3075
Early Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy of Triple Negative Breast Cancer using Radiomics on DCE-MRI1MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, United States, 2Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Radiomics, fMRI, Treatment response
We developed models based on radiomic features from dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) MR images and demonstrated that these models have potential to serve as non-invasive biomarkers for early prediction of pathologic complete response (pCR) in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients undergoing neoadjuvant systemic therapy (NAST).Introduction
Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is typically treated with neoadjuvant systemic therapy (NAST), however, the heterogeneity of the disease results in varying responses to the treatment1. Approximately 40-50 % of TNBC patients receiving NAST achieve pathologic complete response (pCR), which is associated with excellent long-term outcomes. Early prediction of response to NAST in TNBC patients could potentially help triage patients without pCR to alternative investigational therapies and avoid unnecessary treatment toxicity.Studies have shown that DCE-MRI radiomic models can serve as promising tools for predicting treatment response in breast cancer patients in general2-4. In this study, we investigated the radiomic features from DCE-MRI acquired at the different time points of NAST for early treatment response prediction in TNBC patients.
Methods
One hundred and eighty two biopsy-confirmed stage I-III TNBC patients enrolled in an IRB-approved prospective clinical trial (NCT02276443) were included in this analysis. All patients underwent DCE-MRI scans on a GE 3T MRI scanner at baseline (BL), after two (C2) and four (C4) cycles of doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide based chemotherapy. Tumors were segmented manually by two fellowship-trained breast radiologists using early phase (2.5 min) DCE-MRI subtraction images with a Matlab toolbox developed in-house.Ten first-order radiomic features and 300 grey-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM) features, as well as their absolute differences (AD) and relative differences (RD) between the 3 imaging time points, were derived from the tumor ROIs. The patients were divided into training (N=122) and testing (N=60) cohorts in a 2:1 ratio. For a univariate analysis, area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUC ROC) was calculated to determine the features most predictive of pCR/non-pCR. Wilcoxon Rank Sum test was used to test the statistical significance of the predictive performance. In a multivariate analysis, radiomic models were established using logistic regression with elastic net regularization followed by 5-fold cross validation for the performance assessment.
Results
Eighty-eight (48%) patients had pCR (59 training, 29 testing) and 94 (52%) patients had non-pCR (63 training, 31 testing) according to the pathological findings of the surgical specimen.Per univariate analyses, 28 radiomic features (7 from C4, 14 from C4 & BL differences, 7 from C4 & C2 differences) were statistically significant with AUC ≥ 0.7 in both training and testing cohorts. The 7 significant features at C4 (mean, maximum, minimum, percentile 1, percentile 5, percentile 95 and percentile 99) had AUCs of 0.71-0.79 for the training cohort and 0.73-0.83 for the testing cohort. None of the GLCM features had AUC ≥ 0.7 for both training and testing cohorts. Changes measured between C4 and BL or C2 showed AUCs between 0.70-0.85 in the training and 0.70-0.84 in the testing groups.
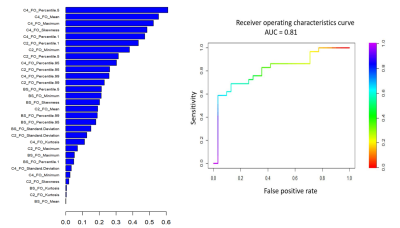
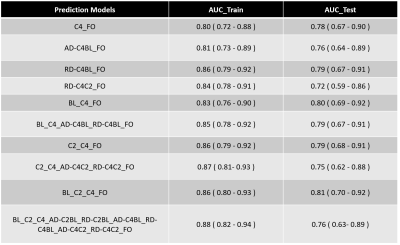
Of the 51 multivariate regression models evaluated, 10 with radiomic features at BL, C2, C4, as well as their AD and RD (AD-C4BL, AD-C4C2, AD-C2BL, RD-C4BL, RD-C4C2, RD-C2BL) showed AUCs between 0.80-0.88 for the training and 0.72-0.81 for testing cohorts (Table 1). Radiomic model based on first order features from BL, C2 and C4 (BL_C2_C4_FO) showed the best AUC for the testing cohort (AUC_test = 0.81) (Figure 1).
Conclusions
Our study results demonstrated that DCE-MRI first-order and GLCM radiomic features can be used to generate models capable of predicting NAST response for TNBC with high accuracy. Upon further validation, these radiomic models can serve as potentially useful pretreatment biomarkers to guide an optimal treatment strategy for TNBC patients.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Rouzier R, Perou CM, Symmans WF, et al. Breast cancer molecular subtypes respond differently to preoperative chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(16):5678-5685.
2. Cain EH, Saha A, Harowicz MR, Marks JR, Marcom PK, Mazurowski MA. Multivariate machine learning models for prediction of pathologic response to neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer using MRI features: a study using an independent validation set. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019;173(2):455-463. 3. Ahmed A, Gibbs P, Pickles M, Turnbull L. Texture analysis in assessment and prediction of chemotherapy response in breast cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;38(1):89-101.
4. Fan M, Wu G, Cheng H, Zhang J, Shao G, Li L. Radiomic analysis of DCE-MRI for prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Eur J Radiol. 2017;94:140-147.
Figures