3219
Clinical application of direct signal control and other B1 shimming methods for infratentorial region T2 weighted imaging at 7T
Xiaoyu Wang1, Jianxun Qu2, Tomi-Tricot Raphael3, Shaihan J Malik4, Song Wang1, Xiangbing Bian1, and Xin Lou1
1Department of Radiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Siemens Healthineers Ltd, Beijing, China, 3Siemens Healthineers Ltd, United Kingdom, United Kingdom, 4King's College London, United Kingdom, United Kingdom
1Department of Radiology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Siemens Healthineers Ltd, Beijing, China, 3Siemens Healthineers Ltd, United Kingdom, United Kingdom, 4King's College London, United Kingdom, United Kingdom
Synopsis
Keywords: Tumors, Data Acquisition, direct signal control
This was a clinical application study of direct signal control (DSC) technology on 7T MRI. The result suggests that DSC-T2w provides good-quality for whole-brain imaging. When imaging region is restricted, we can also use static B1 shimming with a dedicated shimming region. This study demonstrated that DSC technology can improve the image quality in 7T brain scan.Introduction
T2 weighted imaging (T2w) is of vital importance in the diagnosis of neurological disease. With the increased magnetic field, the intrinsic signal-to-noise (SNR), and the transverse relaxation, T2 decreases, which are beneficial for high-resolution T2-weighted imaging (T2w) at 7T. However, due to the markedly deteriorated B1 field at 7T, the practice of T2w is problematic. The spatially inhomogeneous B1 field strength can alter the contrast and even bring in a dark band, especially in the infratentorial region, where B1 strength is reduced. The advances in parallel transmit techniques hold the potential to mitigate, or even eliminate, such imaging inhomogeneity. Traditionally, a static B1 shimming is performed to improve the overall B1 homogeneity of the imaging volume. Such an approach is practical for restricted regions but compromised when the imaging region increases. Recently, a new technique was proposed for alleviating the problem for regions under the curtain. Specifically, the Direct Signal Control (DSC) technology, which directly targets a uniform signal distribution across the field of view, with a signal evolution following that obtained with an ideal refocusing train [1][2]. This study aimed to investigate the utility of DSC-T2w for evaluating image quality and lesion details and compared the DSC approach with other B1 shimming strategies.Methods
This study included six subjects, with informed consent acquired before the study. The experiment was performed on a whole-body 7T scanner (MAGNETOM Terra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) equipped with an 8-channel transmit and 32-channel receive coil. All the subjects underwent MR examination, including T2w with radio-frequency transmission in TrueForm (circularly polarized, CP) mode, patient-specific (PS) mode, volume-specific (VS) mode, and the research DSC-T2w. In the PS mode, a static B1 shimming was performed for the whole imaging region. In the VS mode, the shimming was optimized for the manually designated area, which covered the cerebellum in our experiment (Fig.2D). The imaging parameters for the different T2w sequences were kept the same, as the following: TR/TE 7000/65ms, FOV 210 x 210mm, scan matrix = 512 x 358, slice thickness, 2.0 mm, reconstructed voxel size 0.2x0.2x2.0 mm, phase-encoding acceleration factor 2, refocus pulse flip angle 120-degree, slice number 52, and the acquisition time 6 min 18 sec. The echo time is located at the seventh echo in the echo train. T2w images of different shimming settings were blinded and evaluated independently and consecutively by two experienced radiologists in terms of overall image quality, infratentorial image quality, supratentorial image quality, perceived signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), image contrast, image sharpness, and residual artifacts with scores ranging from 1 (nondiagnostic) to 5 (excellent). The scoring criteria are shown in Table 1. Evaluations were performed for each subject based on a complete set of axial images.Result
A subject’s DSC-T2w image quality is shown in Figure 1. The displayed homogeneity was acceptable for the structure under the curtain. Among the comparison of different B1 shimming strategies, CP mode (Fig. 2A) provides poor quality for the subtentorial region; VS mode (Fig. 2D) has the best quality of the cerebellum region. However, in regions outside the manually designated B1 shimming volume, the image homogeneity is poor. The whole brain imaging results are of good quality in both the PS mode and the DSC approach (Fig. 2A and 2B). Comparing DSC-T2w and PS-T2w, the scoring criteria of DSC-T2w were higher than PS-T2w (Fig. 3).Discussion
This preliminary study compared the performance of DSC, and the other static B1 shimming strategies. DSC-T2w can constantly improve image homogeneity in the whole brain examination. In general, DSC outperformed the static shimming methods, though in some cases (Fig.4), the improvement was limited.Conclusion
DSC technology was effective in mitigating image inhomogeneity for the whole brain scan. For lesions located in a restricted region, static B1 shimming with a dedicated shimming region could also be used.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] S.J. Malik, F. Padormo, A.N. Price, J.V. Hajnal, Spatially resolved extended phase graphs: modeling and design of multipulse sequences with parallel transmission, Magnetic resonance in medicine 68(5) (2012) 1481-94.
