3513
The value of diffusion kurtosis imaging in evaluating the mild cognitive impairment of occupational aluminum workers1College of Medical Imaging, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China, 2Department of Radiology, First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Alzheimer's Disease, Alzheimer's Disease, Alzheimer’s disease; aluminum exposure; diffusion kurtosis imaging
In this work, we focused on the Al-exposed workers and confirm the findings that DKI can discriminate MCI from NC, furthermore we assess the severity of cognitive impairment in Al-exposed workers, and find the MK, Kr, MD and FA values are correlated with MoCA scores,which may provide quantitative imaging biomarkers for Al-exposed MCI workers.Objectives
To investigate whether diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) can distinguish mild cognitive impairment (MCI) from normal controls (NC) in aluminum (Al)-exposed workers, and to explore the association of DKI with cognitive performance and plasma Al concentration.Methods
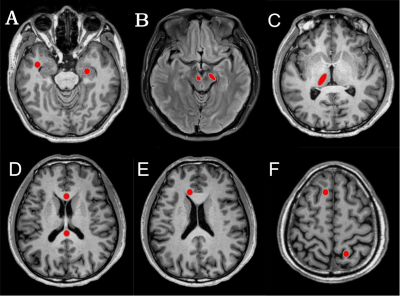
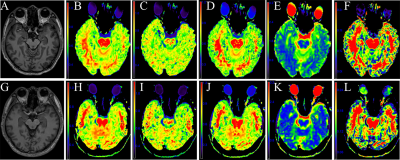
28 patients with MCI and 25 NC at Al factory were enrolled in this study. All subjects underwent conventional MRI and DKI scans. The mean kurtosis (MK), axial kurtosis (Ka), radial kurtosis (Kr), mean diffusivity (MD) and fractional anisotropy (FA) parameters of the hippocampus, substantia nigra, red nucleus, thalamus, anterior cingulate gyrus, genu and crus of the corpus callosum, frontal, parietal and temporal lobe were measured. To compare the parameters between the two groups, the Mann-Whitney rank sum test was used. The correlation of parameter values with cognitive performance and plasma Al concentration was analyzed using Spearman correlation analysis.Results
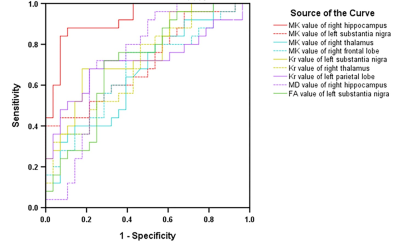
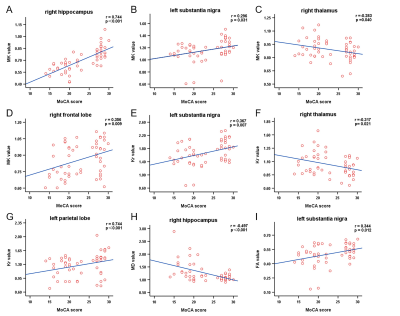
Compared with the NC group, the MK, Ka, Kr, and FA values in the MCI group were significantly decreased, and the MD values were significantly increased (P<0.05). For the diagnosis of MCI, MK in the right hippocampus showed the largest AUC (0.924). The MK, Kr, MD and FA values were correlated with the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scores, and MK values in the right hippocampus showed the greatest correlation with MoCA scores,(r=0.744,P<0.001). For the diagnosis of MCI, MK in the right hippocampus showed the largest AUC. Although there was no significant difference in plasma Al between the two groups (P=0.057), plasma Al in the MCI group was higher than that in the NC group. There was no correlation between DKI parameters and plasma Al.Conclusions
The DKI method can provide sensitive imaging biomarkers to discriminate MCI from NC and assess the severity of cognitive impairment. MK in the right hippocampus appeared to be the best independent predictor. There was no significant difference in plasma Al between the two groups. No correlation was found between DKI parameters and plasma Al. The pathogenesis of MCI still needs to be further studied.Acknowledgements
Thanks to all the people who have worked hard for this work and their families. Thanks to the participants who took part in the study and data collection.References
[1] Batum K, Çinar N, Sahin S, et al. The connection between MCI and Alzheimer disease: neurocognitive clues [J]. Turk J Med Sci, 2015, 45(5): 1137-40. doi:10.3906/sag-1404-179.
