3103
Unsupervised model for removing Nyquist/motion artifacts in SPatiotemporal Encoding MRI
Qingjia Bao1, Liyang Xia2, Kewen Liu2, Xinjie Liu1, Peng Sun3, Lucio Frydman4, and Chaoyang Liu1
1Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, 4Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel
1Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, 4Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel
Synopsis
Keywords: Image Reconstruction, Susceptibility
Although a major advantage of SPEN vs EPI is a higher immunity to artifacts, it suffers from Nyquist or motion artifacts. We proposed a new unsupervised CNN model that takes advantage of both physical model and Deep learning. The model consists of three parts: phase feature extraction module, which can extract the phase features of even/odd phase differences or motion-caused phase differences in multi-shot echo data. Then, the phase maps are generated with these phase difference features. Lastly, the phase correction modules to remove artifacts. The results show that the proposed model can effectively correct Nyquist/motion artifacts in single-shot/multi-shot SPEN.INTRODUCTION
Single-shot magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can shorten the scanning time of multi-scan MRI from several minutes to tens of milliseconds and has achieved great applications in function MRI, diffusion imaging, etc. Echo Planar Imaging (EPI) is one of the most commonly used single-shot imaging methods. However, due to its inherently low phase-encoding bandwidth, the image will be seriously distorted in the phase-encoding direction. Similar to EPI, odd and even gradient echoes will result in Nyquist artifacts in the phase-encoding dimension due to the eddy currents and gradient delays. Moreover, the motion during the multi-shot scan will also cause artifacts in high-resolution diffusion-weighted images. However, one advantage of SPEN is that it can directly obtain low-resolution images. Thus, the phase information for correcting Nyquist/motion artifacts can be obtained directly by calculating the phase difference between low-resolution even and odd echo images. However, due to the low resolution and phase unwrapping problem, the traditional pixel-level phase difference calculation algorithm2,3 can not completely remove the Nyquist/motion artifacts in SPEN. In recent years, the deep neural network has been widely used in various fields because of its efficient feature extraction ability. Unlike traditional methods, deep learning-based methods can implicitly learn multi-parametric information. However, the supervised deep learning network4,5 needs paired reference images. This work aims to design a new deep unsupervised learning network model which is based on the overall features of the images and the inherent characteristics of SPEN, and can achieve a better Nyquist/motion artifact correction effect compared with traditional methods.METHODS
The overall architecture of the proposed single-shot model is shown in Figure 1(a), and the overall architecture of the proposed multi-shot model is shown in Figure 2. They include three main components: 1) The phase feature extraction module. It is based on the encoder structure with a residual connection, as shown in Figure 1(b). The main function is to extract the deep feature information of SPEN images through multiple cascaded encoders and provide the phase feature information for the phase map generation module. At the same time, the residual structure can effectively avoid over-fitting caused by the deep networks. 2) The phase map generation module. The input of this module includes two pre-defined basis matrices (H×a, a×W respectively) and a phase feature map (a×a) obtained through the phase feature extraction module, as shown in Figure 1(c). The phase feature map can be linearly mapped using the basis matrices to obtain a sufficiently smooth phase map. 3) The phase correction module. In this module, the phase information of the even echo data is corrected by using the phase map to keep the phase consistent with the original odd echo data, and the even echo data after phase correction is interleaved with the original odd echo data.RESULTS
Figure 3 shows the Nyquist correction results of various comparison methods (Chen’s and Lee’s are state-of-the-art supervised Nyquist artifacts correction methods) on the single-shot human brain simulation data. The figure illustrates that the proposed method can obtain better image sharpness and details, particularly from the zoomed regions and the error maps. Figure 4 shows the Nyquist artifacts correction results of various comparison methods on the single-shot real sampled data. As can be seen, the RARE images have high resolution with the clear texture of details, which comes at the cost of about 1 min acquisition time for a single image. The EPI images are distorted due to the inhomogeneous magnetic fields and chemical shifts. The Nyquist artifacts in SPEN images have been removed of traditional method and the proposed method. However, the traditional method needs to take about 40 seconds to correct a single image, while the proposed method takes only 4 milliseconds. Figure 5 shows the Nyquist/motion artifacts correction results of various comparison methods on the multi-shot human brain simulation data. The figure illustrates that the proposed method can retain sufficient image details while removing most Nyquist/motion artifacts.DISCUSSION & CONCLUSION
