3785
Hybrid-space reconstruction for simultaneous multi-slab DWI with blipped-CAIPI1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Image Reconstruction, Diffusion Tensor Imaging
3D simultaneous multi-slab imaging (SMSlab) can achieve high-resolution DWI with high SNR efficiency. Multi-band acceleration can also achieve less SNR reduction. Recently, we integrated SMSlab DWI with blipped-CAIPI gradients to reduce the g-factor penalty and proposed a 4D k-space framework (kx-ky-kz-km) to model the signal encoding, with km representing the multi-band encoding. Because the blipped-CAIPI gradients are applied along the slice direction, they introduce kz deviations from the nominal k-space location. This study proposed a hybrid-space reconstruction algorithm, REACH, to solve the phase interferences introduced by the blipped-CAIPI gradients.
Introduction
3D simultaneous multi-slab (SMSlab) 1-4 excites multiple 3D slabs simultaneously. It can achieve high-resolution whole-brain DWI with high SNR efficiency 5. Moreover, multi-band acceleration can utilize the coil sensitivities in the slice direction, thus less SNR reduction is achieved via enlarging the excited FOV. Recently, we integrated SMSlab imaging with blipped-controlled aliasing in parallel imaging (blipped-CAIPI) 6 to reduce the g-factor penalty. However, phase interferences are introduced by the blipped-CAIPI gradients 7. The purpose of this study is to develop a reconstruction algorithm based on hybrid-space SENSE 8 to solve this problem.Theory and Methods
SMSlab with blipped-CAIPI (blipped-SMSlab)The blipped-SMSlab sequence is shown in Figure 1A. In particular, the multi-band RF pulses are used for excitation and refocusing. A table of kz gradients is used to encode the intra-slab slices. One shot is acquired for each kz. During the first echo train, blipped-CAIPI gradients are added between different sub-echoes along the slice direction for multi-band encoding. Then a 4D k-space framework (kx-ky-kz-km) is formulated to model the signal encoding, with km representing multi-band encoding.
If the blipped-CAIPI gradients are combined with SMSlab, two parts of phase interferences are introduced. Figure 1D shows an example with two slabs (slab 1 and slab 1’) simultaneously excited. First, due to the gap between the centers of the simultaneously excited slabs (zgap), an extra phase offset is introduced to slab 1’, which differs across different kz.
$$\varphi_{\text {gap }}=2 \pi \cdot z_{\text {gap }} / F O V_z \cdot n_{k z} \cdot n_m . (1)$$
FOVz is the slab thickness. nkz is the index of kz encoding in k-space, and nm is the slab index in the image domain. RF phase modulation can be used to compensate for it by introducing -φgap to the multi-band RF pulses.
Second, because the km gradients and the kz gradients share the same physical gradient direction, the blipped-CAIPI gradients introduce kz deviations from the nominal k-space location (Figure 1C) 7. The deviations along kz are referred to as the ramp phase,
$$\varphi_{\text {ramp }}=2 \pi \cdot \Delta z / F O V_m \cdot n_{k m} \cdot n_z . (2)$$
Δz is slice thickness. FOVm=Rmb∙zgap is the defined FOV in the multi-band dimension, and Rmb is the MB factor. nkm is the index of km encoding in k-space, and nz is the intra-slab slice index in the image domain. The correction of φramp is illustrated as follows.
REconstruction with phAse Correction in a Hybrid space (REACH)
For b=0 s/mm2 images, φramp can be directly removed after 1D iFFT along kz. However, for diffusion-weighted images, iFFT along kz cannot be applied because of the inter-kz phase variations. In this study, the correction for both φramp and the motion-induced phase of DWI is achieved by integrating them into a forward model, which is reconstructed in a hybrid space.
First, the k-space signals are transformed into the hybrid space (x-ky-kz-km) via 1D iFFT and represented by d, which enables a separate reconstruction for each x index 8. Then, a 4D representation of blipped-SMSlab DWI signals becomes
$$\mathrm{F}_{\mathrm{u}} \Psi \mathrm{SPI}=\mathrm{d}. (3)$$
Fu is an undersampled 3D FFT operator on y, z, and m dimensions. The ramp phase is represented by Ψ(nkm,nz )=φramp. S represents coil sensitivities. P represents motion-induced inter-kz phase variations. I is the full-sampled image.
