3450
iZoom applying tilted 2D Echo-Planar RF excitation improved the image quality of reduced FOV DWI for uterine cervical cancer: a preliminary study1Department of Radiology, Chiba University, Chiba-shi, Japan, 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology and Radiation Oncology, Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba University, Chiba-shi, Japan, 3Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 4Philips Healthcare (Shanghai) Ltd., Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Uterus, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques, uterine cervical cancer
Reduced field-of-view (rFOV) DWI is the essential sequence for the diagnosis and staging of uterine cervical cancer (CC). We compared the image quality of rFOV DWI taken with iZoom, which applies tilted 2D Echo-Planar RF excitation, and that of conventional Zoom combined with Reconstruction with Image-space Sampling (Zoom-IRIS) for CC patients. Reduced FOV DWI with iZoom showed higher image quality than Zoom-IRIS both in quantitative and qualitative evaluation. Anatomical details display and lesion conspicuity were mainly improved in quantitative evaluation. iZoom can be helpful for the diagnosis and staging of CC.INTRODUCTION
The role of MRI in the diagnosis and staging of uterine cervical cancer (CC) has greatly increased since the most recent revision of the FIGO staging system was announced in 2018(1, 2). Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), especially reduced field-of-view (rFOV) DWI, is the essential sequence for assessing tumor invasion.To improve the image quality of rFOV DWI, various imaging techniques have been developed. Zonally magnified oblique multislice (Zoom) enabled us to acquire images with reduced FOV with a single shot acquisition(3). The Image Reconstruction with Image-space Sampling (IRIS) scheme by two-dimensional (2D) navigated multi-shot SENSE EPI can be combined with Zoom (Zoom-IRIS) and succeeded in reducing artifacts(4). However, it remains challenging to constantly acquire high-quality images. The new technique “iZoom” (5) applies a tilted 2D Echo-Planar RF excitation by only tilting the k-space along the phase-encoding direction, which reduces crosstalk artifacts and scan-time, has better fat suppression effects and is expected to achieve further improvement in image quality.
The purpose of this study was to evaluate and compare the image quality of rFOV DWI taken with iZoom and Zoom-IRIS in CC patients.
METHODS
Six histologically proven CC patients who underwent MRI at our institution between September and October 2022 were included. One patient was pregnant, and the other 5 patients used 20 mg intramuscular hyoscine butyl bromide to reduce the peristaltic artifacts.All MRIs were acquired on a 1.5T MRI (Ingenia or Achieva dStream 1.5T, Philips Healthcare) and included both iZoom and Zoom-IRIS rFOV DWI, which had the exact same anatomical coverage, slice thickness, and inter-slice gap. Scanning parameters are summarized in Figure 1. T2WI (axial, sagittal, oblique), T1WI (axial), fat-saturated T1WI (axial), and conventional DWI (axial) were also acquired.
The image quality was assessed by consensus of two radiologists (Radiologist 1 with 9 years of pelvic MRI experience; radiologist 2 with 16 years of experience). The two rFOV DWI sequences were viewed separately with the order shuffled regarding DWI sequence presentation. Overall image quality, anatomical details display, distortion, artifacts, and lesion conspicuity were assessed with a four-point scale, respectively (Figure 2).
Radiologist 1 set region of interests (ROIs) on the iZoom and Zoom-IRIS, respectively at the same slice. ROItumor was manually placed in the tumor at the slice with the largest diameter, and ROIGM was placed in the gluteus muscles (GM) on the same slice with the lesion (Figure 3). The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) was defined as the average signal of the tumor (SItumor) divided by the standard deviation (SDtumor) (SNR = SItumor/SDtumor)(6). Contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) was defined as the absolute average signal difference between the lesion and GM divided by the standard deviation of GM (CNR = (SItumor −SIGM)/SDGM). The mean ADC value of the ROItumor was also measured.
Qualitative scores, SNR, CNR, and the mean ADC between iZoom and Zoom-IRIS were compared using Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
RESULTS
The mean age of the six patients was 60 years old (30-84 y.o.). Five patients had squamous cell carcinoma, and one had adenocarcinoma.Regarding quantitative evaluation, rFOV DWI with iZoom showed significantly higher SNR and CNR than Zoom-IRIS (p=0.031 and 0.031).
Regarding qualitative evaluation, iZoom DWI got higher image quality scores on all evaluation factors than Zoom-IRIS, and there were significant differences in anatomical details display, lesion conspicuity, and overall image quality (p=0.037,0.048, and 0.048). There was no significant difference in mean ADC values (p=0.563). All statistical results are summarized in Figure 4.
