2961
Application of MultVane XD combined with compressed sensing in T2-weighted imaging of uterus
Haonan Zhang1, Qingwei Song1, Jiazheng Wang2, and Ailian Liu1
1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
1Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Pelvis, Uterus
Through the radial K-space filling, MultiVane XD(MVXD) can significantly reduce magnetic motion artefacts. As the filling percentage increases, artifacts are significantly reduced, but the scanning time gradually increases. The purpose of this study is to investigate the appropriate compressed sensing(CS) acceleration factor(AF) and filling percentage for clinical uterus T2WI.Introduction
Uterine peristalsis is an inevitable physiological activity, and the resulting motion artifacts may affect MR image diagnosis. MVXD uses radial K-space to reduce motion artefacts, it has been used in brain, neck, shoulder, abdomen, cervical spine, and knee, etc1. A higher filling percentage can reduce the artifacts more effectively. However, the filling percentage is too large, which will double the scanning time and affect the clinical application. Compressed sensing (CS) can significantly shorten the scan time through sparse sampling, while ensuring the image quality to meet the diagnostic requirements2,3. The purpose of this study is to investigate the appropriate CS AF and filling percentage for clinical uterus T2WI sequence.Materials and methods
This study has been approved by the local IRB. 10 healthy volunteers (age 23.56±2.30 years) were recruited in this study. The uterus T2WI sequence were performed in a 3.0 T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands). Different combinations of acceleration factor and filling percentage include T2WI without CS and MVXD. CS acceleration factor is 2, filling percentage is 200%, CS acceleration factor is 2, filling percentage is 250%, CS acceleration factor is 2, filling percentage is 300%, CS acceleration factor is 3, filling percentage is 300%, CS acceleration factor is 4, filling percentage is 300%, CS acceleration factor is 4, filling percentage is 350%, and they are defined as group A to G, respectively. Scan parameters are shown in table 1. The subjective independent scoring was performed by two radiologists according to anatomical structure, diagnostic certainty and artifact. Five-point scoring criteria of image quality was used (Table 2), and the score more than 3 was considered to meet the clinical demand. The Kappa test was used to evaluate the consistency of the scores between the two radiologists. If the consistency is good, select the subjective scores of senior physicians for subsequent analysis. Then regions of interest were placed manually on the uterine conjunctive zone, muscle layer and subcutaneous fat to measure the signal intensity and standard deviation (Figure 1). Meanwhile, signal to noise ratio (SNR) and contrast to noise ratio (CNR) were also calculated. The Frideman test was used to assess the difference of SNR, CNR and score among all sequences. The Wilcoxon test was used to make a pairwise comparison.Results
Images of uterus from group A to group G were shown in Figure 2. Score measured by two observers are in good agreement (p = 0.834). SNR, CNR and subjective scores from each group were shown in Table 3. There are no significantly different among each groups (Table. 4).Conclusions
Taken the scan time and image quality into consideration, CS factor of 4 and filling percentage of 300% is recommended for clinical the uterus T2WI sequence.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Nagatomo K, Yabuuchi H, Yamasaki Y, et al. Efficacy of periodically rotated overlapping parallel lines with enhanced reconstruction (PROPELLER) for shoulder magnetic resonance (MR) imaging[J]. Eur J Radiol,2016,85(10):1735-1743. 2. Naresh N K, Malone L, Fujiwara T, et al. Use of compressed sensing to reduce scan time and breath-holding for cardiac cine balanced steady-state free precession magnetic resonance imaging in children and young adults[J]. Pediatr Radiol,2021. 3. Kim D, Heo Y J, Jeong H W, et al. Compressed sensing time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography with high spatial resolution for evaluating intracranial aneurysms: comparison with digital subtraction angiography[J]. Neuroradiol J,2021:1952777789.Figures
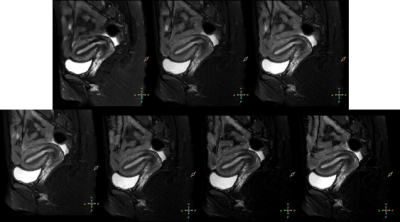
Figure
2, 27 years old.The first row, from left to right: Group A to C. The second
row, from left to right: Group D to G.
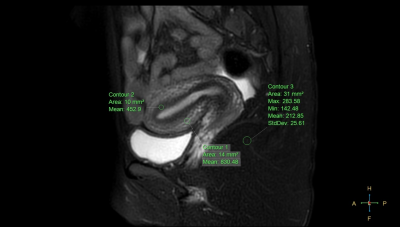
Figure 1, 27
years old, healthy volunteer. Use ROI to measure SI and SD on uterine
conjunctive zone, muscle layer and subcutaneous fat. The measured uterine
conjunctive zone SI value was 452.9, muscle layer SI value was 830.48, subcutaneous
fat SI value was 212.85, and subcutaneous fat SD value was 25.61.
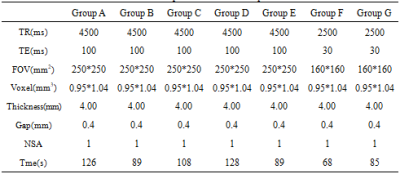
Table 1. parameters of each
sequence
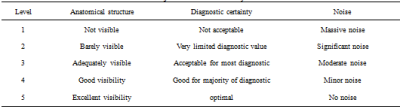
Table 2. Subjective score criteria system
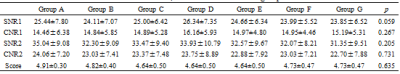
Table 3.SNR, CNR and score of each
groups
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2961