The flowchart of REACH is shown in Figure 2. In step 1, the motion-induced phase maps are extracted from the reconstructed navigators and smoothed by a Gaussian filter. In step 2, the k-space signals are transformed to the x-ky-kz-km space and reconstructed using the following cost function.
$$\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{REACH} } \quad = \operatorname{argmin}\left\|\mathrm{d}-\mathrm{F}_{\mathrm{u}} \Psi \mathrm{SPI}\right\|_2^2. (4)$$
Results & Discussion
Blipped-SMSlab images with 1.5-mm isotropic resolution were acquired to show the effect of φramp correction in REACH (Figure 3). Positive values in the error maps represent artifacts introduced to the images if φramp correction is not done. For both the diffusion-weighted images and the b=0 s/mm2 images, without correction, residual ghost-like aliasing exists (yellow arrows).The benefit of blipped-CAIPI was evaluated via a comparison between SMSlab acquisitions with and without blipped-CAIPI (Figure 4). The resolution is 1.5-mm isotropic. Blipped-CAIPI gradients increase the 1/g-factor compared with SMSlab without blipped-CAIPI. The mean 1/g-factors of the two slabs improve from 0.39 and 0.38 to 0.45 and 0.42, respectively. Because the distances between two simultaneously excited slabs were larger than 70 cm, their coil sensitivities are very different. The 1/g-factor improvement is not as large as that of MB>26.
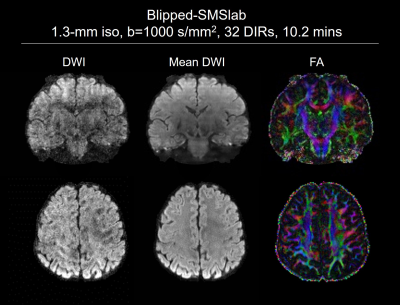
A DTI dataset acquired with blipped-SMSlab and reconstructed by REACH is shown in Figure 5. 1.3-mm isotropic resolution and b=1000 s/mm2 with 32 directions were used. Topup acquisition 9 was used for the b=0 images. With TR=1.8 s and 10 kz steps for each slab, it took 18 s to acquire one diffusion direction. However, applying the topup acquisition only for b=0 images may have limited performance in distortion correction, which will be improved in the other abstract.
Conclusion
This study proposed a hybrid-space reconstruction algorithm, REACH, for 3D SMSlab DWI data acquired with blipped-CAIPI gradients (blipped-SMSlab). It can straightforwardly solve the phase interferences introduced by the blipped-CAIPI gradients and compute diffusion images correctly.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Dai E, Wu Y, Wu W, et al. A 3D k-space Fourier encoding and reconstruction framework for simultaneous multi-slab acquisition. Magn Reson Med 2019;82(3):1012-1024.
2. Frost R, Jezzard P, Porter DA, Tijssen R, Miller K. Simultaneous multi-slab acquisition in 3D multi-slab diffusion-weighted readout-segmented echo-planar imaging. Proceedings of the 21st Annual Meeting of ISMRM. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA, 2013. p. 3176.
3. Dai E, Liu S, Guo H. High-resolution whole-brain diffusion MRI at 3T using simultaneous multi-slab (SMSlab) acquisition. NeuroImage 2021;237:118099.
4. Bruce IP, Chang H-C, Petty C, Chen N-K, Song AW. 3D-MB-MUSE: A robust 3D multi-slab, multi-band and multi-shot reconstruction approach for ultrahigh resolution diffusion MRI. NeuroImage 2017;159:46-56.
5. Moeller S, Ramanna S, Lenglet C, et al. Self‐navigation for 3D multishot EPI with data‐reference. Magnetic resonance in medicine 2020;84(4):1747-1762.
6. Setsompop K, Gagoski BA, Polimeni JR, Witzel T, Wedeen VJ, Wald LL. Blipped-controlled aliasing in parallel imaging for simultaneous multislice echo planar imaging with reduced g-factor penalty. Magn Reson Med 2012;67(5):1210-1224.
7. Zahneisen B, Aksoy M, Maclaren J, Wuerslin C, Bammer R. RF-Encoding for Simultaneous Multi Slab Imaging. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med. Singapore, 2016. p.
8. Zhu K, Dougherty RF, Wu H, et al. Hybrid-space SENSE reconstruction for simultaneous multi-slice MRI. IEEE transactions on medical imaging 2016;35(8):1824-1836.
