3449
Less-distorted cervical ADC maps improved subjective diagnosis efficacy on cervical cancer and reliability of measurements
liu hui1, liu wei yin2, and ou xiao rong1
1xiangya hospital, changsha, China, 2GE, taiwan, China
1xiangya hospital, changsha, China, 2GE, taiwan, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Pelvis, Cancer, DWI
Differentiation of patients with IB-IIA from those with IIB-IIC assist track treatment selection for cervical cancer. A diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequence based on field-of-view optimized and constrained undistorted single shot (FOCUS) combined with multiplexed sensitivity-encoding (MUSE) technique (named FOCUS-MUSE DWI) was used in our study to explore the differentiation performance on stages of cervical cancer. We found the reliability of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) for FOCUS MUSE-DWI is the highest among single-shot DWI (ss-DWI), FOCUS-DWI and MUSE-DWI, and better image quality, SNR, and CNR than the former two. There was no significant difference of ADC values for four DWI sequence between IB-IIA group and IIB-IIIC, but ADC values were consistent with previous studies.Introduction and Purpose
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is widely used in the clinical staging of CC,DWI plays an critical role in the evaluation of tumor response after chemotherapy,the local staging, pathological uterine cervix. Conventional DWI could yield clear pitfalls, including poor spatial resolution, ghosting, and susceptibility artifacts. Besides, with the large scope of full field-of-view (f-FOV), it also involves liquid, gas and other substances, which may cause motion, so high-resolution imaging is vital for the evaluation of gynecological tumors. A new multi-shot DWI sequence (multi-plexed sensitivity-encoding DWI [MUSE DWI] in GE, has been applied to evaluate diseases in various organs, such as liver, breast, and central nervous system with a better SNR. This article was conducted to examine the reliability of ADC measurements, using FOCUS DWI, MUSE DWI and SS DWI as references to compare their image quality and to systematically investigate the feasibility of FOCUS-MUSE DWI in the use of cervical cancer.Methods
This prospective study was approved by our institutional review board-approved. Pelvic DWIs ( b = 50, 800 s/mm2 ) were performed in 39 patients confirmed cervical cancer pathologically (mean age, 56.51 ± 11.15 years; age range, 36–75 years) on 3.0 T MRI (Signa Premier, GE Healthcare, USA) using ss-DWI, FOCUS-DWI, MUSE-DWI and FOCUS MUSE-DWI. The scan parameters were kept the same as much as possible in four DWIs. ADC and SNR, CNR were measured in the largest slice of the tumor in axial plane and region of interest (ROI) was drawn avoiding hemorrhage necrosis lesion (Figure 1). The signal to noise ratio (CNR) was calculated using the following equation: SNR=SItumor/SDbackground. CNR = (SItumor-SInormal)/SDnormal. The calculations were performed on the b = 800 s/mm2 images. Image quality (4-point scale for each of severity of artifacts, sharpness of boundaries, interslice signal homogeneity and overall image quality) was also assessed. Values were compared using paired t-test or non-parametric wilcoxon signed rank depending on data normality and equality of variance. The sequence with the optimal clinical utility was determined by systematically comparing the ADC repeatability, CNR and image quality. Individual reliability and inter-rater repeatability of ADC were analyzed with intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). An ICC over 0.80 represents a good agreement. P values less than 0.05 were considered significant difference.Results
Demographics: Between October 2021 and May 2022, 39 consecutive patients (mean age, 56.51 ± 11.15 years; age range, 36–75 years) were enrolled in this study. Of all 39 patients, FIGO stages of the patients included IB (n =10), IIA (n = 6), IIB (n = 10), IIIA (n =2), IIIB (n = 1), IIIC (n = 7), IV (n = 3). The demographics of patients in this study was shown in (Table 1). Consistency: Interobserver agreement of the CNR, geometric distortion, image blurring, ghosting artifacts, lesion conspicuity and overall image quality were good or excellent in four DWI sequences (Table 2). Among the four sequences, FOCUS MUSE-DWI had the most reliable interobserver agreement (intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC= 0.915). ADC values of four sequences: The average ADC values for FOCUS-MUSE, MUSE, FOCUS and SS-EPI DWI were (0.9558±0.168) × 10-3mm2/s, (0.944±0.191) ×10-3mm2/s, (0.975±0.182) × 10-3mm2/s, and (0.890 ± 0.052) × 10-3mm2/s, respectively. No statistical difference of ADC value was observed between the four sequences (Figure 2) . Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of image quality: The comparison of image quality scores assessed by two radiologists between the four DWI is shown in Table 3. The Focus DWI shared the highest SNR and CNR with the mean value of 10.50±3.91 and 6.96±3.16 respectively.While Focus-muse DWI had the highest scores in the subjective image quality and were significantly higher than other three sequences(Figure 3). ADC values in different stage and histological type: There was no significantly different ADC value between cervical adenocarcinoma and cervical squamous cell carcinoma(Table 4). We found that IB-IIA group tend to have higher ADC values than IIB-IIIC (P>0.05)(Table 5).Discussion and conclusion
We demonstrated the mean ADC values of cervical cancer acquired by four different DWI sequences range from 0.941 – 0.955 ×10 -3 mm2/sec fell in the range of previous reports. Moreover, FOCUS-MUSE DWI had the highest inter-observer agreements of ADC measurements, attributing to less susceptibility artifacts with the FOCUS technique and shorter T2 signal decay with MUSE method. Therefore, FOCUS-MUSE DWI may be sufficiently reliable and repeatable in diagnosing cervical cancer. Newly-developed FOCUS-MUSE DWI, FOCUS DWI and MUSE DWI sequences overcame the disadvantage of the conventional DWI in the inherently small cervix. Additionally, the higher (IIB-IV) FIGO staging cases have lower ADC values. ADC values has been considered to effectively predict histological subtype of cervical cancer, tumor grade and treatment response. In this study, we indicated that FOCUS-MUSE DWI had superior subjective image quality compared with the other three sequences with consistent ADC values despite lower SNR than MUSE DWI only. Overall, we considered that FOCUS-MUSE DWI generated ADC values has great potential in assessment of FIGO staging in cervical carcinoma.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Xie M, Ren Z, Bian D, et al. High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging with readout segmentation of long variable echo-trains for determining myometrial invasion in endometrial carcinoma. Cancer Imaging. 2020 Sep 21;20(1):66.
