2885
Potential anti-HER2 target therapy beneficiaries: can MRI radiomics identify the status of HER2-low in breast cancer?1The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China, 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Intelligent Medicine, China Medical University, Shenyang, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Shanghai, China, 4Pharmaceutical Diagnostics, GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Radiomics, Breast
Recently, HER2-low expression tumor was proposed as a new entity in the field of breast cancer and radiomics studies related to HER2-low are rare. This study investigated whether multiparametric MRI-based radiomics can distinguish HER2- low from HER2-positive and HER2-zero in breast cancer. Results showed that clinico-radiomics nomograms including hormone receptor status and radiomics signatures combined contrast-enhanced T1-weighted and apparent diffusion coefficient map performed best in both prediction tasks: HER2-positive vs. HER2-negative and HER2-low vs. HER2-zero. This suggests that multiparametric MRI radiomics achieved effective prediction of HER2-low, which might be further guidance of the anti-HER2 targeted therapy in breast cancer.Background
Recently, HER2-low expression breast cancer from the HER2-negative subgroup has been proposed as a potential beneficiary from anti-HER2 target therapy such as novel antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) [1, 2]. Given the unique clinicobiological features of HER2-low expression tumors compared to HER2-zero expression [3, 4]. In addition to differentiating between HER2-positive and HER2-negative expression in clinical practice, further differentiation between HER2-low and HER2-zero expression within the negative subgroup is equally important for drug selection of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) in breast cancer. However, due to the heterogeneity of HER2 expression [5, 6], a small specimen may not always be representative of the entire tumor and deep biopsy is an invasive procedure. Therefore, based on the multiparametric MRI (contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (T1CE) apparent diffusion coefficient map (ADC-map)) radiomics, we designed two tasks: HER2-positive vs. HER2-negative (Task 1) and HER2-low vs. HER2-zero (Task 2) to identify HER2-low breast cancer from HER2-positive and HER2-zero using a non-invasive technique.Methods
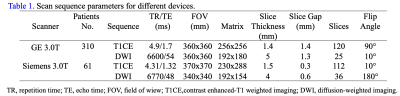
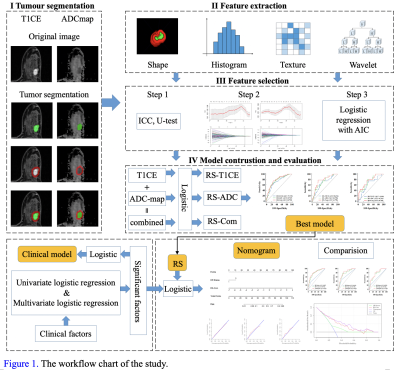
This study collected 369 breast cancer patients who performed MRI examinations including T1CE and ADC-map on GE (SIGNATM Pioneer, GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA) (a primary cohort, n = 310) or Siemens (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) (an external cohort, n = 59) 3T scanners. The breast MRI protocols and parameters of GE and Siemens systems were listed in Table 1. The primary group was devided into the training (n=207) and internal validation (n=103) cohorts using stratified sampling at a ratio of 2:1. The Mann-whitney U test, the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) and Akaike's information criterion (AIC) were employed for feature selection. Logistic regression model was used to establish multiple radiomics signatures: RS-T1CE, RS-ADC and combined sequences (RS-Com). Then, clinical factors were added to the best model to construct the clinico-radiomic nomogram. The differences in clinicopathological characteristics were analyzed by the Mann-Whitney U test or chi-square test. The receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve and decision curve analyses (DCA) were used to evaluate the model performance and clinical benefit. Statistical significance was considered as a two-sided p-value < 0.05. Figure 1 illustrated the experimental flow of this study.Results
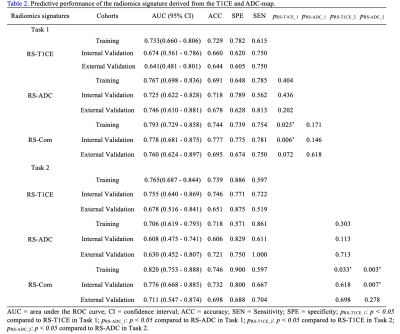
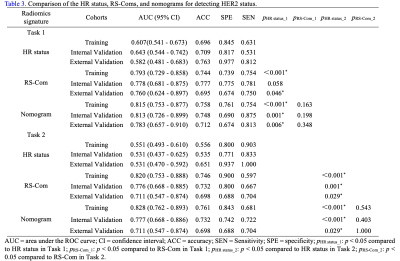
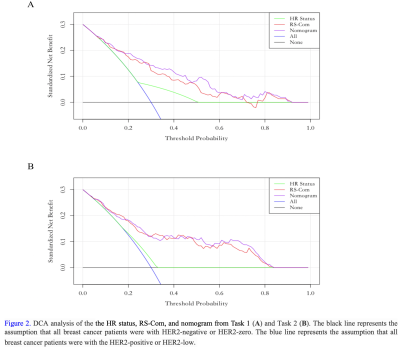