9. Andersson JL, Skare S, Ashburner J. How to correct susceptibility distortions in spin-echo echo-planar images: application to diffusion tensor imaging. NeuroImage 2003;20(2):870-888.
10. Robson PM, Grant AK, Madhuranthakam AJ, Lattanzi R, Sodickson DK, McKenzie CA. Comprehensive quantification of signal-to-noise ratio and g-factor for image-based and k-space-based parallel imaging reconstructions. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 2008;60(4):895-907.
11. Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TEJ, Woolrich MW, Smith SM. FSL. NeuroImage 2012;62(2):782-790.
12. Zhang J, Liu S, Dai E, et al. Slab boundary artifact correction in multislab imaging using convolutional‐neural‐network–enabled inversion for slab profile encoding. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 2022;87(3):1546-1560.
Figures
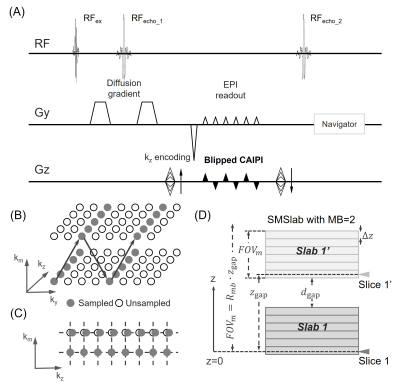
Figure 1. 3D SMSlab EPI with blipped-CAIPI (blipped-SMSlab). (A) and (B) show the sequence diagram and the trajectory in 4D k-space, respectively. Some gradients are omitted in (A) for simplification, including the slice-selection gradients, the Gx gradients, and so on. (C) shows the deviation along the kz dimension due to the blipped-CAIPI gradients. The dashed lines represent the nominal k-space locations. (D) shows the SMSlab sampling with MB=2. The grids within each slab represent the intra-slab slices. The isocenter (z=0) is marked in the subfigure.
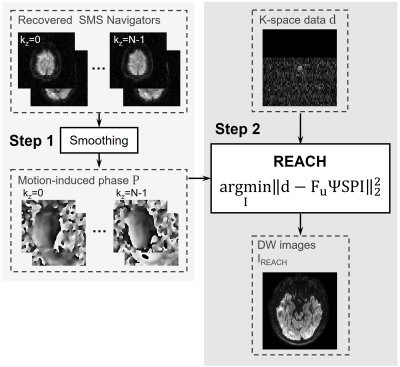
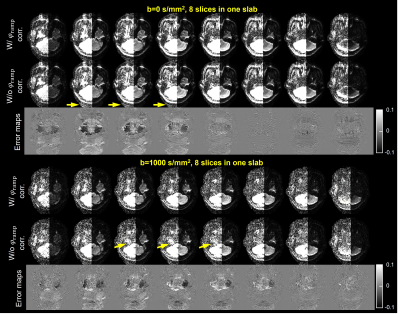
Figure 3. Comparison between the blipped-SMSlab images reconstructed with and without φramp correction. TR=1.9 s, Ry × MB=2×2, and 1.5-mm isotropic resolution were used. Nine slabs were acquired with 8 slices for each (2 of them for oversampling). The left half of each image is rescaled by a factor of 8. The ghost-like aliasing is pointed out by the yellow arrows. The error maps of the images without φramp correction with respect to the images with φramp correction are normalized by the maximum amplitude of the images with φramp correction.
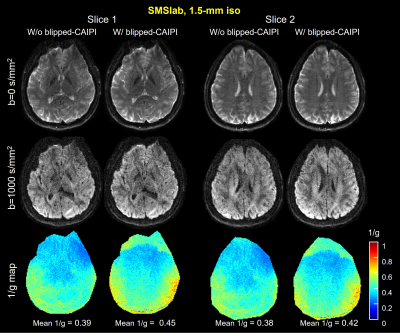
Figure 4. A comparison between SMSlab imaging with and without the blipped-CAIPI gradients. The acquisition parameters are the same as Fig. 5. 1.5-mm isotropic resolution were used. The g-factors were calculated via a Monte-Carlo-based method with 128 repetitions 10. Two slices from different slabs are shown. The b=0 images, the b=1000 s/mm2 images, and the 1/g-factor maps of b=0 images are shown from top to bottom. The mean values of 1/g-factor in both slabs are marked below the 1/g-factor maps.