2960
Reduced acquisition time of female pelvis diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) using LIPO-only (LION) DWI
Daichi Murayama1, Masami Yoneyama2, Takayuki Sakai1, Iain Ball3, and Shigehiro Ochi4
1Radiology, Eastern Chiba Medical Center, Chiba, Japan, 2Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Australia & New Zealand, North Ryde, Australia, 4Eastern Chiba Medical Center, Chiba, Japan
1Radiology, Eastern Chiba Medical Center, Chiba, Japan, 2Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 3Philips Australia & New Zealand, North Ryde, Australia, 4Eastern Chiba Medical Center, Chiba, Japan
Synopsis
Keywords: Pelvis, Diffusion/other diffusion imaging techniques
We hypothesized that LIPO-only (LION) DWI might be one of the best solutions to reduce the acquisition time of female pelvis DWI if it is further optimized to increase the robustness of fat suppression. We compared the image quality of DWI in the female pelvis between the conventional method (SPAIR-DWI) and the proposed method (LION-DWI) to investigate their clinical usefulness. LION-DWI showed correct signal decay because fat suppression pre-pulse was not applied . LION-DWI can reduce acquisition time of the pelvis DWI while maintaining the SNR and sufficient image contrast.Purpose
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used in evaluation of malignant and benign diseases of the female pelvis due to its exquisite soft tissue contrast and anatomical details. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is routinely added as part of the MRI protocol [1.2]. Pelvic DWI basically requires a number of signal averages to obtain sufficient signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) especially at 3.0T, resulting in long scan time. Therefore, reducing acquisition time in the DWI without deterioration of SNR would be a major advantage.Slice selection gradient reversal (SSGR, LIPO) [3] technique is commonly used in combination with fat-suppression pre-pulse (SPIR/SPAIR) to increase the robustness of fat suppression at high fields. We hypothesized that LIPO-only (LION) DWI might be one of the best solutions to reduce the acquisition time of female pelvis DWI if it is further optimized to increase the robustness of fat suppression. LION-DWI is expected to improve SNR because it does not require pre-pulse type fat suppression. In this study, we compared the image quality of DWI in the female pelvis between the conventional method (SPAIR-DWI) and the proposed method (LION-DWI) to investigate their clinical usefulness.Methods
The extent of displacement of the fat slice relative to the water slice (D) is defined by D=∂*B0/Gz, where ∂ is relative chemical Shift (ppm), B0 is field strength (T), and Gz is slice selection gradient amplitude (mT/m) [3]. LIPO performance is better with low gradient strength and low RF transmit bandwidth (BW) of excitation and refocusing pulses. This can be understood as the thicknesses of the fat slices being reduced as low BW means fat can partly or completely fall out of the transmission BW. (Fig.1) The displaced fat slice should be ≥ slice thickness/2 [3]. In fact, B0 inhomogeneity can also cause water and fat boxes to be shifted further and usually closer to each other which is not a desirable condition for LIPO. To prevent the B0 inhomogeneity effects for robust LIPO performance, the ratio between excitation and refocusing selection gradient strengths has been optimized to increase the fat slice shifts from the excitation and refocusing pulses with respect to water in this study.We used a 3.0T MRI (Ingenia CX; Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands) for SPAIR-DWI and LION-DWI imaging in a group of patients with ovarian cysts (5 patients), mature cystic teratomas (5 patients) and endometriotic cysts (5 patients). SPAIR-DWI and LION-DWI adjusted to the same SNR in the phantom study. Consequently, the actual acquisition time was set to 2.20 minutes for the SPIAIR-DWI and to 1.08 minute for the LION-DWI.SNR and contrast ratio (CR) were calculated with ROIs placed in muscle and lesion areas. ADC values of lesions were measured from the ADC-map. (Fig.2). Imaging parameters for pelvis DWI were; Axial, voxel size = 2.0 x 2.0 x 5.0 mm3, 25 slices, gap 0.5 mm, FOV = 160 × 160 mm2, b-value = 1000 s/mm2, SENSE factor = 2, TR = 6000 ms, TE = 72 ms, conventional DWI à fat suppression = SPAIR, NSA = 1 and total acquisition time = 2 min 21 sec. LION-DWI à fat suppression = LION, NSA = 1 and total acquisition time = 1 min 12 sec.Results and Discussion
There were no significant differences in SNR and ADC values between SPAIR-DWI with 2minutes acquisition and LION-DWI with one minute acquisition. For the CR between cystic lesions and surrounding muscle signals, LION-DWI was significantly lower than that of SPAIR-DWI with all lesions (Fig.3 and 4). Cystic lesions basically have high ADC values which should show low signal on the high b-value images but applying SPAIR may prevent such signal decay due to its magnetization transfer effect. Thus, LION-DWI showed correct signal decay because fat suppression pre-pulse was not applied.Although further clinical investigation, including malignancy lesions should be needed, LION-DWI might be promising because it can halve the imaging time with comparable SNR and better CR compared to the SPAIR-DWI.Conclusion
LION-DWI can reduce acquisition time of the pelvis DWI while maintaining the SNR and sufficient image contrast.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Bakir B, Sanli S, Bakir VL et al (2017) Role of diffusion weighted MRI in the differential diagnosis of endometrial cancer, polyp, hyperplasia, and physiological thickening. Clin Imaging 41:86–94.
2. Manoharan D, Das CJ, Aggarwal A, Gupta AK (2016) Diffusion weighted imaging in gynecological malignancies - present and future. World J Radiol 8:288–297.
3. Nagy Z, Weiskopf N. Efficient fat suppression by slice-selection gradient reversal in twice-refocused diffusion encoding. Magn Reson Med. 2008 Nov;60(5):1256-60.
Figures
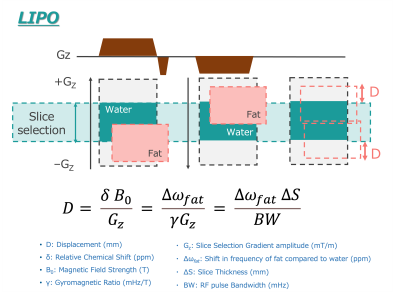
Fig. 1 Illustration of the LION-DWI method of fat saturation.

Fig. 2 SNR and CR were calculated with ROIs placed in muscle and lesions areas. ADC values of lesions were measured from the ADC-map.
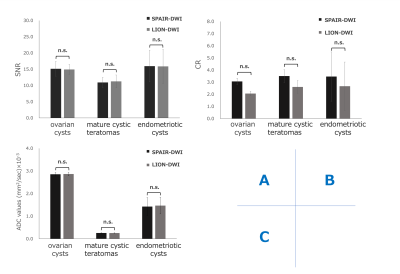
Fig. 3 Compared SNR(A), CR(B) and ADC values(C) of SPAIR-DWI and SSGR-DWI in this study.
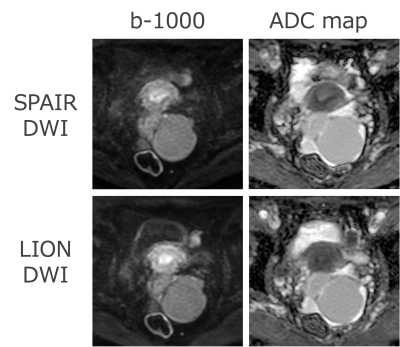
Fig. 4 A 56-year-old woman who had a endometroid cysts in clinical examination.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2960