2. Fu Q, Kong XC, Liu DX, et al. Clinical comparison of single-shot EPI, readout-segmented EPI and TGSE-BLADE for diffusion-weighted imaging of cerebellopontine angle tumors on 3 tesla. Magn Reson Imaging. 2021 Dec;84:76-83.
Figures
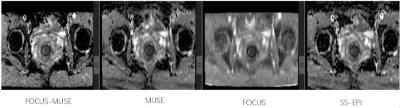
Figure 1 Illustration of ROI measurements on cervical diffusion
weighted images using four DWI sequences.
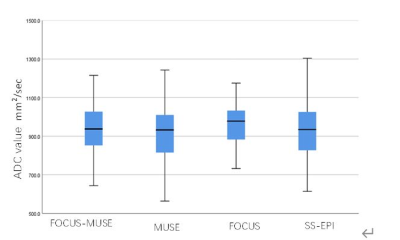
Figure 2 Mean ADC
values in the manually drawn region of interest for four DWI sequences
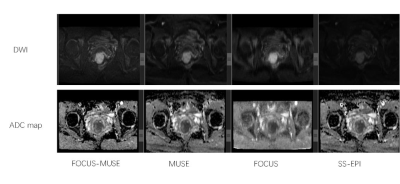
Figure 3. Comparisons
of image quality of SS-, FOCUS-, MUSE-, and FOCUS MUSE- DWI. Diffusion-weighted
images at b=800 s/mm2) with the corresponding ADC maps are arrayed.
Image quality with FOCUS MUSE-DWI was significantly different from SS-DWI and FOCUS-DWI
in severity of artifacts, sharpness of boundaries, interslice signal
homogeneity and overall image quality (p < 0.05). FOCUS MUSE-DWI was
slightly superior to the MUSE-DWI in overall image quality (p > 0.05).
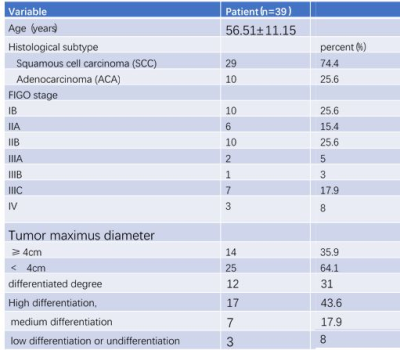
Table 1 Demographic
summary of patients recruited in this study
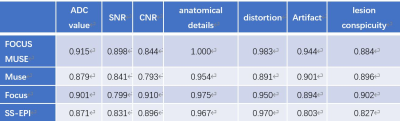
Table 2 ICC for inter-reader measurements of four DWI
sequences
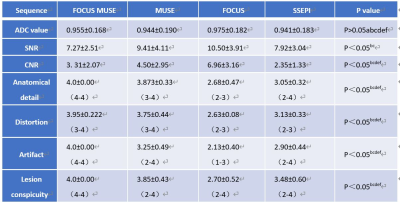
Table 3 Objective and subjective assessment of four DWI sequences.
Comparisons between 1 and 2 (a), 1 and 3 (b), 1 and 4 (c), 2and 3 (d), 2 and 4 (e), 3 and 4 (f)
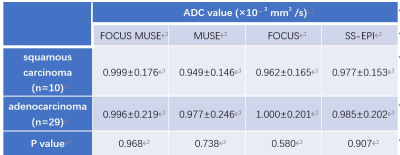
Table 4 ADC values of patients with
different stage and histological types of four DWI sequences.

Table 5 ADC values for ROIs with
different disease stages of four DWI sequences
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/3449