2917
Visualization of Collateral Vessels in 4D TRANCE MR Angiography Compaired with 3D TOF in Moyamoya Disease
Zhihua Chen1, Kaiyin Liang1, Yongkun Lan1, and Wen Zhou1
1PEKING UNIVESITY SHENZHENG HOSPITAL, Shen Zheng, China
1PEKING UNIVESITY SHENZHENG HOSPITAL, Shen Zheng, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Visualization, Blood vessels
Compared with 3D-CE-MRA, TOF technology isn't conducive to display slow blood flow. Moreover, TOF angiography is a static approach that lacks flow dynamic information. In our study, the 4D TRANCE MRA depicted the proximal arteries better than 3D TOF and may replace TOF angiography. Our study also indicated that LMA collaterals were better visualized in 4D TRANCE angiography and visualization of distal cerebral arteries and collateral vessels with Moyamoya disease with 4D TRANCE MR angiography was good to excellent. Besides conventional MRA to show the shape and distribution of blood vessels, it can also provide hemodynamic information of vascular diseases.Introduction
TOF technology has some disadvantages: it is not conducive to the display of slow flow blood flow. Some patients may have obvious saturation phenomenon of blood flow in volume, resulting in some vessels not developing, which is difficult to distinguish from real vascular occlusion. Moreover, TOF MR angiography is a static approach that lacks flow dynamic information. It is thus of limited usefulness in moyamoya disease, especially for the evaluation of flow dynamics. 3D time-of-flight (TOF) MR angiography (MRA) is insensitive to slow-flow. 4D TRANCE uses 3D-TFE/EPI sequence to visualize the morphology and dynamic blood flow of blood vessels by using arterial spin labeling (ASL) technique without contrast agent. It is an imaging examination technology similar to DSA, which can provide hemodynamic information of vascular diseases. The purpose of this study was to correlate 4D TRANCE and 3D TOF MRA with the results of conventional angiography during collateral circulation of Moyamoya disease and to determine the accuracy of 4D TRANCE MRA.Methods
Thirty-five consecutive patients with symptoms of MMD who were referred to our department from May 2018 to June 2019 were included in this study. 3D-TOF and 4D TRANCE angiography were performed on a 3-T MR system (Ingenia, Philips Healthcare, Netherlands).4D TRANCE also is a cardiac triggered 3D TSE technique that subtracts images from different phases in the cardiac cycle to obtain high resolution arterial images with bright vessels and dark background. It uses 3D-TFE/EPI sequence to visualize the morphology and dynamic blood flow of blood vessels by using arterial spin labeling (ASL) technique. TOF MR angiography was performed by using geometry, spatial resolution, and imaging time identical to those used for AccASL MR angiography. Two radiologists evaluated the vessel visualization on 4D TRANCE and TOF angiograms with a grading scale (Table 1) as the qualitative evaluation of vessel visualization. Visualization of the terminal ICAs, distal middle cerebral arteries (MCAs), Moyamoya vessels and LMA collaterals from posterior circulation, was assessed by using DSA findings as the reference standard. The two radiologists used a four-point scale to assess vessel visualization. Visualization of terminal ICAs, distal MCAs, Moyamoya vessels, and LMA collaterals was assessed with the criteria used for arteries.Results