For Task 1, the RS-ADC always obtained higher prediction performance than RS-T1CE in terms of AUC in the training (0.767 vs. 0.733), internal validation (0.725 vs. 0.674), and external validation (0.746 vs. 0.641) sets. The RS-Com (AUC = 0.793, 0.778, and 0.760, separately) showed a higher prediction performance compared to RS-ADC (DeLong test p = 0.025, 0.006, and 0.072, separately) or RS-T1CE (DeLong test p = 0.171, 0.146 and 0.618, separately) in three cohorts. The nomogram demonstrated the best AUC value of 0.815, 0.813, and 0.783 separately, compared with HR status (Delong test p < 0.001, p = 0.001 and p = 0.006, separately) or RS-Com (Delong test p = 0.163, 0.198 and 0.348, separately) alone in three cohorts. For Task 2, the RS-T1CE yielded higher prediction capabilities than RS-ADC in terms of AUC in the training (0.765 vs 0.706), internal validation (0.755 vs 0.608), and external validation (0.678 vs 0.630) sets. The RS-Com (with AUC of 0.820, 0.776, and 0.711, separately) also had a higher prediction performance than RS-T1CE (DeLong test p = 0.033, 0.618, and 0.698, separately) or RS-ADC (DeLong test p = 0.003, 0.007 and 0.278, separately) in three cohorts. The nomogram achieved higher AUC of 0.828, 0.777, and 0.711 separately, compared with HR status (Delong test p < 0.001, p < 0.001 and p = 0.029, separately) or RS-Com (Delong test p = 0.543, 0.403 and 1.000, separately) alone in three cohorts. All details of the model performance were shown in Table 2, Table 3, and Figure 2.Discussion
This study confirmed that the models of multiparametric MRI radiomics were a promising tool for predicting HER2-low expression and external validation on the different scanner (Siemens) also confirmed the stability and robustness of the models in this study. we found that the developed RS-ADC in Task 2 had poorer discrimination performance compared to Task 1. It is conceivable that there is less perfusion-related functional variances between HER2-low and HER2-zero expression compared with HER2-positive and HER2-negative expression subgroup. The comparable performance of RS-T1CE in both tasks may indicate that a more refined distinction between HER2-low and HER2-zero needs to rely on T1CE sequences with high spatial resolution. Therefore, further study is necessary to differentiate HER2-low and HER2-zero based on T1CE sequences with different phases and pharmacokinetic parameters. Studies [5, 7] showed that HR status was a major driver of underlying biology in HER2 therapy cohort. In our study, HR status was predictive in two tasks, and individually generated values of AUC ranging from 0.530 to 0.65. By integrating the RS-Coms and HR status, the nomograms exhibited improved performance for prediction of both Task 1 and Task 2. This may demonstrate that radiomics features were importantly complementary to HR status for HER2 status prediction.Conclusion
Radiomics achieved an effective prediction of HER2-low, which might be further assistant guidance of the anti-HER2 targeted therapy in breast cancer. Further prospective validation in a larger NAC cohort is necessary prior to clinical application.Keywords
breast cancer; radiomics; contrast-enhanced T1-weighted; apparent diffusion coefficient map; HER2-lowAcknowledgements
No.References
1. Tarantino P, Hamilton E, Tolaney SM, Cortes J, Morganti S, Ferraro E, et al. HER2-Low Breast Cancer: Pathological and Clinical Landscape. JCO. 2020 Jun 10;38(17):1951–62.
2. Rinnerthaler G, Gampenrieder S, Greil R. HER2 Directed Antibody-Drug-Conjugates beyond T-DM1 in Breast Cancer. IJMS. 2019 Mar 5;20(5):1115.
3. Zhang G, Ren C, Li C, Wang Y, Chen B, Wen L, et al. Distinct clinical and somatic mutational features of breast tumors with high-, low-, or non-expressing human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status. BMC Med. 2022 Apr 29;20(1):142.
4. Denkert C, Seither F, Schneeweiss A, Link T, Blohmer JU, Just M, et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of HER2-low-positive breast cancer: pooled analysis of individual patient data from four prospective, neoadjuvant clinical trials. The Lancet Oncology. 2021 Aug;22(8):1151–61.
5. Schettini F, Chic N, Brasó-Maristany F, Paré L, Pascual T, Conte B, et al. Clinical, pathological, and PAM50 gene expression features of HER2-low breast cancer. npj Breast Cancer. 2021 Dec;7(1):1.
6. Li Y, Abudureheiyimu N, Mo H, Guan X, Lin S, Wang Z, et al. In Real Life, Low-Level HER2 Expression May Be Associated With Better Outcome in HER2-Negative Breast Cancer: A Study of the National Cancer Center, China. Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 17;11:774577.
7. Montemurro F, Di Cosimo S, Arpino G. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive and hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: new insights into molecular interactions and clinical implications. Annals of Oncology. 2013 Nov;24(11):2715–24.