A new unsupervised CNN model for removing Nyquist/motion artifacts in single-shot/multi-shot SPEN. This model can extract the phase maps of SPEN images and remove Nyquist/motion artifacts by correcting the phase of SPEN data. The proposed model does not need paired reference images, and is based on the overall features of the images and the inherent characteristics of SPEN, which offers a promising deep learning framework for scan time reduction in artifacts correction applications in SPEN.Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support by National Major Scientific Research Equipment Development Project of China (81627901), the National key of R&D Program of China (Grant 2018YFC0115000, 2016YFC1304702), National Natural Science Foundation of China (11575287, 11705274), and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (YZ201677).References
1. Tal A, Frydman L. Spatial encoding and the single-scan acquisition of high definition MR images in inhomogeneous fields[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2006, 182(2):179-194. 2. Seginer A, Schmidt R, Leftin A, Solomon E, Frydman L, et al. Referenceless reconstruction of spatiotemporally encoded imaging data: Principles and applications to real-time MRI[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Official Journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2015, 72(6):1687-95. 3. Yun, Seong, Dae, et al. Referenceless one-dimensional Nyquist ghost correction in multicoil single-shot spatiotemporally encoded MRI[J]. Magnetic resonance imaging: An International journal of basic research and clinical applications, 2017, 37:222-233. 4. Chen X, Zhang Y, She H, et al. Reference-free Correction for the Nyquist Ghost in Echo-planar Imaging using Deep Learning[C]. ICBBE: 2019 6th International Conference on Biomedical and Bioinformatics Engineering. 2019.Figures
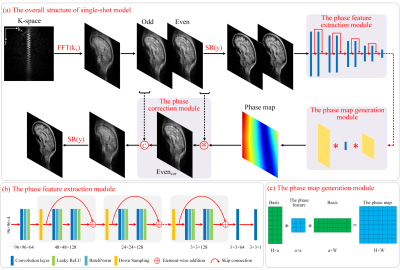
FIGURE 1. (a) The overall architecture of the proposed single-shot model for removing
Nyquist artifacts in single-shot SPEN, with a slice containing the k-space data
with phase distortion as input, and the high-resolution image without artifacts
as output. (b) The phase feature extraction module, which contains multiple
cascaded encoders with residual connection. (c) The phase map generation module.
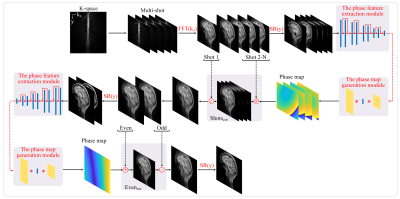
FIGURE 2. The
overall architecture of the proposed multi-shot model for removing Nyquist/motion
artifacts in multi-shot SPEN, with a slice containing the k-space data with
phase distortion as input, and the high-resolution image without artifacts as
output.
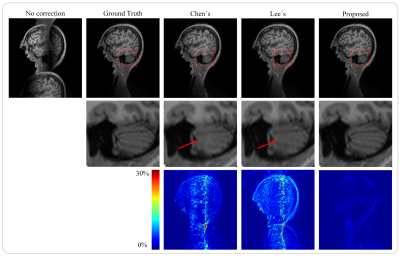
FIGURE 3. Artifacts correction results of various comparison methods on the single-shot
human brain simulation data. Columns of the first row from left to right show the artifacts-uncorrected
image, reference image, and artifacts-corrected images obtained by Chen’s
method, Lee’s method, and the proposed method, respectively. Columns of the second
row from left to right show the zoomed regions of the correction results of
various comparison methods. Columns of the third row from left to
right show the error maps of various comparison methods.
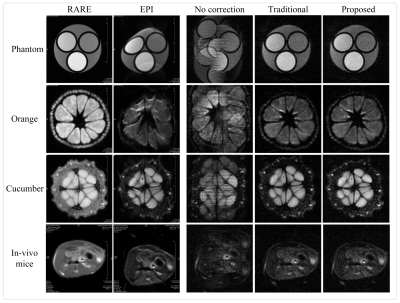
FIGURE 4. Artifacts correction
results of various comparison methods on the single-shot real sampled
data. From top to bottom,
from left to right are the RARE images, EPI images, artifacts-uncorrected SPEN
images, artifacts-corrected SPEN images obtained by traditional method and the
proposed method of phantom, orange, cucumber and in-vivo mice.
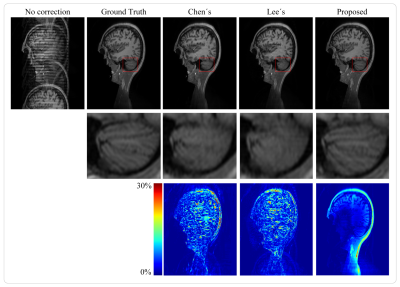
FIGURE 5. Artifacts
correction results of various comparison
methods on the multi-shot human brain
simulation data. Columns of the first row from left to right show the
artifacts-uncorrected image, reference image, and artifacts-corrected images
obtained by Chen’s method, Lee’s method, and the proposed method, respectively.
Columns of the second row from left to right show the zoomed regions of the
correction results of various methods. Columns of the third row from left to
right show the error map of various methods.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/3103