[2] Ferris S, Nordberg A, Soininen H, et al. Progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease: effects of sex, butyrylcholinesterase genotype, and rivastigmine treatment [J]. Pharmacogenet Genomics, 2009, 19(8): 635-46. doi:10.1097/FPC.0b013e32832f8c17.
[3] Baumgart M, Snyder H M, Carrillo M C, et al. Summary of the evidence on modifiable risk factors for cognitive decline and dementia: A population-based perspective [J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2015, 11(6): 718-26. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2015.05.016.
[4] Giulietti G, Torso M, Serra L, et al. Whole brain white matter histogram analysis of diffusion tensor imaging data detects microstructural damage in mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer's disease patients [J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2018, doi:10.1002/jmri.25947.
[5] Raja R, Rosenberg G, Caprihan A. Review of diffusion MRI studies in chronic white matter diseases [J]. Neurosci Lett, 2019, 694(198-207. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2018.12.007.
[6] Kumar A, Singh S, Singh A, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging based white matter changes and antioxidant enzymes status for early identification of mild cognitive impairment [J]. Int J Neurosci, 2019, 129(3): 209-16. doi:10.1080/00207454.2018.1521401.
[7] Yu J, Lam C L M, Lee T M C. White matter microstructural abnormalities in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis of whole-brain and ROI-based studies [J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2017, 83(405-16. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.10.026.
[8] Allen J W, Yazdani M, Kang J, et al. Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment May be Stratified by Advanced Diffusion Metrics and Neurocognitive Testing [J]. J Neuroimaging, 2019, 29(1): 79-84. doi:10.1111/jon.12588.
[9] Stahl R, Dietrich O, Teipel S J, et al. White matter damage in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: assessment with diffusion-tensor MR imaging and parallel imaging techniques [J]. Radiology, 2007, 243(2): 483-92. doi:10.1148/radiol.2432051714.
[10] Jensen J H, Helpern J A, Ramani A, et al. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Magn Reson Med, 2005, 53(6): 1432-40. doi:10.1002/mrm.20508.
[11] Liu D, Li K, Ma X, et al. Correlations Between the Microstructural Changes of the Medial Temporal Cortex and Mild Cognitive Impairment in Patients With Cerebral Small Vascular Disease (cSVD): A Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Study [J]. Front Neurol, 2019, 10(1378. doi:10.3389/fneur.2019.01378.
[12] Sejnoha Minsterova A, Klobusiakova P, Pies A, et al. Patterns of diffusion kurtosis changes in Parkinson's disease subtypes [J]. Parkinsonism Relat Disord, 2020, 81(96-102. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.10.032.
[13] Yuan L, Sun M, Chen Y, et al. Non-Gaussian diffusion alterations on diffusion kurtosis imaging in patients with early Alzheimer's disease [J]. Neurosci Lett, 2016, 616(11-8. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2016.01.021.
[14] Zawilla N H, Taha F M, Kishk N A, et al. Occupational exposure to aluminum and its amyloidogenic link with cognitive functions [J]. J Inorg Biochem, 2014, 139(57-64. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.06.003.
[15] Lu X, Liang R, Jia Z, et al. Cognitive disorders and tau-protein expression among retired aluminum smelting workers [J]. J Occup Environ Med, 2014, 56(2): 155-60. doi:10.1097/jom.0000000000000100.
[16] Li H, Xue X, Li L, et al. Aluminum-Induced Synaptic Plasticity Impairment via PI3K-Akt-mTOR Signaling Pathway [J]. Neurotox Res, 2020, 37(4): 996-1008. doi:10.1007/s12640-020-00165-5.
[17] Magisetty O, Dowlathabad M R, Raichurkar K P, et al. First magenetic resonance imaging studies on aluminium maltolate-treated aged New Zealand rabbits:an Alzheimer’s animal mode [J]. Psychogeriatrics, 2016, 16(4): 263-7. doi:10.1111/psyg.12158.
[18] Sexton C E, Kalu U G, Filippini N, et al. A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease [J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2011, 32(12): 2322.e5-18. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.05.019.
[19] Klingberg T. Development of a superior frontal-intraparietal network for visuo-spatial working memory [J]. Neuropsychologia, 2006, 44(11): 2171-7. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2005.11.019.
