3784
Simultaneous Multi-slice Single-shot Spiral Acquisitions for Accelerated Diffusion-weighted Imaging1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Data Acquisition, Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Single-shot acquisition techniques are commonly used to acquire diffusion-weighted images due to their high sampling efficiency. Single-shot uniform-density spiral sampling combined with in-plane under-sampling has been used to achieve diffusion imaging. In this study, we investigated simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) -accelerated single-shot spiral imaging (SMS-SSH-Spiral) to further improve the scan efficiency of DWI. The in vivo results demonstrate the feasibility of SMS-SSH-Spiral acquisitions for diffusion tensor imaging with 2-fold slice acceleration and 3-fold in-plane acceleration. Diffusion data with 1.5mm isotropic resolution is acquired using our multi-band single-shot acquisition strategy.Introduction
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) can provide valuable information for clinical diagnosis and neuroscience research. Single-shot imaging is the fastest and most efficient acquisition scheme in all MR samplings. Currently, single-shot spiral technique combined with an in-plane acceleration has been utilized in diffusion imaging 1-7. If the single-shot spiral acquisition can be combined with simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) imaging techniques 8-10, then the scan efficiency can be further improved. Therefore, the aim of this work is to demonstrate the feasibility of the SMS accelerated single-shot spiral acquisition (SMS-SSH-Spiral) for diffusion imaging. In this work, both through-plane and in-plane acceleration are used to achieve single-shot spiral diffusion imaging.Methods
1. Data acquisitionAll diffusion data were acquired using a single-shot uniform-density spiral acquisition (Figure 1A) on an Ingenia CX 3.0T scanner (Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands) equipped with a 32-channel head coil. Multi-band RF pulses were used to excite two slices simultaneously. The gradient system was operated at a maximum gradient strength of 31 mT/m and with a maximum slew rate of 200 mT/m/ms. Phantom studies were conducted first for the sequence development. Two healthy volunteers were participated in the following experiments. This study was approved by the local Institutional Review Board and written informed consent was obtained from all participants. The detailed acquisition parameters were listed in the Table 1.
Experiment 1: FOV=210×210×138mm3, resolution=1.6×1.6×3.0mm3, acquisition matrix=132×132, b value=500 s/mm2, 3 diffusion directions, TE/TR=55/3000ms, readout duration=24.0ms, MB=1 and 2. 46 axial slices (no gap) cover the whole brain.
Experiment 2: FOV=210×210×138mm3, resolution=1.5×1.5×3.0mm3, matrix=140×140, b value=800 s/mm2, 12 diffusion directions, TE/TR=60/3000ms, readout duration=27.0ms. 46 axial slices (no gap) covering the whole brain were acquired using MB=1 and MB=2 acquisitions, respectively.
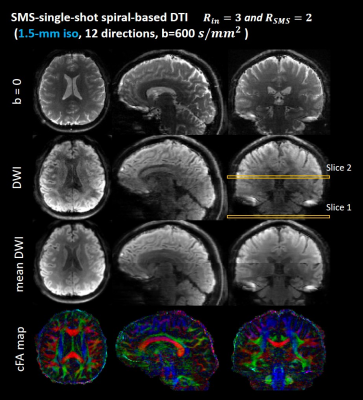
Experiment 3: FOV=210×210×138mm3, 1.5-mm isotropic resolution, b value=600s/mm2, 12 diffusion directions, TE/TR=57/3000ms, readout duration=27.0ms, MB=2. 92 axial slices (no gap) cover the whole brain.
In all experiments, Spectral Presaturation with Inversion Recovery (SPIR) technique was used to suppress fat signals. In addition, low-resolution B0 field maps acquired using a multi-echo GRE sequence were used for deblurring.
2. Image reconstruction
The single-shot spiral diffusion weighted images were off-line reconstructed. Figure 1B illustrates the basic reconstruction pipeline for SMS-SSH-Spiral DWI. For single-band diffusion data, in-plane unfolding can be resolved using SENSE 11 or in-plane GRAPPA 12. For multi-band diffusion images, the first step is to unfold the aliased slices using through-plane GRAPPA 13, then in-plane GRAPPA or SENSE was used to unfold the in-plane aliasing.
3.Image processing
Conjugate phase correction (CPR) method was used for off-resonance correction 14. Color-coded FA maps were calculated using dtifit in FMRIB Software Library (FSL) 15. Monte-Carlo-based pseudo multiple replica method was used to calculate the SNR maps 16. Then SNR-efficiency map can be obtained according to the equation: SNR efficiency=SNR/√(unit time).
Results and Discussion
Figure 2 shows the single-band and multi-band single-shot spiral diffusion-weighted images. The DW images from 3 diffusion directions and mean DWI images from two simultaneously excited slices are shown. The top two rows show the reconstructed single-shot diffusion images with NSA=1. The bottom two rows show the results with improved SNR when NSA=3 was used. The in-vivo results indicate the feasibility of the SMS-SSH-Spiral acquisition strategy with a net acceleration factor of 6.The b=0, DWI from one diffusion direction, mean DWI images, as well as color-coded FA maps obtained by the single-band and multi-band single-shot spiral acquisitions are shown in Figure 3A. The in vivo results demonstrate that SMS-SSH-Spiral diffusion imaging can provide correct DTI metrics.
Figure 3B shows the SNR-efficiency maps of the single-band and multi-band single-shot acquisitions. The SMS-SSH-spiral acquisition demonstrates higher SNR efficiency over the conventional SSH-spiral acquisition.