DISCUSSION
In this study, iZoom improved image quality compared with Zoom-IRIS both in quantitative and qualitative evaluation without affecting the mean ADC. In particular, anatomical details display and lesion conspicuity were greatly improved. We present two example cases in Figure 5, which showed obvious improvement with iZoom.Since the revision of the FIGO 2018 staging system, the primary tumor size for determining clinical stage has been assessed mainly on MRI rather than physical examination(1, 2). Improvement in anatomical details display and lesion conspicuity would highly contribute to the accurate assessment of tumor size and invasion. Consequently, it would lead to the appropriate staging and treatment decisions.
This study has some limitations. Firstly, the small sample size is the most critical. However, despite the small sample size, significant differences were found in both qualitative and quantitative evaluation, suggesting that the results are of clinical value. Secondly, it is necessary to compare lesions visualized in rFOV DWI with tissue specimens and to confirm the accuracy of the diagnosis.
CONCLUSION
This preliminary study showed the potential clinical feasibility and superiority of iZoom for the diagnosis and staging of uterine CC. Although further investigation is needed to validate this preliminary result, iZoom can be a helpful tool for the evaluation of CC.Acknowledgements
No.References
1. Lee SI, Atri M. 2018 FIGO Staging System for Uterine Cervical Cancer: Enter Cross-sectional Imaging. Radiology. 2019;292(1):15-24.
2. Bhatla N, Aoki D, Sharma DN, Sankaranarayanan R. Cancer of the cervix uteri. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2018;143 Suppl 2:22-36.
3. Wilm BJ, Svensson J, Henning A, Pruessmann KP, Boesiger P, Kollias SS. Reduced field-of-view MRI using outer volume suppression for spinal cord diffusion imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2007;57(3):625-30.
4. Jeong HK, Gore JC, Anderson AW. High-resolution human diffusion tensor imaging using 2-D navigated multishot SENSE EPI at 7 T. Magn Reson Med. 2013;69(3):793-802.
5. Banerjee S, Nishimura DG, Shankaranarayanan A, Saritas EU. Reduced field-of-view DWI with robust fat suppression and unrestricted slice coverage using tilted 2D RF excitation. Magn Reson Med. 2016;76(6):1668-76.
6. An H, Ma X, Pan Z, Guo H, Lee EYP. Qualitative and quantitative comparison of image quality between single-shot echo-planar and interleaved multi-shot echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging in female pelvis. Eur Radiol. 2020;30(4):1876-84.
Figures
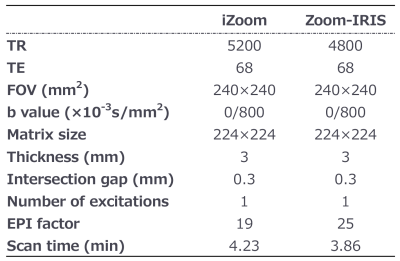
Fig.1 Summary of rFOV DWI scanning parameters.
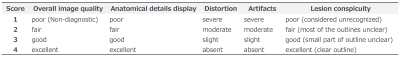
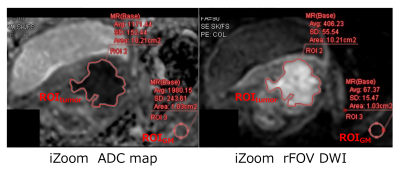
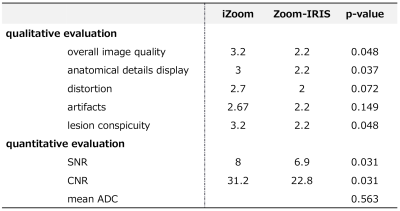
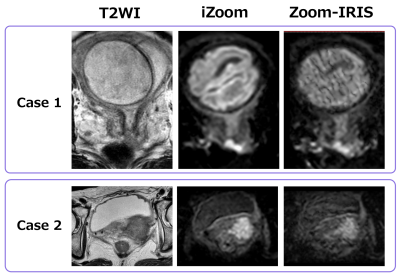
Fig.5 Two example cases that showed obvious improvement in image quality with iZoom.
Case 1: Pregnant patient with stage IB2 cervical cancer. She could not use hyoscine butyl bromide. Lesion conspicuity in T2WI and Zoom-IRIS was poor to fair, while rFOV DWI with iZoom depicted the tumor with a sharp boundary.
Case 2: Patient with stage IIB cervical cancer. Anatomical details display and lesion conspicuity are much better in rFOV DWI with iZoom than with Zoom-IRIS.