3254
Multiparametric MRI-based Radiomics for Preoperative Prediction of Multiple Biological Characteristics in Endometrial Cancer1Department of Radiology,, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, China, 2Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, China, 3Clinical & Technical Support, Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Pelvis, Uterus
Different biological characteristics of endometrial cancer (EC) may lead to different treatment efficacies and prognoses, so stratification of biological characteristics in EC is important for treatment planning.Introduction and Purpose
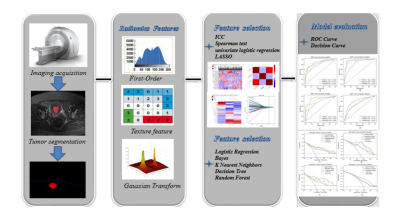
This study aims to develop and validate multi-parametric MRI (MP-MRI)-based radiomics models for noninvasive and precise prediction of several biological characteristics in EC.Materials and Methods
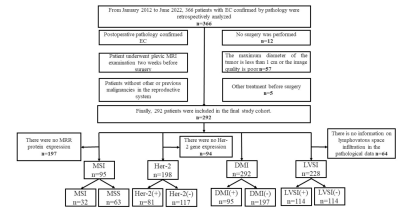
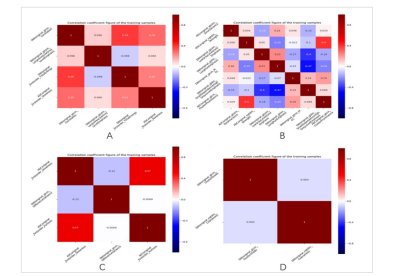
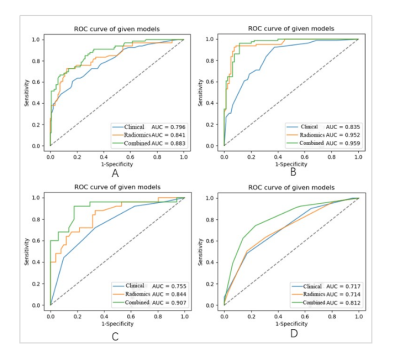
This study consisted of 292 patients with EC who received MP-MRI examination before surgery. We focused on evaluating four postoperative biological characteristics: LVSI (n = 228), DMI (n = 292), MSI (n = 95), and Her-2 (n = 198).Total 2316 radiomics features were extracted from MP-MRI images and some clinical factors (age, FIGO stage, differentiation degree, pathological type, menopausal state, and irregular vaginal bleeding) were included. Five classifiers were applied (Bayes, KNN, RF, decision tree, and logistic regression) to construct radiomics models for predicting biological characteristics. The diagnostic efficiency of the construction models was evaluated by ROC curves and quantified by AUC. Delong's test was used to assess the AUC values between the models. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) logistic regression and intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) were used to select radiomics features; univariate and multivariate logistic regression were used to select clinical parameters.Results
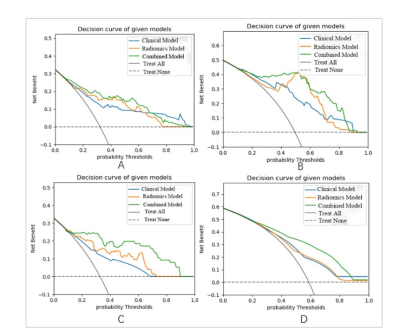
RF radiomics model performed the best performance among the five classifiers for the three subgroups according to AUC values (MSI, AUC = 0.844; LVSI, AUC = 0.952; DMI, AUC = 0.840) in the training cohort. The AUC of decision tree radiomics model was relatively higher for Her-2 (AUC = 0.714) in the training cohort. In the training cohort, the combined model was significantly better than the clinical model in each subgroup (MSI, P = 0.002; Her-2, P = 0.011; DMI, P = 0.004; LVSI, P<0.001). Nevertheless, in the validation cohort, there were significant difference between the two models only in the DMI and LVSI subgroups (DMI, P = 0.033; LVSI, P=0.002).Discussion and Conclusion
In this study, we constructed radiomics models based on MP-MRI (T2WI, DWI, and ADC) using five classifiers for prediction of four prognosis-related biological characteristics (DMI, LVSI, MSI, and Her-2) in EC patients. Our study showed that these models obtained satisfactory performances with the AUC values greater than 0.8 in the training cohort (except for Her-2, AUC = 0.714). Meanwhile, we added several clinical characteristics to the optimal radiomics models for building the combined models, although they barely improved the performance of prediction. We obtained moderately efficient radiomics signatures, which showed promising prediction performance in the independent validation sets and probably help to guide the further treatment planning in EC.The challenge in preoperative staging and surgical planning of EC is the assessment of biological risk factors such as DMI, LVSI, etc. Radiomics approaches can provide a comprehensive, non-invasive, and reproducible assessment of tumor biology. Nowadays, the application of radiomics to simultaneously predict multiple biological characteristics of tumors has became a trend.
