3737
B1 improvement of a birdcage coil using a flexible metamaterials at 7 T1Departamento de Fisica, UNAM, Mexico City, Mexico, 2Department of Physical Intelligence, Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, Stuttgart, Germany, 3Electrical Engineering, UAM Iztapalapa, Mexico City, Mexico
Synopsis
Keywords: RF Arrays & Systems, RF Arrays & Systems
This work presents a flexible metasurface to improve the B1 and the image SNR of a transceiver quadrature birdcage coil for preclinical MRI applications at 7 T. The metasurface was not tuned so no passive components were used. The imaging phantom was entirely covered with the metasurface and produced an improvement of both B1 and the SNR. This easy-to-implement approach offers an alternative to improve the B1 field for preclinical applications at high field.
Introduction
The magnetic field, B1 of a standard RF coil for MRI plays an important role to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The introduction of metamaterials has shown potential to importantly improve B1 of different types of RF coils and coil arrays [1]. Kretov et. al. have experimentally demonstrated the use of metamaterials to increase the SNR as a function of their position [2]. We have previously studied the theoretical performance of a metasurface [3] and the SNR improvement using dielectric materials [4]. These results motivated us to experimentally investigate the performance of a birdcage coil and metamaterial at 7 T and using a preclinical MR imager.Method
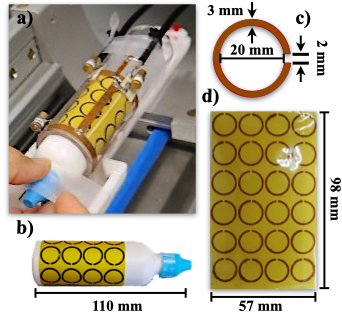
A high-pass birdcage coil was designed with a 4 cm diameter and 64 cm long and 4 rungs to obtain a low specific absorption rate (SAR) [5], giving diameter/length = 0.625 to avoid field homogeneity problems and to drastically affect the SNR. This birdcage coil was quadrature driven, operated in the transceiver mode and tuned to 300 MHz. Fig. 1. a) shows a photograph of the coil prototype. The metasurface was formed by an array of 4 x 6 C-shape (see Fig. 1.d) units and constructed using flexible hydrocarbon ceramic laminates (RO4003C3: 𝜖 = 3.55 and tan(𝛿) =0.0027, thickness = 0.508 mm, 98 mm long and 57 mm wide). The C-shaped unit had a 20 mm diameter and a gap of 2 mm and a 2 mm strip width and were printed on this flexible material above (Fig. 1.c). This metasurface is based on the cylinder of split-ring resonators reported by Vakili et. al. [6]. We acquired phantom images using a cylindrical phantom (30 mm diameter and 110 mm) filled with saline solution and the metasurface was wrapped around the phantom as shown in Fig. 1.b). Then, the phantom and the metasurface were inserted in the birdcage coil for the imaging experiments and shown in Fig. 1.a). To test the validity of the metasurface, phantom images were acquired using a standard gradient echo sequence. The acquisition parameters were: TE/TR = 4.39 ms/200 ms, FOV = 40 mm x 40 mm, matrix size = 256 x 256, Flip angle = 450, slice thickness= 2 mm, NEX = 1. Additionally, phantom images without the metasurface were also acquired for comparison purposes. All MRI experiments were performed on a 7T/30cm Bruker imager (Bruker, BioSpin MRI, GmbH, Germany).Results and Discussion
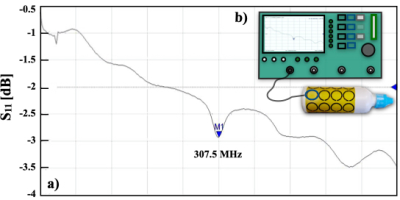
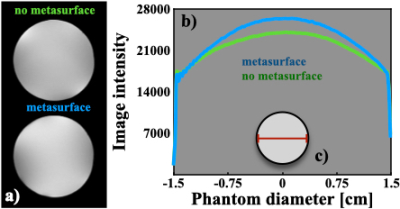
The experimental S11-parameter of the C-shaped unit cell was experimentally calculated giving a resonant frequency of 307.5 MHz as shown in Fig. 2. A very good agreement between the resonant frequency of the C-shaped unit and the bio-inspired surface coil one can be appreciated. Phantom axial images were acquired with our birdcage coil prototype and a cylindrical saline-filled phantom and the metasurface to demonstrate the feasibility to be operated at 300 MHz and compatibility with standard pulse sequences. The phantom images of Fig. 3.a) and their corresponding uniformity profiles (Fig. 3.b) were obtained and showed a good B1 uniformity in the axial plane. The image SNR values were 85.5 and 98.4 without and with the metasurface, respectively. An improvement of the B1 and SNR can be appreciated for the phantom images acquired with the phantom and the metasurface. These are rather encouraging results since the cells in the metasurface were not tuned to the resonant frequency of 300 MHz, using passive components and/or no dielectric materials were added. Unlike other results published elsewhere, the metasurface proposed here actually covers the entire phantom volume and no passive components were used for the MRI experiments [2,8]. The orientation of the C-shaped cells plays an important role to improve the birdcage coil performance, this still remains to be investigated.Conclusions
Our experimental results demonstrate that using a metasurface covering the field of view under investigation, it is possible to improve the performance of standard birdcage coil. This easy-to-implement approach offers an alternative to improve the B1 field for preclinical applications at high field.Acknowledgements
This project received funding from the UAM Division of Basic Science and Engineering under the Special Program for Education and Research (DCBI-190-2022).References
1. Wiltshire, M. C. K. (2007). Radio frequency (RF) metamaterials. Physica Status Solidi (b), 244(4), 1227-1236. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.200674511.
2. Kretov, E. I. et. al. ( 2018) Impact of wire metasurface eigenmode on the sensitivity enhancement of MRI system. Applied Physics Letters, 112(3), 033501. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5013319.
3. Vazquez, F. et. al. (2017) Theoretical quality factor of a cyclic metamaterial antenna. 34th ESMRMB. Abs. No. 291, pp. S276-S277.
4. Vazquez, F. et. al.( 2011) Signal-to-noise ratio improvement with a dielectric periodical array, 28th ESMRMB. Abs. No. 591, p. 145.
5. Martin, R. et. al. (2016) SAR of a birdcage coil with variable number of rungs at 300 MHz. Measurement, 82, 482-489. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.01.013.
6. Vakili, I. et. al. (2014). Sum rules for parallel-plate waveguides: experimental results and theory. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 62(11), 2574-2582. 10.1109/TMTT.2014.2354592.
7. Marrufo, O. et. al. (2011) Slotted cage resonator for high-fieldmagnetic resonance imaging of rodents. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 44(15), 155503. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/44/15/155503.
8. Chen, H. et. al. (2020). Metamaterial-inspired radiofrequency (RF) shield with reduced specific absorption rate (SAR) and improved transmit efficiency for UHF MRI. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 68(4), 1178-1189. 10.1109/TBME.2020.3022884.
Figures