3153
Influence of Different uCS Acceleration Factors on Three-dimensional Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Image Quality
Chen Lihua1, Song Qingwei1, Nan Wang1, Yongming Dai2, Dan Yu2, Guobin Li2, and Ailian Liu1
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2MR Collaboration,Central Research Institute, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China
1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2MR Collaboration,Central Research Institute, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Liver, MR Value
To investigate the effects of different united compressed sensing (uCS) acceleration factors (AFs) on three-dimensional magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (3D-MRCP) image quality and to compare the quality with that using conventional parallel imaging (PI).Purpose
To investigate the effects of different united compressed sensing (uCS) acceleration factors (AFs) on three-dimensional magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (3D-MRCP) image quality and to compare the quality with that using conventional parallel imaging (PI).Materials and Methods
We retrospectively collected11volunteers (60.5 ±10.2 years) who underwent 3D-MRCP scanning using a 3T MRI system (uMR Omega, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China). The coronaryT2-mx3d-trig images were acquired using uCS with different AFs (3, 4, 5, 6, and 7) and PI with an AF of 2.7.Detailed parameters are listed in Table 1. After reconstruction with maximum intensity projection (MIP) using a quartet-scale method (Fig 1), the image quality was scored by two observers (six and four years of experience in MRI diagnostic, respectively) according to the structural details distinction, the sharpness, and the diagnostic accuracy of common bile duct, common hepatic duct, cystic duct, intrahepatic bile duct, and pancreatic duct (Table 2).Cohen's kappa statistic was applied to assess the inter-reader agreement. Friedman test was conducted to evaluate the differences in the scores under different accelerating settings. Moreover, apair-wise comparison using Wilcoxon test was performed for significant differences revealed in the Friedman test.Results and Discussion
Image quality scores were consistent between two observers (Table 3).There was no significant differences in scores of common bile duct, common hepatic duct, and cystic duct under different accelerating settings (Table 4). There were significant differences in scores of intrahepatic bile duct and pancreatic duct under different accelerating settings. The score of intrahepatic bile duct descended when uCS = 7, and the score of pancreatic duct descended when uCS = 6 (Table 5). uCS-based 3D-MRCP shows high feasibility and clinical applicability: it can shorten the scanning time while ensuring image quality.Conclusion
uCS-based 3D-MRCP could save scanning time without losing image quality, compared with conventional MRI using PI method. With satisfactory image quality and tight clinical time-constraint balanced, the AF of ACS is commended to be 2.5 or 3 in routine MR scanning.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.Figures
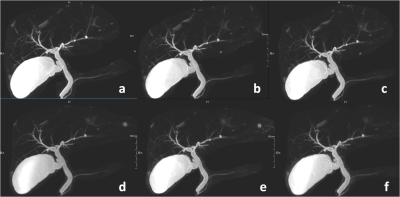
Fig 1. The T2-mx3d-trig images
under different accelerating settingsfor a representativecase. (a-f)The
T2-mx3d-trigimages with PI AF=2.7, uCS AF=3, 4, 5, 6, and 7, respectively.
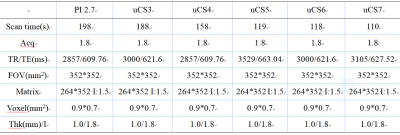
Table 1 Sequence parameters of coronary T2-mx3d-trig
images
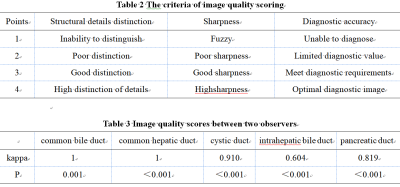
Table 2 The criteria of image quality scoring
Table 3 Image quality scores between two observers
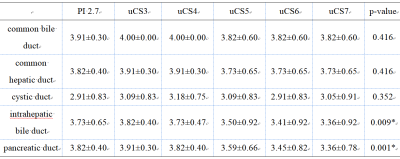
Table 4 The Comparisons of scoreunder different accelerating
settings
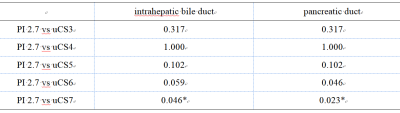
Table 5
The p values
for the pair-wise comparisonsof scores
in
intrahepatic bile duct and pancreatic duct
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/3153