The reconstructed multi-band single-shot spiral diffusion images with 1.5-mm isotropic resolution are shown in Figure 4. Axial, coronal and sagittal planes of b=0, single-direction DWI, mean DWI and color-coded FA maps are shown.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates the feasibility of simultaneous multi-slice single-shot spiral (SMS-SSH-Spiral) acquisitions for diffusion imaging with 2-fold slice acceleration and 3-fold in-plane acceleration. Diffusion data with 1.5-mm isotropic resolution was acquired by using our multi-band single-shot acquisition strategy.Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Junyu Wang in University of Virginia for discussions and suggestions.References
1. Li G, Shao X, Ye X, and Hua Guo. Whole-brain Diffusion Tensor Imaging Using Single-Shot Spiral Sampling. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. 2021; 1312.
2. Börnert P, Eggers H, Nehrke K, et al. Single-shot Diffusion-weighted Spiral Imaging in the Brain on a Clinical Scanner. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. 2019; 0243.
3. Wilm BJ, Roesler M, Hennel F, et al. Diffusion Imaging with Very High Resolution and Very Short Echo Time. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. 2020; 0965.
4. Wilm BJ, Barmet C, Gross S, et al. Single-shot spiral imaging enabled by an expanded encoding model: Demonstration in diffusion MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2017;77(1):83-91.
5. Lee Y, Wilm BJ, Nagy Z, et al. High-Resolution Diffusion MRI: In-Vivo Demonstration of the SNR Benefit of Single-Shot Spiral Acquisition vs. EPI. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. 2019; 0767.
6. Wilm BJ, Hennel F, Roesler MB, et al. Minimizing the echo time in diffusion imaging using spiral readouts and a head gradient system. Magn Reson Med. Dec 2020;84(6):3117-3127.
7. Lee Y, Wilm BJ, Brunner DO, et al. On the signal-to-noise ratio benefit of spiral acquisition in diffusion MRI. Magn Reson Med. Apr 2021;85(4):1924-1937.
8. Barth M, Breuer F, Koopmans PJ, et al. Simultaneous multislice (SMS) imaging techniques. Magn Reson Med. 2016;75(1):63-81.
9. Larkman DJ, Hajnal JV, Herlihy AH, et al. Use of multicoil arrays for separation of signal from multiple slices simultaneously excited. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001;13(2):313-317.
10. Breuer FA, Blaimer M, Heidemann RM, et al. Controlled aliasing in parallel imaging results in higher acceleration (CAIPIRINHA) for multi-slice imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2005;53(3):684-691.
11. Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med. Nov 1999;42(5):952-62.
12. Luo T, Noll DC, Fessler JA, Nielsen JF. A GRAPPA algorithm for arbitrary 2D/3D non-Cartesian sampling trajectories with rapid calibration. Magn Reson Med. 2019 Sep;82(3):1101-1112.
13. Sun C, Yang Y, Cai X, et al. Non-Cartesian slice-GRAPPA and slice-SPIRiT reconstruction methods for multiband spiral cardiac MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2020;83(4):1235-1249.
14. Noll DC, Pauly JM, Meyer CH, et al. Deblurring for non-2D fourier transform magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1992; 25: 319- 333.
15. Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, et al. FSL. Neuroimage 2012;62(2):782-790.
16. Robson PM, Grant AK, Madhuranthakam AJ, et al. Comprehensive quantification of signal-to-noise ratio and g-factor for image-based and k-space-based parallel imaging reconstructions. Magnetic resonance in medicine 2008;60(4):895-907.
Figures
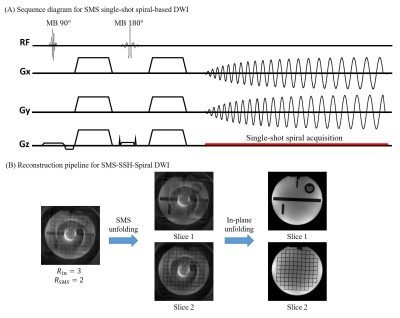
Figure 1: (A) The sequence diagram of simultaneous multi-slice single-shot spiral acquisition (SMS-SSH-spiral) for accelerated diffusion-weighted imaging. Multi-band RF pulses were used to excite two slices simultaneously. In-plane acceleration factor of 3 was used to reduce the single-shot spiral readouts in this work.
(B) The basic reconstruction pipeline of SMS-SSH-spiral-based diffusion imaging. The first step is to unfold the aliased slices using slice-GRAPPA, then in-plane artifacts are further removed by in-plane GRAPPA or SENSE.
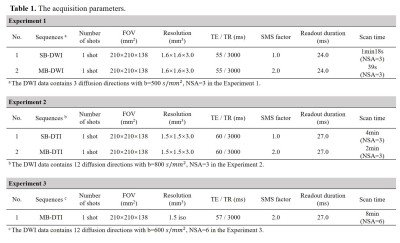
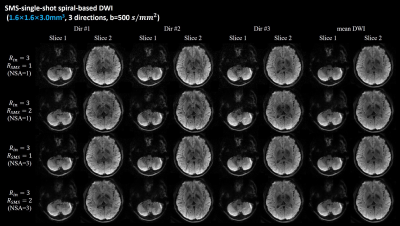
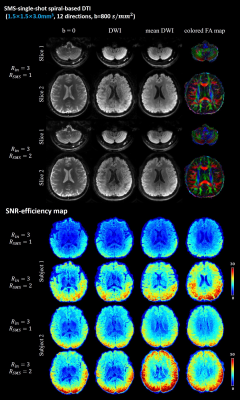
Figure 3: (A) Single-band and multi-band single-shot spiral DWI results: b=0 image, single diffusion weighted image, mean DW image and color-coded FA maps of two simultaneously excited slices. The results indicate that SMS-SSH-Spiral diffusion imaging can provide correct DTI metrics.
(B) SNR-efficiency maps of single-band and multi-band single-shot acquisitions. The SMS-SSH-spiral acquisition demonstrates higher SNR efficiency over the conventional SSH-spiral acquisition.