2802
Modified cerebral small vessel disease total burden is useful to screening study based on community people1the Nanxishan Hospital, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, guilin, China, 2Graduate School of Guilin Medical University, guilin, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China
Synopsis
Keywords: White Matter, White Matter
The objective of this study was to create a modified total load score suitable for community screening study by modifying mild WMH and EPVS. Our study found NCT-A (DST) variable abnormalities even in people with mild EPVS and WMH, suggesting that modified cerebral small vessel disease total burden is useful to screening study based on community people.
Introduction
Because of there are a large number of low-grade white matter hyperintensity (WMH) and enlargement perivascular spaces (EPVS) in the the community health population [1-3], coexisting with the low incidence of severe EPVS and WMH, previous total load method is not suitable for community population studies [4].Thus, the objective of this study was to create a modified total load score suitable for community screening study by modifying mild WMH and EPVS.Methods
Inhabitants aged 40-70 years living in urban community were recruited. All participants underwent neuropsychological tests, and the conventional examinations were performed on a 3.0 T MRI system ( Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands). The Fazekas scale was applied on FLAIR images to quantify the amount of white matter hyperintense lesions. EPVS and grade 1 WMH were grouped according to quantities of quartiles, and then the scores of neuropsychological scales among the groups were statistically analyzed. Statistically significant quartiles were selected as the cerebral small vessel disease(CSVD) total load scoring criteria,subjects with EPVS or WMH severe than this result were given 1 point. Besides, the presence of each of the other three imaging markers (lacunes infarct, cerebral microbleeds and brain atrophy) of CSVD was awarded with 1 point, resulting in a minimum of 0 and a maximum of 5 point. Patients were divided into groups according to the scale given, subjects with zero scores were classified as control group.Results
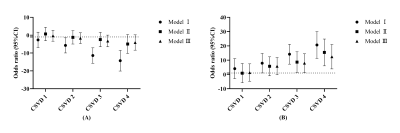
A total of 401 stroke-free participants were included in the present analysis. Number Connection Tests A (NCT-A) and Digital Symbol Test (DST) score was positively correlated with EPVS grouping when EPVS lesions were greater than 7. When WMH> 26 in Fazekas grade 1 group, NCT-A variable was positively associated with WMH grouping, OR:7.906(0.060,15.753). DST score was negatively correlated with WMH grouping when WMH lesions were severe than 12 in Fazekas grade 1 group, OR:-8.547(-13.481,-3.613). For all the results, the higher the total CSVD score, the higher the odds ratio value. Before the adjustment, CSVD grade 2~4 correlation with NST-A(DST). After full adjustment, the result still remains significant.Conclusions
Our study found NCT-A (DST) variable abnormalities even in people with mild EPVS and WMH. Modified cerebral small vessel disease total burden is useful to screening study based on community people.Key Words
cerebral small vessel disease, total load, imaging marker, neuropsychological scales,community-based studyAcknowledgements
This paper has not been presented anywhere, and is not being considered for
publication elsewhere. There are no conflicts of interest for all authors with others.
We have no relevant financial interests to disclose.
References
[1] Debette S, Markus H.The clinical importance of white matter hyperintensities on brain magnetic resonance imaging: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2010; 341: c3666.
[2]Charidimou A, Boulouis G, Haley K, et al. White matter hyperintensity patterns in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and hypertensive arteriopathy. Neurology 2016; 86: 505–511.
[3]Han F, Zhai FF, Wang Q, Zhou LX, Ni J, Yao M, Li ML, Zhang SY, Cui LY, Jin ZY, Zhu YC. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease in a Chinese Population-Based Sample. J Stroke. 2018 May;20(2):239-246.
[4]Huijts M, Duits A, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Kroon AA, de Leeuw PW, Staals J. Accumulation of MRI Markers of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease is Associated with Decreased Cognitive Function. A Study in First-Ever Lacunar Stroke and Hypertensive Patients. Front Aging Neurosci. 2013 Nov 6;5:72.
Figures