2967
The value of Intravoxel incoherent motion quantitative parameters in predicting Peritoneal Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer
Qingling Song1, Ye Li1, and Ailian Liu1
1Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
1Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Pelvis, Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a common fatal malignant tumor in clinic, and it is also a malignant tumor in the female reproductive system, which is third common followed cervical cancer and uterine cancer. It is easy to metastasize, among which peritoneal implantation is a common way of metastasis in the early stage.Synopsis
Ovarian cancer is a common fatal malignant tumor in clinic, and it is also a malignant tumor in the female reproductive system, which is third common followed cervical cancer and uterine cancer. It is easy to metastasize, among which peritoneal implantation is a common way of metastasis in the early stage.Summary of main Findings
This study showed that the standADC, slowADC and f values in peritoneal metastasis positive group were significantly lower than those of peritoneal metastasis negative group. The standADC, was the only independent factor for predicting peritoneal metastasis. The f value had the best predicted performance with the highest AUC 0.754 and the highest specificity 84.21%, however, slowADC had the highest sensitivity 85.71%.Introduction and Purpose
Ovarian cancer is a common fatal malignant tumor in clinic, and it is also a malignant tumor in the female reproductive system, which is third common followed cervical cancer and uterine cancer [1]. It is easy to metastasize, among which peritoneal implantation is a common way of metastasis in the early stage. About 75% of patients with advanced ovarian cancer have extensive peritoneal implantation metastasis [2].Materials and Methods
33 ovarian cancer patients pathologically confirmed with 40 lesions were divided into peritoneal metastasis positive group (19 lesions) and peritoneal metastasis negative group (21 lesions). MR examinations included T1W, T2W, IVIM imaging were performed within two weeks before surgery. All patients were scanned using a 1.5 T MR scanner (GE Signa HDXT) with eight-channel body matrix coil. The specific scanning parameters are shown in Table 1. The ROI of the lesion was manually drawn along the contour of the solid portion of tumor at the largest slice in the IVIM parameter maps (Figure 1). The quantitative parameters of Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) including the standard apparent diffusion coefficient (standADC), low apparent diffusion coefficient (slowADC), fast apparent diffusion coefficient (fastADC) and perfusion fraction (f) were measured. The independent sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U test were used to compare the differences in the parameter values between the two groups. ROC curve was used to calculate the parameters with the statistical difference to evaluate the predicted performance of peritoneal metastasis. Binary logistic regression analysis predicted the independent risk factors of peritoneal metastasis in Ovarian cancer.Results
Patient Characteristics Of the 33 ovarian cancer patients with 40 lesions finally enrolled, 19 lesions were in the peritoneal metastasis positive group, 21 lesions were in the peritoneal metastasis negative group. Agreement on Imaging Parameters among the Three Observers The three observers had high consistency on measurements of the standADC, slowADC,fastADC and f values with the inter-class correlation coefficients higher than 0.75. IVIM Parameters Between Peritoneal Metastasis Positive and Negative groups The standADC, slowADC and f values in peritoneal metastasis positive group were significantly lower than those of peritoneal metastasis negative group (Table 2). The standADC, slowADC and f were involved in the Logistic analysis, multivariate analysis revealed the standADC was the only independent factor for predicting peritoneal metastasis. The performance of IVIM Parameters to predict peritoneal metastasis ROC curves for IVIM parameters standADC, slowADC and f to predict peritoneal metastasis were shown in Fig. 2. The f value had the best predicted performance with the highest AUC 0.754 and the highest specificity 84.21%, however, slowADC had the highest sensitivity 85.71% (Table 3).Discussion and Conclusion
