3453
The application of R2 star map of enhanced T2 star weighted angiography (ESWAN) in diagnosis of ovarian cancer
Qingling Song1, Ye Li1, and Ailian Liu1
1Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
1Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Pelvis, Cancer
Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death of gynecological malignant tumors, however, most of BEOTs can be completely cured. The treatment and prognosis of ovarian cancer and BEOTs are very different, so it is very important to accurately distinguish ovarian cancer from BEOTsSynopsis
Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death of gynecological malignant tumors, however, most of BEOTs can be completely cured. The treatment and prognosis of ovarian cancer and BEOTs are very different, so it is very important to accurately distinguish ovarian cancer from BEOTsSummary of main Findings
This study showed that R2 star values were significant higher in the ovarian cancer group than those in the BEOTs group. The R2 star value had a satisfied differentiated efficiency with AUC 0.824, sensitivity 75.00% and specificity 88.89%. The results revealed that the R2 star of enhanced T2 star weighted angiography (ESWAN) can assist the gynecologist to discriminate ovarian cancer from BEOTs.Introduction and Purpose
Ovarian tumor is one of the most common gynecological tumors, which can be qualitatively divided into benign, malignant and borderline tumors. Ovarian epithelial malignant tumors account for about 95% of ovarian malignant tumors, which is the leading cause of death of gynecological malignant tumors [1]. Borderline epithelial tumors of the ovary (boderline epithelial ovarian tumors, BEOTs) usually occur in women of childbearing age, accounting for about 10% to 15% of ovarian epithelial tumors [2]. Although about 2% of BEOTs has the possibility of malignant transformation, most of BEOTs can be completely cured. if the diagnosis is accurate, fertility-preserving surgery can be performed on patients, which will greatly improve the quality of life of patients after treatment [3]. The treatment and prognosis of ovarian cancer and BEOTs are very different, so it is very important to accurately distinguish ovarian cancer from BEOTs. Enhanced T2 star weighted angiography (ESWAN) is a magnetic sensitivity weighted imaging technique, which can detect the changes of blood oxygen in tissue and is sensitive to iron deposition and blood products. This study aimed to investigate the role of R2 star vale in the differentiation of ovarian cancer from BEOTs.Materials and Methods
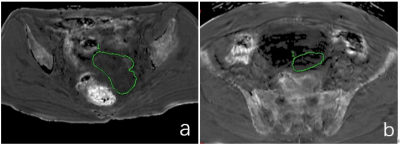
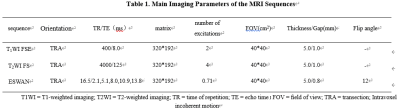
42 ovarian tumor patients pathologically confirmed with 49 lesions were divided into cancer group (40 lesions) and BEOTs group (9 lesions). MR examinations included T1W, T2W, ESWAN imaging were performed within two weeks before surgery. All patients were scanned using a 1.5 T MR scanner (GE Signa HDXT) with eight-channel body matrix coil. The specific scanning parameters are shown in Table 1. The ROI of the lesion was manually drawn along the contour of the solid portion of tumor at the largest slice in the R2 star map by referring to the T1W and T2W sequence. (Figure 1). The quantitative parameter R2 star value was measured. The independent sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U test were used to compare the difference in the R2 star values between the two groups. ROC curve was used to calculate the parameters with the statistical difference to evaluate the performance of predicting ovarian cancer from BEOTs.Results
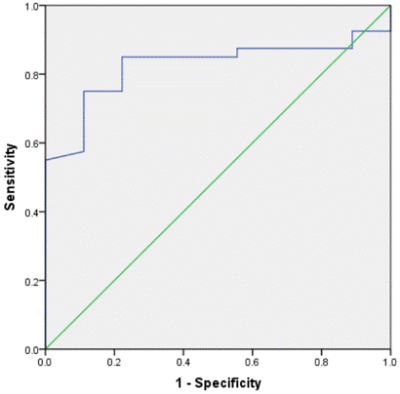
Patient Characteristics Of the 42 ovarian tumor patients with 49 lesions finally enrolled, 40 lesions were in the ovarian cancer group, 9 lesions were in the BEOTs group. Agreement on Imaging Parameters among the Three Observers The three observers had high consistency on measurements of the R2 star values with the inter-class correlation coefficients higher than 0.75. R2 star value Between ovarian cancer and BEOTs group s The R2 star value in ovarian cancer group were significantly higher than those of BEOTs group (8.98±2.86 vs. 6.78±1.18, P=0.029). The performance of R2 star value to differentiate ovarian cancer from BEOTs ROC curves for R2 star value to differentiate ovarian cancer from BEOTs was shown in Fig. 2. The R2 star value had a satisfied differentiated efficiency with AUC 0.824, sensitivity 75.00% and specificity 88.89%.Discussion and Conclusion
The R2* value of ESWAN sequence represents the transverse relaxation rate and is not affected by TE and magnetic field intensity. It can be used to quantitatively measure the changes of deoxyhemoglobin and iron content in tissues. The value of R2 star is sensitive to the determination of microvessels and macrovessels, and the decrease of deoxyhemoglobin leads to the decrease of R2 star [4]. Ovarian cancer is a highly malignant tumor with strong proliferation of tumor cells and the growth of tumor neovascularization. Therefore, compared with borderline tumors, the blood supply of ovarian cancer is more abundant. In addition, malignant tumors have high metabolism and produce more metabolites, resulting in an increase in the concentration of paramagnetic substances, so the value of R2 star was higher. Thus, the results of this showed that the R2 star of enhanced T2 star weighted angiography (ESWAN) was able to assist the gynecologist to discriminate ovarian cancer from BEOTs.Acknowledgements
no acknowledgementsReferences
1. Tu N, Zhong Y, Wang X, Xing F, Chen L, Wu G. Treatment Response Prediction of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Based on Histogram Analysis of Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019 Feb;40(2):326-333. 2. Fang C, Zhao L, Chen X, Yu A, Xia L, Zhang P. The impact of clinicopathologic and surgical factors on relapse and pregnancy in young patients (≤40 years old) with borderline ovarian tumors. BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 21;18(1):1147. 3. Hauptmann S, Friedrich K, Redline R, Avril S. Ovarian borderline tumors in the 2014 WHO classification: evolving concepts and diagnostic criteria. Virchows Arch. 2017 Feb;470(2):125-142. 4. Xin JY, Gao SS, Liu JG, Sun CF, Han Y, Sun XH, Wang XZ, Wang B. The value of ESWAN in diagnosis and differential diagnosis of prostate cancer: Preliminary study. Magn Reson Imaging. 2017 Dec;44:26-31.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/3453