2963
Comparison of Image Quality Improvement between Women’s Pelvic DWI with and without Reverse Encoding Distortion Correction at a 1.5 T MR System1Department of Radiology, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan, 2Canon Medical Systems Corporation, Otawara, Japan, 3Department of Radiology, Fujita Health University Bantane Hospital, Nagoya, Japan, 4Joint Research Laboratory of Advanced Medical Imaging, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan
Synopsis
Keywords: Pelvis, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques
We hypothesized that RDC is able to improve image quality on DWI with b value with reducing distortion artifact in women’s pelvic field, when compared DWI without RDC. The purpose of this study was to determine the capability for image quality improvements between women’s pelvic DWI with and without RDC at a 1.5 T MR system.Introduction
It has been reported that diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI),which is usually obtained by single-shot echo-planar imaging (EPI), has been suggested as useful for diagnosis of female pelvic diseases such as uterine and ovarian tumors. However, a major disadvantage of conventional DWI is that it is considerably prone to artifacts, particularly susceptibility artifacts at tissue interfaces and image blurring. Therefore, several approaches for DWI such as parallel transmit EPI or readout-segmented multi-shot EPI, reduced field-of-view (FOV) in the phase-encoding direction, and 2D navigator phase correction, etc. have been tested for improving image quality and reducing artifacts due to various causes (1-6). Under the above-mentioned situations, Canon Medical Systems Corporation introduces and clinically sets reverse encoding distortion correction (RDC) for body DWI with applying deep learning reconstruction (DLR) in 2022. Currently, reverse encoding direction techniques with different approaches has been suggested as useful for reducing distortion artifact and improve image quality on DWI in central nervous system field. No major reports are not assessed the capability of RDC for improving image quality and influence for ADC measurement accuracy in women’s pelvic field. We hypothesized that RDC is able to improve image quality on DWI with reducing distortion artifact in women’s pelvic field, when compared DWI without RDC. The purpose of this study was to determine the capability for image quality improvements between women’s pelvic DWI with and without RDC at a 1.5 T MR system.Materials and Methods
Thirty-one consecutive female patients with various pelvic diseases (mean 41 years, range 24-80 years) underwent DWIs at b value as 1000 s/mm2 with and without RDC at a 1.5T MR system, and each ADC map was reconstructed. For quantitative image quality assessments, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) on each DWI and ADC value of gluteal muscle were determined based on ROI measurements. For qualitative image quality assessments, two board certified radiologists assessed overall image quality (OIQ), deformation severity (DS) and diagnostic confidence level (DCL) by 5-point scales, and each final score was determined as consensus of two readers. On quantitative image quality evaluations, SNR was compared between both DWIs by paired t-test. Then, correlation of ADC value between both DWIs were evaluated by Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient. Moreover, the limits of agreement of ADC between both DWIs were also evaluated by Bland-Altman analysis. For qualitative image quality evaluations, inter-observer agreement on each DWI was assessed by κ statistics followed by χ2 test. Finally, each qualitative index was compared each other by Wilcoxon signed–rank test.Results
Representative case is shown in Figure 1. There was no significant difference of SNR between DWI with RDC (10.7±1.2) and that without RDC (10.8±1.2, p>0.05). There was significant correlation of ADC value between DWIs with and without RDC (ρ=0.92, p<0.001). The limits of agreement between DWIs with and without RDC is shown in Figure 2. The limits of agreement were determined as 0.009 ± 0.067×10-3mm2/s, although there were no significant differences of ADC values between both DWIs (p>0.05). Inter-observer agreements for all qualitative indexes were determined as ‘substantial’ or ‘almost perfect’ (0.78<κ<0.97, p<0.0001). Compared results of OIQ, DS and DCL between DWIs with and without RDC are shown in Figure 3. OIQ and DCL of DWI with RDC (OIQ: Median 5, IQR 4-5; DCL: Median 5, IQR 5-5) were significantly higher than those without RDC (OIQ: Median 4, IQR 3-5, p=0.0004; DCL: Median 5, IQR 4-5, p=0.03). DS of DWI with RDC (Median 1, IQR 1-2) was significantly lower than that without RDC (Median 2, IQR 1-3, p=0.0004). Conclusion: RDC is able to improve image quality without any influence on ADC evaluation on women’s pelvic DWI at 1.5 T system.Conclusion
RDC is able to improve image quality without any influence on ADC evaluation on women’s pelvic DWI at 1.5 T system.Acknowledgements
This work was technically and financially supported by Canon Medical Systems Corporation.References
- Porter DA, Heidemann RM. High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition. Magn Reson Med. 2009; 62(2): 468-475.2.
