3451
Feasibility of Accelerated T2 Mapping for the Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment of Endometrial Carcinoma
Zanxia Zhang1 and Shujian Li1
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Uterus, Uterus
The objectives of this study were to investigate the feasibility of accelerated T2 mapping in the clinical diagnosis of the pathologic subtypes and histologic grades of endometrial carcinoma (EMC), and to compare synthetic T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted (sT2W/DW) images to conventional T2W and diffusion-weighted (cT2W/DW) images for the myometrial invasion depth. 56 EMC patients underwent T2mapping and DW. Distinct T2 values were obtained for the various pathologic and histologic grades of EMC. Furthermore, pathologic EA grading was more accurate with the T2 values than ADC values. Additionally, in terms of detecting deep myometrial invasion, sT2W/DW showed similar accuracy to cT2W/DW.Purpose
To investigate the feasibility of accelerated T2 mapping in the clinical diagnosis of the pathologic subtypes and histologic grades of endometrial carcinoma (EMC), and to compare synthetic T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted (sT2W/DW) images to conventional T2W and diffusion-weighted (cT2W/DW) images for the myometrial invasion depth.METHODS:
Fifty-six patients with pathologically confirmed EMC and 17 healthy volunteers were prospectively enrolled in this study. All the participants underwent pelvic magnetic resonance imaging, including T2-weighted turbo spin-echo, DWI, and accelerated T2 mapping before treatment. The T2 and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of different pathologic EMC features were extracted and compared. Furthermore, the myometrial invasion depth was assessed by sT2W/DW and cT2W/DW images. The receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to analyze the diagnostic efficacy of the T2 and the ADC values in distinguishing the pathologic subtypes and histologic grades of EMC.RESULTS:
The T2 and ADC values of the EMC were significantly lower than those of normal endometrium (both p < 0.05). The T2 and ADC values were significantly different between endometrioid adenocarcinoma (EA) and non-EA (both p < 0.05) and EMC tumor grades (all p < 0.05) but not for EMC clinical types (both p > 0.05). The area under the ROC curve (AUC) value was higher for T2 values than for ADC values for predicting grade 3 EA (0.939 vs. 0.764). Furthermore, the accuracy of sT2W/DW and cT2W/DW in predicting deep myometrial invasion was comparable (78.6%vs. 82.1%, p > 0.05).CONCLUSION:
In patients with EMC, the accelerated T2 mapping may be useful for evaluating tumor invasion depth and its histologic grade.Acknowledgements
NoneReferences
1. Li S, Liu J, Zhang F, et al (2020) Novel T2 Mapping for Evaluating Cervical Cancer Features by Providing Quantitative T2 Maps and Synthetic Morphologic Images: A Preliminary Study. J Magn Reson Imaging 52:1859-1869.
2. Raudner M, Schreiner M, Hilbert T, et al (2020) Accelerated T2 Mapping of the Lumbar Intervertebral Disc: Highly Undersampled K-Space Data for Robust T2 Relaxation Time Measurement in Clinically Feasible Acquisition Times. Invest Radiol 55:695-701.
3. Mai J, Abubrig M, Lehmann T, et al (2019) T2 Mapping in prostate cancer. Invest Radiol 54:146-152.
Figures
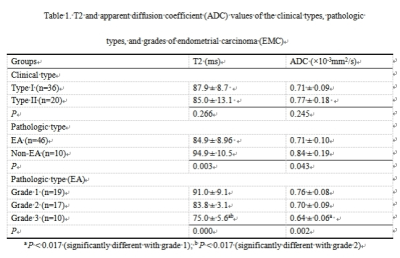
T2 and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of the clinical types, pathologic types, and grades of endometrial carcinoma (EMC)
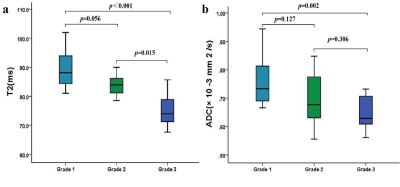
The T2 and ADC values of different histologic grades of EA. (a) Boxplots show the T2 values of different histologic grades of EA. (b) Boxplots show the ADC values of different histologic grades of EA.
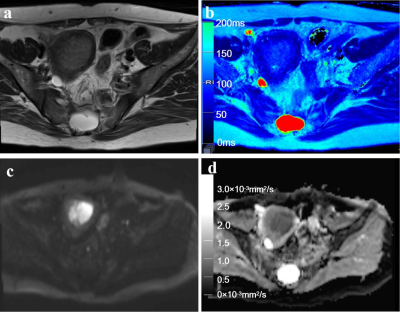
Representative T2WI and DWI and the corresponding axial T2 and ADC maps of the endometrium region of a 53-year-old patient with stage IA endometrial carcinoma.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/3451