2947
Image distortion correction for diffusion MRI using U-Net and Transformer1Graduate School of Science and Technology, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan, 2Radiology center, The University of Tokyo Hospital, Tokyo, Japan, 3School of Medicine, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, United States, 4Department of Radiology, The University of Tokyo Hospital, Tokyo, Japan
Synopsis
Keywords: Data Processing, Machine Learning/Artificial Intelligence, Diffusion weighted image/Diffusion tensor image
Although several end-to-end deep neural networks have been proposed to correct image distortion directly from distorted images, no study has verified the distortion correction performance for high b-values diffusion-weighted image (DWI) and diffusion tensor image (DTI) parameters. For example, the U-Net-based Synb0-DisCo was only validated for distortion correction of b0 images. Here, we used two networks, U-Net and Trans-DisCo, to verify distortion correction performance for DWIs and DTI parameter images. Trans-DisCo is our proposed model that replaces the convolutional neural network in U-Net with Swin Transformer, and we have shown that it outperforms U-Net.INTRODUCTION
Diffusion MRI is acquired using echo planar imaging sequences and suffers from severe image distortion. As implemented in FSL 1 and other tools, state-of-the-art distortion correction requires additional scans and tedious post-processing. To address this issue, a distortion correction method using a deep neural network (DNN) called Synb0-DisCo 2, which does not require additional scans and simplifies post-processing, has been proposed and shown to have performance comparable to conventional methods. However, this model has not been validated for high b-value diffusion-weighted images (DWIs) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) parameters. Furthermore, Synb0-DisCo uses U-Net with convolutional neural networks (CNNs), but CNN has a narrow receptive field, and global information necessary for distortion correction is not effectively utilized in the network 3. Meanwhile, Transformer-based DNNs have a wide effective receptive field and have recently been shown to outperform CNN in various image-processing tasks 4-5. However, Transformer has not been applied to the diffusion MRI distortion correction task. Therefore, this study is performed for the following two purposes:(1) To expand U-Net (Synb0-DisCo) to perform high-b value DWI distortion correction and verify the correction performance of DTIs and diffusion kurtosis images (DKIs) (Experiment 1).
(2) To propose a Transformer-based U-Net, Trans-DisCo, for DWI distortion correction and verify that it outperforms U-Net (Experiment 2).
METHOD
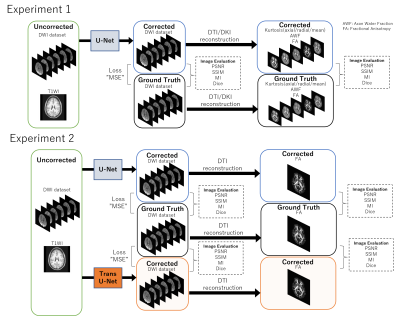
The study workflow is shown in Figure 1. T1-weighted images (T1Ws) and uncorrected DWIs with different b-vectors of 60/64 (for DKI/DTI) (Experiment 1) or 6 (Experiment 2) were used as network input, and the corresponding DWIs were used as output.For training and validation, the FSL-corrected DWIs were used as the ground truth (GT) images, and the mean square error (MSE) between the GT images and the output images was used as the loss function. The peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity (SSIM), mutual information (MI), and Dice score were calculated for the corrected DWIs and GT DWIs. In addition, DTI parameters were calculated from the corrected DWIs, and PSNR, SSIM, MI, and DICE between those parameter maps and the corresponding GT maps (calculated from the GT DWIs) were calculated.
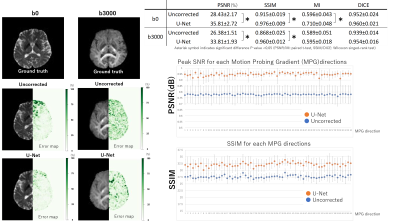
Experiment 1: We used the 3D U-Net (Synthesized b0 for diffusion distortion correction (Synb0-DisCo)) (Figure 1) as a distortion correction DNN. We used the DWI dataset taken with a Siemens Magnetom Skyra 3.0 T at our facility. From the DWI dataset for DTI and DKI, 28/7/9 cases and 93/23/29 cases were used for training/validation/testing, respectively.
