquisitions). Thus, to minimize off-resonance effect, increasing the number of shots is required. Our results indicate that the denoising can suppress noise in the diffusion images, so the number of signal averages can be reduced to 3. Such a strategy can also be transferred to multi-shot spiral (e.g. 6 shots with R=2). In addition, in this work, diffusion data were acquired at 3.0T, the R=6 diffusion images are noisy. A future study can be carried out to acquire sub-millimeter diffusion images using this single-shot acquisition strategy at 7.0T or higher field strength (even with powerful gradients), then the SNR of diffusion images will be improved further.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates the reconstruction feasibility of single-shot spiral acquisition with a large under-sampling factor of 5 or 6 to achieve sub-millimeter diffusion tensor imaging with off-resonance well controlled. High quality diffusion-weighted images with an in-plane resolution of 0.77×0.77mm2 are acquired by using a single-shot spiral acquisition with an acceleration factor of 6.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Li G, Shao X, Ye X, and Guo H. Whole-brain Diffusion Tensor Imaging Using Single-Shot Spiral Sampling. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. 2021; 1312.
2. Börnert P, Eggers H, Nehrke K, et al. Single-shot Diffusion-weighted Spiral Imaging in the Brain on a Clinical Scanner. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. 2019; 0243.
3. Wilm BJ, Roesler M, Hennel F, et al. Diffusion Imaging with Very High Resolution and Very Short Echo Time. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. 2020; 0965.
4. Wilm BJ, Barmet C, Gross S, et al. Single-shot spiral imaging enabled by an expanded encoding model: Demonstration in diffusion MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2017;77(1):83-91.
5. Lee Y, Wilm BJ, Nagy Z, et al. High-Resolution Diffusion MRI: In-Vivo Demonstration of the SNR Benefit of Single-Shot Spiral Acquisition vs. EPI. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. 2019; 0767.
6. Wilm BJ, Hennel F, Roesler MB, et al. Minimizing the echo time in diffusion imaging using spiral readouts and a head gradient system. Magn Reson Med. Dec 2020;84(6):3117-3127.
7. Lee Y, Wilm BJ, Brunner DO, et al. On the signal-to-noise ratio benefit of spiral acquisition in diffusion MRI. Magn Reson Med. Apr 2021;85(4):1924-1937.
8. Lustig M, Pauly JM. SPIRiT: Iterative self-consistent parallel imaging reconstruction from arbitrary k-space. Magn Reson Med. 2010;64(2):457-471.
9. Noll DC, Pauly JM, Meyer CH, et al. Deblurring for non-2D fourier transform magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1992; 25: 319- 333.
10. Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, et al. FSL. Neuroimage 2012;62(2):782-790.
11. Ye X, Ma X, Pan Z, et al. Non-local low rank denoising method for complex-valued DWI. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. 2022; 3041.
Figures