2822
Relationship between white matter hyperintensity load and cognitive decline in patients with carotid artery stenosis
Wen Zhang1, Xiance Zhao2, and Bing Zhang1
1Radiology, The Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
1Radiology, The Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Dementia, White Matter, carotid artery stenosis
Patients with carotid artery stenosis (CAS) have a high prevalence of cognitive impairment. White matter hyperintensity (WMH) is one of the most common imaging signs of chronic brain injury in the elderly. We investigated the relationship between WMH load and cognitive decline in CAS patients. Our results suggested that Fazekas score and WMH volume quantification can be a potential simple biomarker for predicting cognitive function in CAS patients.Introduction
Patients with carotid artery stenosis (CAS) have a high prevalence of cognitive impairment. White matter hyperintensity (WMH) is one of the most common imaging signs of chronic brain injury in the elderly. Our aim was to investigate the relationship between WMH load and cognitive decline in CAS patients.Methods
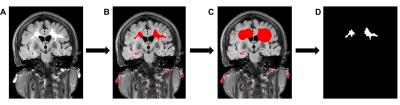
100 CAS patients were enrolled in this study. All participants underwent fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) scan and Montreal cognitive assessment (MoCA) assessment. Cognitive decline was identified by MoCA score < 26. Fazekas scores and WMH volume were quantified from FLAIR. Multivariate regression equation (stepwise method) was used to analyze the independent influencing factors of MoCA scores. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to describe predictive effect of WMH load evaluation of cognitive function.Results
Our results suggested that hyperlipidemia, history of transient ischemic attack or infract, higher body mass index (BMI) and increased WMH volume were related with cognitive decline. Increased Fazekas score and increased normalized WMH volume were independent risk factors for cognitive decline, which were significantly negatively correlated with the MoCA score. The ROC curve revealed that the area under the curve (AUC) of Fazekas score to predict cognitive decline was 0.756 and the best cut-off value was 2 (sensitivity=45.9% and specificity=90.0%). The AUC of normalized WMH volume to predict cognitive decline was 0.791 and the best cutoff value was 1.91% (sensitivity=63.9% and specificity=82.5%).Conclusion
Fazekas score and WMH volume quantification can be a potential simple biomarker for predicting cognitive function in CAS patients.Acknowledgements
NoneReferences
- Wardlaw JM, Smith C, Dichgans M. Small vessel disease: mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Jul;18(7):684-696.
- Ye H, Wang Y, Qiu J, Wu Q, Xu M, Wang J. White matter hyperintensities and their subtypes in patients with carotid artery stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2018 May 16;8(5):e020830.
- Ghaznawi R, Vonk JM, Zwartbol MH, Bresser J, Rissanen I, Hendrikse J, Geerlings MI; UCC-SMART Study Group. Low-grade carotid artery stenosis is associated with progression of brain atrophy and cognitive decline. The SMART-MR study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022 Oct 16:271678X221133859.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2822