3617
Accelerating High Resolution Diffusion Tensor Imaging Using Intra- and Inter-image Correlation
Zhongbiao Xu1, Rongli Zhang2, Wei Huang1, Junying Cheng3, Yingjie Mei4, Yihao Guo5, Hengwen Sun1, Yaohui Wang6, and Zhifeng Chen7
1Department of Radiotherapy, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, Guangzhou, China, 2Department of Imaging and Interventional radiology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, HongKong, China, 3Department of MRI, The first Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, zhengzhou, China, 4School of Biomedical Engineering, Southern Medical University, guangzhou, China, 5Hainan General Hospital, hainan, China, 6Institute of Electrical Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, beijing, China, 7Monash Biomedical Imaging, Department of Data Science and AI, Monash University, Clayton, Australia
1Department of Radiotherapy, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, Guangzhou, China, 2Department of Imaging and Interventional radiology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, HongKong, China, 3Department of MRI, The first Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, zhengzhou, China, 4School of Biomedical Engineering, Southern Medical University, guangzhou, China, 5Hainan General Hospital, hainan, China, 6Institute of Electrical Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, beijing, China, 7Monash Biomedical Imaging, Department of Data Science and AI, Monash University, Clayton, Australia
Synopsis
Keywords: Image Reconstruction, Diffusion Tensor Imaging
DTI is challenged by the prolonged scan time in frontier studies and clinical applications. Parallel imaging can reduce the scan time, but with the SNR loss and the limitation of acceleration factor. In this work, we combined SENSE with self-supervised BM4D reconstruction model to improve image quality. The in vivo experiments demonstrated that the proposed method can obtain greatly improved image quality even with high acceleration factor of 5, compared to conventional methods.Introduction
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has been widely used in frontier studies and clinical applications, such as mapping connectivity of human brain, evaluating damage caused by stroke in brain1. However, high quality diffusion images for DTI analysis often require acquisition repetition to compensate the SNR loss and multishot acquisition2,3 to mitigate image distortion. These dramatically prolong the scan time, challenging the practical usage of DTI. Conventional parallel imaging4,5 can reduce the scan time, but with the limitation of acceleration factor. By utilizing intra- and inter-image correlation, the SNR of diffusion images can be greatly improved6. Herein, we propose to integrate the constraint of intra- and inter-image correlation across different diffusion directions into the SENSE reconstruction to improve the quality of diffusion images with high under-sampling rate.Methods
BM4D is an excellent denoising method exploiting the redundancy information of intra- and inter-image7. In this work, we incorporated the self-supervised BM4D model into the SENSE reconstruction and iteratively solved the inverse problem with POCS:$$\hat{I}_\textit{t} = \mathop{\arg\min}_{I} \ \ \| \textit{M} \cdot \textit{F} \cdot \left(\textit{S} \cdot \textit{I}\right) - \textit{d}\|_{2}^{2} + \lambda\|\textit{I} - \textit{I}_\textit{t-1}\|_{2}^{2}$$
$$\textit{I}_\textit{t} = \mathop{\arg\min}_{I} \ \ \| \textit{I} - \hat{I}_\textit{t}\|_{2}^{2} + \beta\|\textit{R}_\textit{t}( \textit{I} )\|_{1}$$
M is the under-sampling mask, F is Fourier transform, S represents the coil sensitivity maps, d is the under-sampling k-space data of all diffusion directions, λ and β are regularization parameters, and Rt is the adaptive BM4D constraint for the to-be-restored multiple directions diffusion images I.
To evaluate the performance of the proposed method, a multi-shot brain dataset was acquired on a Philips Achieva 3.0T scanner (Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands) using an 8-channel head coil. The acquisition parameters included: in-plane resolution = 1.2 × 1.2 mm2, number of signal average (NSA) = 2, number of shots = 5, b-value = 800 s/mm2, and number of diffusion gradients = 10. The images reconstructed by using IRIS3 from the fully acquired multishot data were used as the reference. One of five shots was extracted for the experiment with an acceleration factor of 5 to assess the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm. The proposed method was compared with conventional SENSE reconstruction and SENSE reconstruction with total variation constraint (TV-SENSE) in terms of the estimated FA map and diffusion images.