- Setsompop K, Cohen-Adad J, Gagoski BA, et al. Improving diffusion MRI using simultaneous multi-slice echo planar imaging. Neuroimage. 2012; 63(1): 569-580.3.
- Yıldırım İO, Sağlık S, Çelik H. Conventional and ZOOMit DWI for Evaluation of Testis in Patients With Ipsilateral Varicocele. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017; 208(5): 1045-1050.4.
- Wilm BJ, Svensson J, Henning A, Pruessmann KP, Boesiger P, Kollias SS. Reduced field-of-view MRI using outer volume suppression for spinal cord diffusion imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2007; 57(3): 625-630.5.
- Gallichan D, Andersson JL, Jenkinson M, Robson MD, Miller KL. Reducing distortions in diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging with a dual-echo blip-reversed sequence. Magn Reson Med. 2010; 64(2): 382-390.6.
- Schilling KG, Blaber J, Hansen C, et al. Distortion correction of diffusion weighted MRI without reverse phase-encoding scans or field-maps. PLoS One. 2020; 15(7): e0236418.
Figures
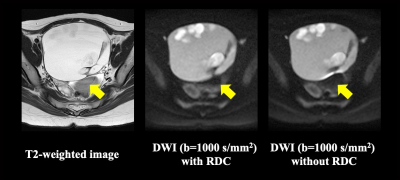
Figure 1. 35-year-old female patient with ovarian mature teratoma (L to R: T2WI, DWI with RDC, DWI without RDC).
DWI with RDC reduces image deformation and demonstrate ovarian mature teratoma more clearly as compared with DWI without RDC. When applied RDC technique, ovarian mature teratoma demonstrates without any distortion on DWI and well matched with T2WI (yellow arrows).
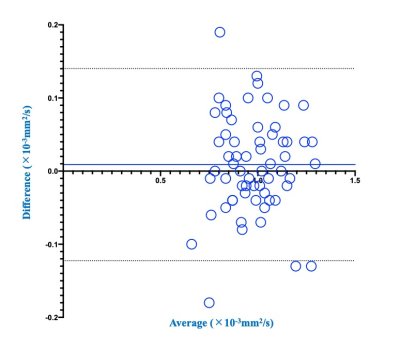
Figure 2. Compared results of the limits of agreement of ADC between DWIs with and without RDC.
The limits of agreement were determined as 0.009 ± 0.067×10-3mm2/s, and small enough for clinical purpose.
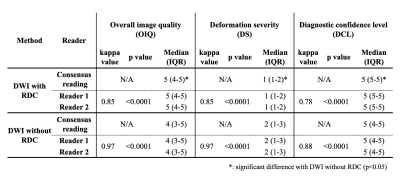
Figure 3. Compared results of overall image quality, deformation severity and diagnostic confidence level between DWI with and without RDC.
OIQ and DCL of DWI with RDC (OIQ: Median 5, IQR 4-5; DCL: Median 5, IQR 5-5) were significantly higher than those without RDC (OIQ: Median 4, IQR 3-5, p=0.0004; DCL: Median 5, IQR 4-5, p=0.03). DS of DWI with RDC (Median 1, IQR 1-2) was significantly lower than that without RDC (Median 2, IQR 1-3, p=0.0004).