This study is also the first research to assess the expression of Her-2 gene and MSI in EC based on MP-MRI radiomics model approach. Recently, some studies [1, 2 have pointed out that the overexpression of Her-2 gene in EC is significantly correlated with cell transformation, tumor formation, tumor metastasis, drug resistance and poor prognosis.
Detection of MSI status in EC patients can help screen the Lynch syndrome, evaluate disease progress, and thus provide personalized and precise treatments [3, 4]. However, assessment of MSI status in EC by biopsy or whole tumor resection is invasive and postoperative. A small fraction of tissue captured by a biopsy may not be sufficient to accurately reflect the MSI status of a tumor [5, 6].
This study associated the radiomics features of MP-MRI with four biological characteristics (DMI, LVSI, MSI, and Her-2) related to the aggressiveness of EC. The established comprehensive models made it possible to predict more critical biological characteristics of EC and achieved favorable prediction abilities. Therefore, the models are expected to noninvasively evaluate the risk stratification of EC and provide valuable guidance for clinical decision-making.
Acknowledgements
No.References
[1]. Meng X, Li H, Kong L, Zhao X, Huang Z, Zhao H, Zhu W, Li X, Yu J, Xing L: MRI In rectal cancer: Correlations between MRI features and molecular markers Ki-67, HIF-1alpha, and VEGF. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging : JMRI 2016, 44(3):594-600.33.
[2]. An HJ, Song DH, Kim YM, Jo HC, Baek JC, Park JE: Significance of HER2 and VEGFR2 in Early-stage Endometrial Cancer. In Vivo 2022, 36(2):723-730.
[3]. Black D, Soslow RA, Levine DA, Tornos C, Chen SC, Hummer AJ, Bogomolniy F, Olvera N, Barakat RR, Boyd J: Clinicopathologic significance of defective DNA mismatch repair in endometrial carcinoma. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2006, 24(11):1745-1753.
[4]. Arabi H, Guan H, Kumar S, Cote M, Bandyopadhyay S, Bryant C, Shah J, Abdul-Karim FW, Munkarah AR, Ali-Fehmi R: Impact of microsatellite instability (MSI) on survival in high grade endometrial carcinoma. Gynecologic oncology 2009, 113(2):153-158.
[5]. Itakura H, Achrol AS, Mitchell LA, Loya JJ, Liu T, Westbroek EM, Feroze AH, Rodriguez S, Echegaray S, Azad TD et al: Magnetic resonance image features identify glioblastoma phenotypic subtypes with distinct molecular pathway activities. Science translational medicine 2015, 7(303):303ra138.
[6]. Sacher AG, Dahlberg SE, Heng J, Mach S, Jänne PA, Oxnard GR: Association Between Younger Age and Targetable Genomic Alterations and Prognosis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA oncology 2016, 2(3):313-320.
Figures