3512
White matter fiber characteristics in Alzheimer's disease using fixel-based analysis1Department of Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China, 2Department of Neurology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China, 3Institute of Artificial Intelligence and Clinical Innovation, Neusoft Medical Systems Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China, 4Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia, 5MR Scientific Marketing, SIEMENS Healthineers Ltd., Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Alzheimer's Disease, Alzheimer's Disease
We collected diffusion-weighted images of all subjects and divided them into four groups: HC, MCI, mild AD and moderate AD. The differences of FD, FC and FDC were analyzed by FBA method. The results showed that the three metrics in AD group were significantly lower than those in HC Group, but there was no significant difference in MCI Group. This study indicates that there is a microstructural or macrostructural degeneration in the white matter of AD patients.Purpose
Fixel-based analynsis (FBA) was used to explore the characteristics of white matter (WM) fibers among patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and healthy controls (HC).Methods
This study included 19 mild AD, 25 moderate AD and 19 MCI patients, as well as 29 gender and age matched healthy controls that were recruited from local communities. All participants underwent cranial MRI scanning on a 3T system (MAGNETOM Prisma, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) with a 64-channel phased array head coil. The DWI parameters were: TR = 10000 ms, TE = 83 ms, FOV = 280×280 mm2, voxel size = 2.3×2.3×2.3 mm3, 65 slices, flip angle = 90°, 64 diffusion gradient directions (b = 3000 s/mm2), 4 volumes without diffusion weighting (b = 0 s/mm2), acquisition time 11 min 52s. MRI data processing was performed using MRtrix3 (www.mrtrix.org)[1], following the recommended procedures outlined in MRtrix3 documentation. FBA method was used to analyze fibre density (FD), fibre-bundle cross-section (FC), fibre density and cross-section (FDC) between groups. Connectivity-based smoothing and statistical inference was performed using the connectivity-based fixel enhancement (CFE) approach[2]. Family-wise error (FWE) correction was applied to control false positives. Significant differences were defined using PFWE < 0.05. The relevant WM tracts were identified using the JHU white-matter tractography atlas as reference[3]. Significantly reduced streamlines between groups were colored by percentage effect.Results
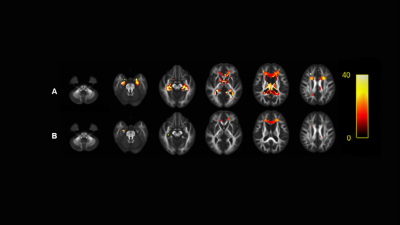
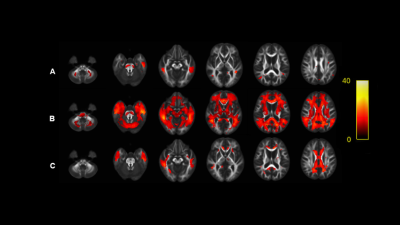
As shown in Figure 1-3: FD, FC and FDC in AD group were lower than those in HC Group and MCI Group. Compared with HC Group, moderate AD group had the most significant decreases in FD, FC and FDC and involved more extensive fiber pathways. In patients with moderate Alzheimer's disease, fiber density in some fiber pathways, such as the corpus callosum and the parahippocampal cingulum were decreased by more than 40% compared with healthy controls. The decrease of FC in AD patients was less than that of FD, but the fiber pathway involved was more extensive. It is well known that the fiber density representing the micro-structure and the fibre-bundle cross-section representing the macro-structure were combined (i.e. , FDC) , we found that FDC decreased more significantly than FD or FC. In addition, when MCI patients were compared with healthy controls, no significant decreases were observed for any of these three metrics.Conclusion
In patients with Alzheimer's disease, significant white matter fiber degeneration was found in both microstructures and macrostructures, but not in patients with mild cognitive impairment.Discussion
In this study, we used FBA method to investigate the changes of white matter fiber characteristics in AD and MCI patients. Fixel-based analysis (FBA) is a new technique proposed by Raffelt et al. in recent years[4]. The term “fixel” represents all fibers bundles with different orientations within a voxel. FBA method can be used to analyze the fiber density from the micro-level, the fibre-bundle cross-section from the macro-level and the effect of combination of these two. Past studies have shown that conventional diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) techniques are not adequate for complex fiber structures and misleading voxel analysis to cross fibers[5]. The DTI techniques can estimate only one major direction of the voxel, while the FBA method can analyze fibers in all directions within one voxel, so it could be more accurate than DTI technique.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Tournier, J.D., et al., MRtrix3: A fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualisation. Neuroimage, 2019. 202: p. 116137.
2. Raffelt, D.A., et al., Connectivity-based fixel enhancement: Whole-brain statistical analysis of diffusion MRI measures in the presence of crossing fibres. Neuroimage, 2015. 117: p. 40-55.
3. Szeszko, P.R. and P.B. Kingsley, MRI atlas of human white matter. Concepts in Magnetic Resonance Part A, 2006. 28A(2): p. 180-181.
4. Raffelt, D.A., et al., Investigating white matter fibre density and morphology using fixel-based analysis. Neuroimage, 2017. 144(Pt A): p. 58-73.
5. Jeurissen, B., et al., Investigating the prevalence of complex fiber configurations in white matter tissue with diffusion magnetic resonance imaging. Hum Brain Mapp, 2013. 34(11): p. 2747-66.
Figures