2962
Comparison between the application value of reduced FOV multi-shot echo-planar DWI and conventional single-shot echo-planar DWI1School of Medical Technology,Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, China, 2Department of Radiology, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 4School of Medical Imaging, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Pelvis, Tumor
We have compare the performance of reduced field of view (rFOV)image reconstruction using image-space sampling function (IRIS)diffusion weighted imaging (DWI)sequence and full field of view (fFOV) single-shot echo-planar imaging (SSEPI)diffusion weighted imaging(DWI)sequence for rectal cancer patients. And found that compared to fFOV ssEPI-DWI sequence, rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence has a better resolution, reduced sensitivity artifacts, image distortion, and improved image quality in rectal cancer patients.Objectives
To compare the image quality of the reduced field of view (rFOV) image reconstruction using image-space sampling function (IRIS) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequence and full field of view (fFOV) single-shot echo-planar imaging (ssEPI) DWI sequence and explore whether rFOV IRIS-DWI can improve the image quality of rectal cancer patients or not.Methods
All patients who underwent rectal MRI examinations in our institution between June 2022 and August 2022 were retrospectively recruited. The scanning was performed on a 3.0T MR scanner (Ingenia Elition, Philips, Best, The Netherlands). The rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence and fFOV ssEPI-DWI sequence were randomly performed for analysis. Detailed imaging protocols are shown in Table 1. All DWI images were uploaded to the Philips Intelligence Space Portal post-processing workstation (version V10.1) for evaluation and analysis. One senior radiologist with more than 20 years of experience in rectal cancer MRI randomly evaluated the images of two different sequences. All evaluations were randomly performed in rFOV IRIS-DWI images with b=800 s/mm² and fFOV ssEPI-DWI images with b=1000 s/mm², respectively. Image quality evaluation included subjective evaluation and objective evaluation. Subjective image quality included overall quality, artifacts, distortion, lesion contrast and anatomical details according to a 5-point scale reference. And, the objective evaluation of image quality included maximum area of tumor, average maximum area of tumor, tumor volume, ADC value, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR). SPSS 26.0 statistical software was used for data analysis. The subjective scores of image quality between rFOV IRIS-DWI and fFOV ssEPI-DWI were compared by paired Wilcoxon S rank sum test. The comparison of the objective image quality between the two DWI sequences was performed by using paired sample t-test. P<0.05 indicated the difference was statistically significant.Results
Thirty patients with rectal cancer were enrolled in this retrospective study. The average age of all patients was 63.2±10.6 years and, there were 17 (57%) males and 13 (43%) females (Table 2). The overall quality, distortion, artifacts, lesion contrast and anatomical details in the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence were significantly better than the fFOV ssEPI-DWI sequence (P<0.05). The total scores of the subjective evaluation in the rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence and fFOV ssEPI-DWI sequence were 20.6 and 17.4, respectively, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05) (Table 3, Figure 1). The ADC values in rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence and fFOV ssEPI-DWI sequence were 0.85×10-3 mm²/s, 1.07×10-3 mm²/s, respectively. The result showed a significant difference between the two groups with P<0.001(Table 4, Figure 2). The maximum area and average maximum area of rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence were larger than the fFOV ssEPI-DWI sequence (P<0.05) (Table 4, Figure 2). The SNR and CNR in rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence and fFOV ssEPI-DWI sequence were 37.7, 73.1 and 0.85, 0.82, respectively, and the SNR of the two groups were statistically different (P<0.001) (Table 4, Figure 2).Conclusion
Compared to fFOV ssEPI-DWI sequence, rFOV IRIS-DWI sequence has a better resolution, reduced sensitivity artifacts, image distortion, and improved image quality in rectal cancer patients.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Glynne-Jones, R.; Wyrwicz, L.; Tiret, E.; Brown, G.; Rodel, C.; Cervantes, A.; Arnold, D.; Committee, E. G., Rectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2017, 28 (suppl_4), iv22-iv40.
[2] Jang, S.; Lee, J. M.; Yoon, J. H.; Bae, J. S., Reduced field-of-view versus full field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging for the evaluation of complete response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. Abdom Radiol (NY) 2021, 46 (4), 1468-1477.
[3] Xia, C. C.; Liu, X.; Peng, W. L.; Li, L.; Zhang, J. G.; Meng, W. J.; Deng, X. B.; Zuo, P. L.; Li, Z. L., Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging improves the image quality of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in rectal cancer: Comparison with single-shot echo-planar diffusion-weighted sequences. Eur J Radiol 2016, 85 (10), 1818-1823.
Figures
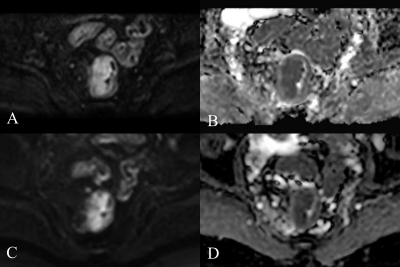
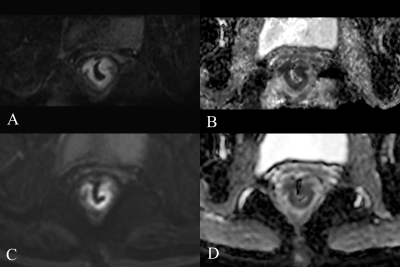
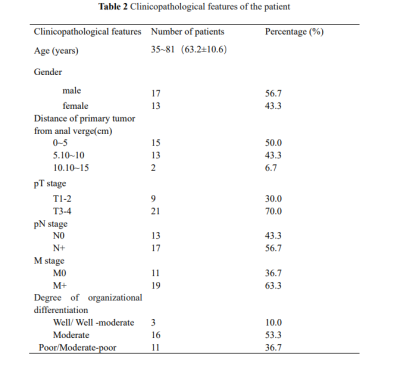
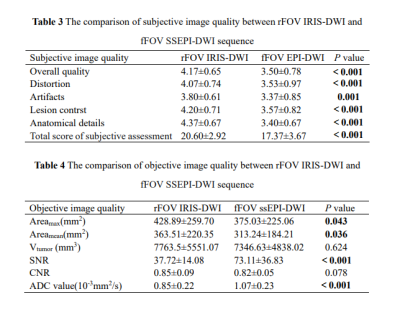
Table 3 The comparison of subjective image quality between rFOV IRIS-DWI and fFOV SSEPI-DWI sequence
Table 4 The comparison of objective image quality between rFOV IRIS-DWI and fFOV SSEPI-DWI sequence
Note: Areamax, maximum layer area of tumor; Areamean, the average area of the maximum layer of the lesion and the sum of the areas above and below it; Vtumor, tumor volume; SNR, signal noise ratio; CNR, contrast to noise ratio; ADCtumor, the apparent diffusion coefficient of tumor; Bold indicates that the difference is statistically significant.
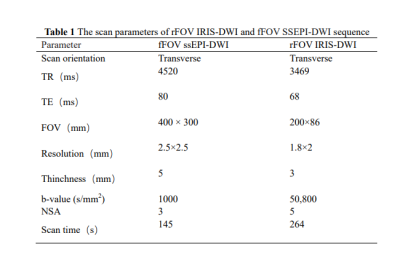
Table 1 The scan parameters of rFOV IRIS-DWI and fFOV SSEPI-DWI sequence
Note:TR:repetition time;TE:echo time;NSA:number of signal averaged.