[20] Wen Q, Mustafi S M, Li J, et al. White matter alterations in early-stage Alzheimer's disease: A tract-specific study [J]. Alzheimers Dement (Amst), 2019, 11(576-87. doi:10.1016/j.dadm.2019.06.003.
[21] Alexander A L, Hasan K, Kindlmann G, et al. A geometric analysis of diffusion tensor measurements of the human brain [J]. Magn Reson Med, 2000, 44(2): 283-91. doi:10.1002/1522-2594(200008)44:2<283::aid-mrm16>3.0.co;2-v.
[22] Blockx I, De Groof G, Verhoye M, et al. Microstructural changes observed with DKI in a transgenic Huntington rat model: evidence for abnormal neurodevelopment [J]. Neuroimage, 2012, 59(2): 957-67. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.08.062.
[23] Yang A W, Jensen J H, Hu C C, et al. Effect of cerebral spinal fluid suppression for diffusional kurtosis imaging [J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2013, 37(2): 365-71. doi:10.1002/jmri.23840.
[24] Julka D, Gill K D. Involvement of altered cytoskeletal protein phosphorylation in aluminum-induced CNS dysfunction [J]. J Biochem Toxicol, 1996, 11(5): 227-33. doi:10.1002/(sici)1522-7146(1996)11:5<227::Aid-jbt3>3.0.Co;2-m.
[25] Van Petten C. Relationship between hippocampal volume and memory ability in healthy individuals across the lifespan: review and meta-analysis [J]. Neuropsychologia, 2004, 42(10): 1394-413. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2004.04.006.
[26] Albert M S, DeKosky S T, Dickson D, et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease [J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2011, 7(3): 270-9. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008.
[27] Falangola M F, Jensen J H, Tabesh A, et al. Non-Gaussian diffusion MRI assessment of brain microstructure in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease [J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2013, 31(6): 840-6. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2013.02.008.
[28] Poulter S, Lee S A, Dachtler J, et al. Vector trace cells in the subiculum of the hippocampal formation [J]. Nat Neurosci, 2021, 24(2): 266-75. doi:10.1038/s41593-020-00761-w.
[29] Wang L. Entry and Deposit of Aluminum in the Brain [J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2018, 1091(39-51. doi:10.1007/978-981-13-1370-7_3.
[30] Hao W, Hao C, Wu C, et al.Aluminum impairs cognitive function by activating DDX3X-NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis signaling pathway[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2021, Nov;157:112591. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2021.112591.Epub 2021 Oct 3. PMID: 34614429.
[31] Giorgianni C M, D'Arrigo G, Brecciaroli R, et al. Neurocognitive effects in welders exposed to aluminium [J]. Toxicol Ind Health, 2014, 30(4): 347-56. doi:10.1177/0748233712456062.
[32] Polizzi S, Pira E, Ferrara M, et al. Neurotoxic effects of aluminium among foundry workers and Alzheimer's disease [J]. Neurotoxicology, 2002, 23(6): 761-74. doi:10.1016/s0161-813x(02)00097-9.
[33] Riihimäki V, Aitio A. Occupational exposure to aluminum and its biomonitoring in perspective [J]. Crit Rev Toxicol, 2012, 42(10): 827-53. doi:10.3109/10408444.2012.725027.
[34] Meyer-Baron M, Schäper M, Knapp G, et al. Occupational aluminum exposure: evidence in support of its neurobehavioral impact [J]. Neurotoxicology, 2007, 28(6): 1068-78. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2007.07.001.
[35]Zhang ZY, Jiang HR, Sun XR, et al. Monitoring mild cognitive impairment of workers exposed to occupational aluminium based on quantitative susceptibility mapping. Clin Radiol. 2022 Jul 8:S0009-9260(22)00290-2. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2022.06.007. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35817609.
[36]Xu SM, Pan BL, Gao D, et al. Blood glucose mediated the effects of cognitive function impairment related to aluminum exposure in Chinese aluminum smelting workers [J].Neurotoxicology, 2022 Jul;91:282-289. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2022.06.001. Epub 2022 Jun 6. PMID: 35679993.
[37]Xu SM, Zhang YW, Ju XF, et al. Cross-sectional study based on occupational aluminium exposure population[J]. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol, 2021, Apr;83:103581. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2020.103581. Epub 2021 Jan 4.
Figures