[2]. Malik SJ, Beqiri A, Padormo F, Hajnal JV. Direct signal control of the steady-state response of 3D-FSE sequences. Magn Reson Med. 2015 Mar 1;73(3):951–63
Figures
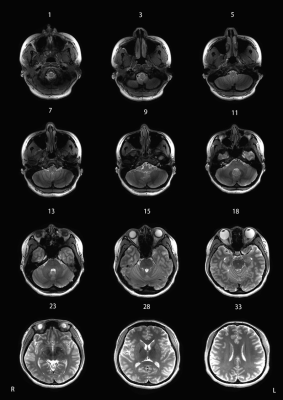
Figure 1:
Application of Direct Signal Control technology on 7T MRI. A series of axial
images in a 28-year-old healthy female subject. Window Level 600, Window Width
1200.
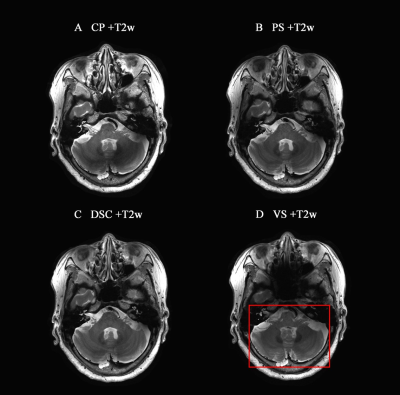
Figure 2:
Comparison of different B1 shimming strategies on 7T MRI. A series of axial
images in a 77-year-old healthy female subject. T2w with (A) circular polarity
(CP) mode, (B) patient-specific (PS) mode, (C) direct signal control (DSC)
mode, and (D) volume-specific (VS) mode. Window Level 600, Window Width 1200.
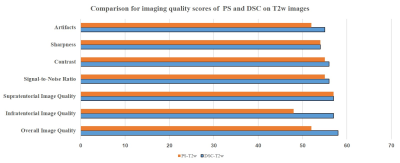
Figure 3:
Comparison of imaging quality scores of patient-specific (PS) and direct signal
control (DSC) on T2w images. Each score was obtained by averaging the scores of
two radiologists.
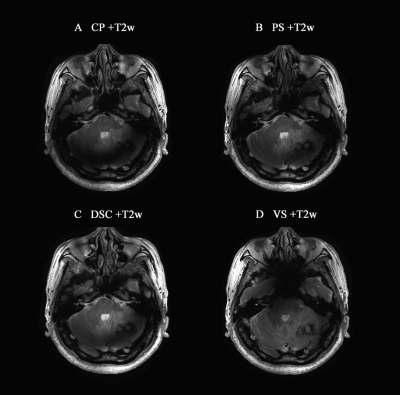
Figure 4:
Comparison of different B1 shimming strategies on 7T MRI. A series of axial
images in a 67-year-old male lung cancer patients with brain metastasis. T2w
with (A) circular polarity (CP) mode, (B) patient-specific (PS) mode, (C)
direct signal control (DSC) mode, and (D) volume-specific (VS) mode. Window
Level 600, Window Width 1200.
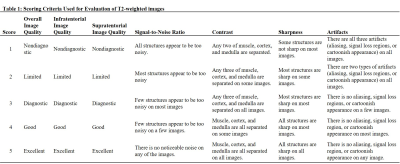
Table 1 Scoring Criteria Used for Evaluation of T2-weighted images
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/3219