2956
CloudBrain-LabelAI: An Online Intelligent Medical Imaging Annotation and Training Platform1Biomedical Intelligent Cloud R&D Center, Department of Electronic Science, National Institute for Data Science in Health and Medicine, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, 2Department of Instrumental and Electrical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, 3School of Computer and Information Engineering, Xiamen University of Technology, Xiamen, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Segmentation
Deep learning and cloud computing technologies have shown remarkable performance in medical imaging research. Using deep learning for clinical research requires a programming foundation, while the annotation of image data is a highly specialized and time-consuming process. In this work, we develop a high-performance online medical image annotation and training platform (CloudBrain-LabelAI). It provides medical image researchers with an efficient image annotation platform for the rapid construction of datasets for deep learning. Meanwhile, it provides codeless image segmentation training and prediction based on cloud computing, which greatly reduces the threshold of medical image segmentation efforts and simplifies the overall workflow.Purpose
Medical image segmentation based on deep learning1, 2, 5, 6 is a research hotspot in recent years, but there are several problems. Firstly, training a model with high accuracy and generalization requires a large amount of image data and labeled data, but in medical image annotation usually has problems such as professionalism and time-consuming, which require professional doctors to spend a lot of time to label data. Secondly, the deep learning data preprocessing, training and prediction process is tedious, which brings troubles to the researchers without a deep learning foundation. Finally, no high-performance computational resources for model training.In this work, we develop a medical image annotation and training platform (CloudBrain-LabelAI) based on cloud computing3, 4 to solve the above problems. CloudBrain-LabelAI focuses on medical image segmentation tasks, integrates modules such as intelligent image annotation, dataset production, neural network visual design, model training and prediction, and provides secure file storage and efficient collaboration functions based on the web. It provides a complete workflow, which can save the time cost of learning different software and focus the researchers on the problem itself.Method
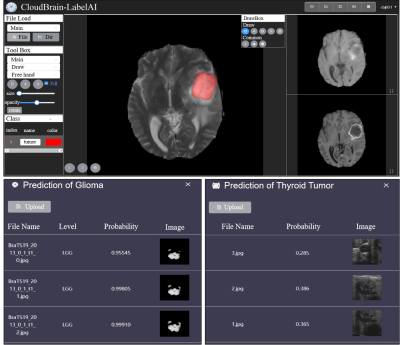
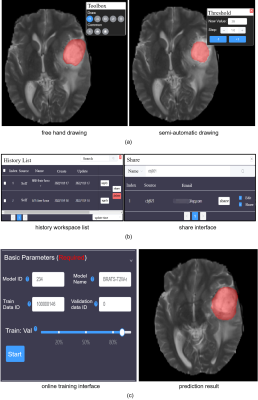
Platform functions: Figure 1 shows the overall interface of CloudBrain-LabelAI. We develop free hand drawing and semi-automatic drawing tools for labeling images. Free hand drawing allows users to freely draw the region and fill the area. Semi automatic drawing is based on the region growing algorithm. Users select a seed point and grow the region by adjusting the threshold. Based on the characteristics of Web interconnection, we develop a high-performance and secure file storage system, it allows users to save workspace files and label records to the cloud so that historical workspaces can be restored anywhere. At the same time, we develop an efficient collaboration function which allows users to easily share working images and labels with colleagues. It can accelerate the labeling work process and improve label detail. Based on high-performance cloud computing, we develop the codeless deep learning online training function. Users can start the model training by simply selecting parameters. After model training, the platform supports online model predict function.Platform architecture: The platform adopts browser/server (B/S) architecture and mainly consists of three parts: browser, server, and data access layer (DAL). The browser layer includes user login, file upload, image annotation, etc. The server layer includes nginx transport, file management, algorithm microservice, etc. The data access layer uses MySQL, Redis, and MongoDB to store various user files.
Results
Up to now, CloudBrain-LabelAI has open accessed at https://csrc.xmu.edu.cn/LabelSystem.html (Test account: lecture_public, Password: lecture_public001). Figure 2 shows the function interface of CloudBrain-LabelAI.For image annotation, CloudBrain-LabelAI can load hundreds of medical image data in a batch and supports smooth wheel switching and multi-window synchronous annotation. Using semi-automatic drawing tools to simplify the traditional annotation process and greatly reduce the time cost of annotation.
For online deep learning training, the visual neural network design and codeless online deep learning transform the abstract deep learning process into a visual and simple process.It reduces the threshold for users to use deep learning for research.
At present, CloudBrain-LabelAI has trained medical image segmentation models such as liver tumors and spine. At the same time, It provides users with a variety of prediction and analysis tools, such as thyroid tumor prediction and brain glioma prediction.
Conclusion
In summary, we have developed CloudBrain-LabelAI, an intelligent online medical image annotation and training platform. CloudBrain-LabelAI can not only improve users' annotation efficiency but also provide visual neural network design and codeless online model training functions for users without a deep learning foundation. It provides a reliable, high-performance and easy-to-use cloud computing platform for medical image segmentation tasks. At present, the platform has deployed multiple available image segmentation models. In the future, we will develop more functions such as disease data analysis and 3D volume segmentation to better serve the medical image research community.Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grants 62122064, 61971361 and 61871341, the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China under grant 2021J011184, the President Fund of Xiamen University under grant 0621ZK1035, and the Xiamen University Nanqiang Outstanding Talents Program. The correspondence should be sent to Prof. Xiaobo Qu (Email: quxiaobo@xmu.edu.cn)References
[1] Ronneberger, Olaf, Philipp Fischer, and Thomas Brox. "U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation." International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, Cham, 2015.
[2] Isensee, Fabian, et al. "nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation." Nature methods 18.2 (2021): 203-211.
[3] M. Armbrust, A. Fox, R. Griffith, A. D. Joseph, R. Katz, A. Konwinski, G. Lee, D. Patterson, A. Rabkin, and I. Stoica, “A view of cloud computing,” Commun. ACM, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 50-58, 2010.
[4] T. Dillon, C. Wu, and E. Chang, “Cloud computing: Issues and challenges.” IEEE International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications (AINA), pp. 27-33, 2010.
[5] Yirong Zhou, Chen Qian, Yi Guo, Zi Wang, Jian Wang, Biao Qu, Di Guo, Yongfu You, Xiaobo Qu, XCloud-pFISTA: A medical intelligence cloud for accelerated MRI, The 43th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society-EMBC’21, pp. 3289-3292, Oct 31 - Nov 4, 2021, Virtual Conference, 2021.
[6] Qinqin Yang, Zi Wang, Kunyuan Guo, Congbo Cai, Xiaobo Qu, Physics-driven synthetic data learning for biomedical magnetic resonance: The imaging physics-based data synthesis paradigm for artificial intelligence, IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, DOI: 10.1109/MSP.2022.3183809, 2022.
Figures