The standADC, slowADC and f values in peritoneal metastasis positive group were significantly lower than those of peritoneal metastasis negative group. The standADC, was the only independent factor for predicting peritoneal metastasis. The f value had the best predicted performance with the highest AUC 0.754 and the highest specificity 84.21%, however, slowADC had the highest sensitivity 85.71%. The results showed that the ovarian cancer with positive peritoneal metastasis had high density, large number and small internal and external space, the activity of water molecules in tumor tissue was obviously limited, and the ADC value was lower than that of ovarian cancer with negative peritoneal metastasis. It is suggested that ADC value has a certain value in predicting peritoneal metastasis of ovarian cancer. IVIM-DWI removes the influence of microcirculation perfusion, eliminates the weakening of DWI signal caused by false diffusion of blood flow and vascular structure, and describes tissue water molecular diffusion alone. Compared with ADC value, its parameter D value can more accurately reflect the molecular movement and diffusion of tumor tissue. The perfusion fraction (f value) representing the volume percentage of water flowing in the capillaries [3]. Ovarian malignant tumors with positive peritoneal metastasis proliferate vigorously and may be accompanied by more new capillaries, but the structure of new capillaries is immature and may not have effective perfusion function, so the f value is smaller than that of ovarian cancer with negative peritoneal metastasis. The standADC, slowADC and f values of IVIM can be used to differentiate peritoneal metastasis of ovarian cancer, help to predict peritoneal metastasis before treatment, and provide reference for clinical staging.Acknowledgements
no acknowledgementsReferences
1. National Cancer Institute: Surveillance E. End Results Program . Cancer Stat Facts: Ovarian Cancer. Bethesda (MD): SEER Cancer Statistics: Reports on Cancer; (2020) 2. Marrelli D, Petrioli R, Cassetti D, D'Ignazio A, Marsili S, Mazzei MA, Lazzi S, Roviello F. A novel treatment protocol with 6 cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) in stage III primary ovarian cancer. Surg Oncol. 2021 Jun;37:101523. 3.Dolciami M, Capuani S, Celli V, Maiuro A, Pernazza A, Palaia I, Di Donato V, Santangelo G, Rizzo SMR, Ricci P, Della Rocca C, Catalano C, Manganaro L. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) MR Quantification in Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer (LACC): Preliminary Study on Assessment of Tumor Aggressiveness and Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. J Pers Med. 2022 Apr 15;12(4):638.Figures
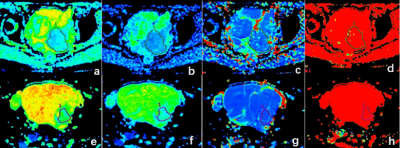
Figure 1. The ROIs
of the primary ovarian cancer. (a-d) the primary ovarian cancer with peritoneal
metastasis positive. (e-h) the primary ovarian cancer with peritoneal
metastasis negative. (a,e) was standADC; (b,f) was slowADC; (c,g) was fastADC;
(d,h) was f.
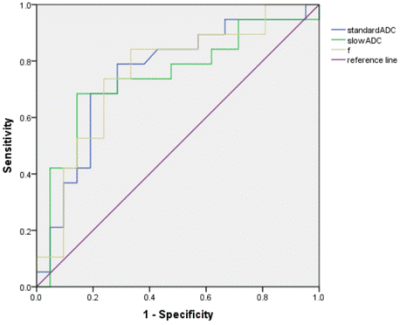
Figure 2. ROC of IVIM
parameters standADC, slowADC and f.
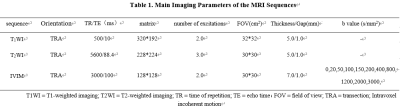
Table 1. Main Imaging Parameters of the MRI
Sequences
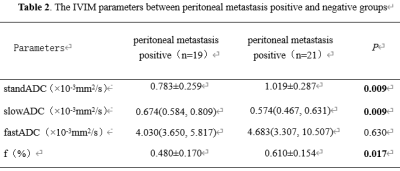
Table 2.
The IVIM parameters between peritoneal metastasis positive and negative groups
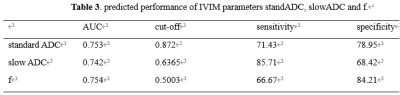
Table
3. predicted performance of IVIM
parameters standADC, slowADC and f.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2967