Another rat’s abdomen DTI dataset was acquired on a 7T animal MR scanner (PharmaScan; Bruker BioSpin, Ettlingen, Germany) using a volume RF coil for transmission in conjunction with a four-channel surface RF coil array for signal reception. Respiratory trigger was used to minimize the effect of respiratory motion. Single shot EPI sequence was performed with the following parameters: in-plane resolution = 0.43 × 0.57 mm2, NSA = 1, acceleration factor = 4, b-value = 500 s/mm2, and number of diffusion gradients = 15.
Results
Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 displayed the results of the in vivo brain experiment with different reconstruction methods. Due to high acceleration factor (up to 5), the noise ruined the structure of tissues in SENSE and TV-SENSE reconstructed results. However, the proposed method greatly reduced noise and preserved image details by introducing the intra- and inter-image correlation-based BM4D constraint model. As a consequence, the proposed method had the most accurate FA map.The results of in vivo rat renal data with an acceleration factor of 4 were shown in Fig. 3. It can also be observed that the proposed method outperformed SENSE and TV-SENSE in terms of image noise, artifacts and structure details.
Discussion
The proposed method utilized the self-supervised BM4D reconstruction model to constrain the intra- and inter-image correlation across different diffusion directions, and incorporated BM4D model into SENSE reconstruction to improve the image quality with high acceleration factor. Compared to SENSE, and TV-SENSE utilizing the image sparsity constraint , the proposed method took advantage of the redundancy information of intra- and inter-image, thereby obtaining the optimal image quality. Due to the advantage of proposed method in experiments with high reduction factors, it has clinical potential for fast DTI application. BM4D model used the correlation of different diffusion directions, thus making the proposed method sensitivity to motion among different diffusion directions.Conclusion
The proposed method can obtain high quality diffusion images for DTI analysis even with a high acceleration factor of 5, and is expected to benefit the clinical application of DTI.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2019A1515111182), National Natural Science Foundation of China (61801205, 62101144), and the Guangdong Medical Scientific Research Foundation under Grant A2019041.References
[1] Le Bihan, et.al. JMRI 2001;13(4):534–546.
[2] Chen, N-k. et.al. NeuroImage 2013;72:41–47.
[3] Jeong, H-k. et.al. MRM 2013; 69:793–802.
[4] Pruessmann K-P, et.al. MRM 1999;42:952–962.
[5] Griswold M-A, et.al. MRM 2002;47:1202–1210.
[6] Zhang, X-Y, et.al. Neuroimage 2017;156:128–145.
[7] Matteo M, et.al. TIP 2013;22:119–133.
Figures
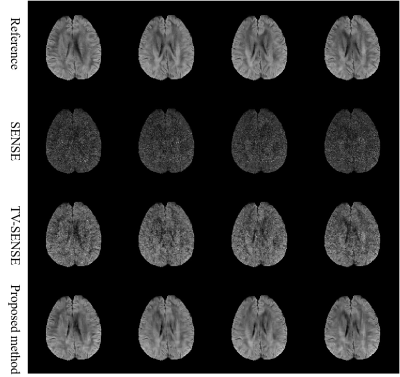
Fig.1 Four representative diffusion directions reconstructed
by different methods using brain data with acceleration factor of 5. Due to
high acceleration factor, the noise ruined in the structure of tissues in SENSE
and TV-SENSE reconstruction. However, the proposed method obtained greatly
improved images by introducing intra- and inter-image correlation constraints.
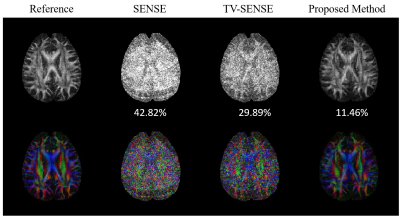
Fig.2 FA maps calculated from diffusion images reconstructed with different methods. RMSEs
of FA were listed at the bottom. Compared to SENSE and TV-SENSE, the proposed
method had the lowest RMSE and was closest to the reference FA.
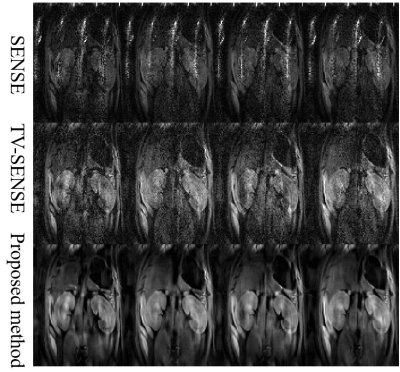
Fig.3 Four representative diffusion directions
reconstructed by using different methods with the rat renal DTI data with an acceleration factor of 4.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/3617