The Suzuki stage of Moyamoya disease was based on the Suzuki stage standard of the improved method[1]. Bilateral vascular changes were classified separately. It indicates an intrinsic compensatory reorganization process of Moyamoya disease. Table 2.Bilateral vascular changes were scored separately. The 4D TRANCE, 3D TOF and DSA data of 35 patients diagnosed by DSA were used to evaluate the vessels of Moyamoya disease. The modified Suzuki grading results of 4D TRANCE, 3D TOF and DSA are shown in Table 3-1.Compared with the golden standard, the correlation coefficient between 4D TRANCE and DSA was 0.92, showing a strong correlation. Table 3-2.Vessel visualization scores are summarized in Table 4.Taking DSA as the gold standard, 4d-trace scored higher and closer to the gold standard in evaluating bilateral terminal ICAS than 3D-TOF. The difference between 3D-TOF and DSA was statistically significant (two observers, P < 0.05).the 4d-trace score of the two observers was significantly higher than the 3D-TOF score. There was a significant difference between the 3D-TOF score and the DSA score (P = 0.013, P = 0.007, P = 0.001, P = 0.000), indicating that 4d-trace has better diagnostic efficacy in the diagnosis of bilateral cervical arteries.Discussion
We found that 4D TRANCE MR angiography was superior to conventional TOF MR angiography in the visualization of distal cerebral arteries and collateral vessels in patients with Moyamoya disease. Inflow dynamic data are acquired multiple times by changing the duration of the marked pulse, and each marked pulse is collected at a single time point. The 4D TRANCE’s ability of arteries visualization was improved and was consistent with the DSA findings. The results indicated that the 4D TRANCE sequence was sensitive enough to identify very slow flow in arteries distal to the steno-occlusive site. In our study, the 4D TRANCE MRA depicted the proximal arteries better than 3D TOF and was desired could replace TOF angiography. Our study also indicated that LMA collaterals were better visualized with 4D TRANCE angiography than with TOF angiography.4D TRANCE angiography could be used in assessment of LMA collaterals effectively from posterior circulation without contrast agents, and the better LMA visualization could affect the therapeutic strategy in patients with Moyamoya disease[2].Conclusion
Visualization of distal cerebral arteries and collateral vessels in patients with Moyamoya disease with 4D TRANCE MR angiography was good to excellent when compared with that attained with DSA, and it was superior to that attained with conventional TOF angiography.4d-asl is helpful for accurate classification, collateral compensatory blood flow information and evaluation of postoperative blood flow reconstruction. When it is caused by arterial stenosis or occlusion, 4d-asl can also accurately evaluate the shape and blood flow change information of stenosis or occlusion vessels.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Liu ZW, Han C, Zhao F, Qiao PG, Wang H, Bao XY, Zhang ZS, Yang WZ, Li DS, Duan L. Collateral Circulation in Moyamoya Disease: A New Grading System. Stroke. 2019 Oct;50(10):2708-2715. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.024487. Epub 2019 Aug 14. PMID: 31409266.
[2] Togao O, Hiwatashi A, Obara M, Yamashita K, Momosaka D, Nishimura A, Arimura K, Hata N, Yoshimoto K, Iihara K, Van Cauteren M, Honda H. 4D ASL-based MR angiography for visualization of distal arteries and leptomeningeal collateral vessels in moyamoya disease: a comparison of techniques. Eur Radiol. 2018 Nov;28(11):4871-4881. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5462-7. Epub 2018 May 8.
Figures
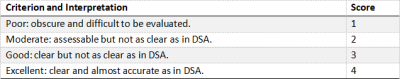
Table 1. Visualization of arteries in comparison with DSA
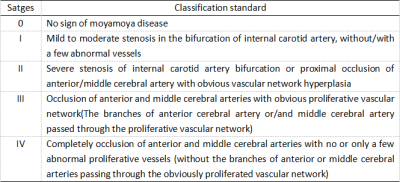
Table 2. Improved Suzuki stage standard for Moyamoya disease
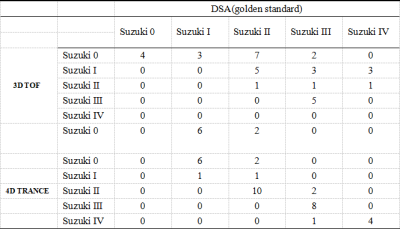
Table 3-1 The Suzuki scores of 3D-TOF and 4d-trance were compared with golden standard(DSA)
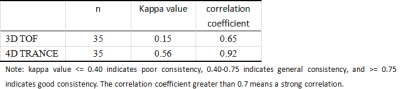
Table 3-2 Consistency test of 3D-TOF, 4d-trance and golden standard
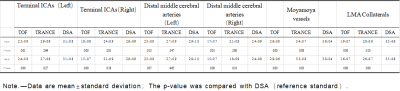
Table 4. Two observers were tested for observer consistency
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2917