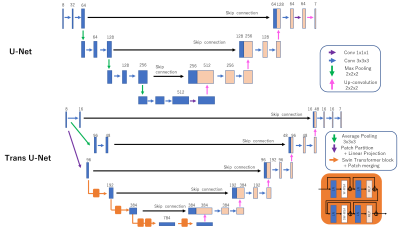
Experiment 2: We used two models as distortion correction DNNs: 3D U-Net and Trans-DisCo. Trans-DisCo is our newly proposed model in which the CNN in 3D U-Net was replaced by Swin Transformer (Figure 2). We implemented Trans-DisCo by modifying the open-source code, TransMorph 6. From the Human Connectome Project brain DWI dataset, 100/20/10 cases were used for training/validation/testing.
RESULTS
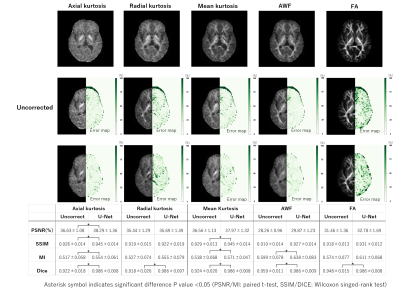
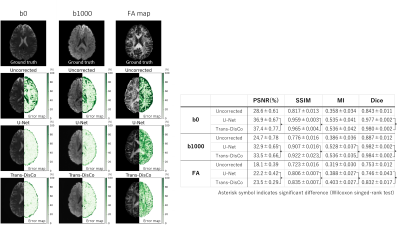
The results of experiment 1 (Figures 3 and 4) showed that DWIs and DTI parameters corrected by the U-Net showed smaller errors with GT and higher scores than uncorrected ones. Especially in axial Kurtosis, SSIM improved from 0.92 to 0.95, and PSNR improved from 34.70 dB to 36.42 dB. These were significant differences in the tests.The results of experiment 2 (Figure 5) showed that the proposed Trans-DisCo generated DWI and fractional anisotropy (FA) images with smaller errors and significantly higher quantitative metrics than U-Net.
DISCUSSION
In this study, we used two networks, U-Net (Synb0-DisCo) and Trans-DisCo, to verify distortion correction performance for high-b value DWIs and DTI parameters.Experiment 1 showed that U-Net can accurately correct various distortions in DWIs and DTI parameter images. This ability to correct multiple image distortions of DWIs with different b-vectors is probably because of the use of T1W as a reference.
In experiment 2, we proposed Trans-DisCo, which replaces the CNN in U-Net with the Swin Transformer, and showed that it exhibits higher image distortion correction than U-Net. This improvement may be attributed to the larger receptive field of the Transformer.
CONCLUSION
We showed that the U-Net-based DNN for image distortion correction could be effectively applied to diffusion MRI. We also proposed the Trans-DisCo using Transformer and showed that it outperforms the U-Net.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by KAKENHI(20K08016) in JAPAN.References
1. Stephan M Smith et al. “Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL” Neuroimage, 23(S1):208-219, 2004
2. K G. Schilling et al. “Synthesized b0 for diffusion distortion correction (Synb0-DisCo)” Magn Reson Imaging. Dec;64:62-70, 2019
3. Li, Shaohua et al. “Medical Image Segmentation using Squeeze-and-Expansion Transformers” ArXiv abs/2105.09511, 2021
4. Dong, B. et al. “Polyp-PVT: Polyp Segmentation with Pyramid Vision Transformers” ArXiv abs/2108.06932 ,2021
5. Guo, Pengfei et al. “ReconFormer: Accelerated MRI Reconstruction Using Recurrent Transformer” ArXiv abs/2201.09376 ,2022
6. Chen, Junyu et al. “TransMorph: Transformer for unsupervised medical image registration” Medical image analysis 82: 102615 ,2022
Figures