2789
Serial Acquisition of radiofrequency pulse MOdes (SAMO) for correction of transmit field inhomogeneities in ultra high field (7T) diffusion MRI.1Radiology, University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia, 2University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia, 3Radiology, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Parkville, Australia, 4Psychology, Monash University, Clayton, Australia, 5Department of Nuclear Medicine and Centre for PET,, Austin Health, Heidelberg,, Australia
Synopsis
Keywords: White Matter, Diffusion Tensor Imaging, 7T DWI, CSD, tractography
This study presents a simple and robust correction of B1+ inhomogeneities in high resolution multi-shell DWI at 7T.Purpose
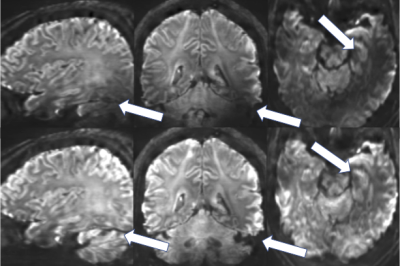
The purpose of this study was to investigate a simple and pragmatic MRI technique to correct for the transmit RF (B1+) inhomogeneity seen in diffusion weighted MRI (DWI) at 7T. This technique acquires two sperate DWI data sets with very different inhomogeneity patterns but when the maximum intensity is determined on a voxel by voxel basis this inhomogeneity is eliminated (Figure 1).Introduction and Background
Despite the improved SNR and resolution of DWI at 7T the B1+ inhomogeneity is the single largest technical problem preventing 7T from being the optimal field strength for DWI [1]. Given DWI is integral to most clinical and clinical research brain MRI protocols it thus limits the translatability of 7T MRI. Radio-frequency pulse time Interleaved acquisition of modes (TIAMO) [2] and boutique parallel transmit (pTx) pulses [3, 4] are highly effective techniques in somewhat overcoming the B1+ issues they are major challenges to their implementation:· TIAMO requires a boutique coil (non-commercial) and hardware setup.· Dedicated pulse sequence and image reconstruction programming is required for TIAMO and pTx pulses.· B1+ correction isn’t perfect and residual inhomogeneities result.· SAR limitations of pTx pulse solutions extend multi-shell DWI acquisition times out to at least 40 mins [4]. This paper will describe a SAMO, a modification of the TIAMO that can be used with a wide variety of commercial MRI sequences on a commercially available 7T system. In particular it has been applied to a 3-shell multi-band DWI sequence for high spatial diffusion tractography in a study of traumatic brain injury (TBI).Methods
A 103 multi-shell (b = 0, 1000, 2000 and 3000), multi-band [5] DWI (1.2x1.2x1.2 mm voxels) protocol was acquired on 16 participants at the University of Melbourne using a pTx head coil (Nova Medical, USA) and a 7T MRI system (Siemens, Germany). The scans were acquired serially using two RF transmit modes, one set to a 45 degree phase difference between the neighbouring 8 RF transmit coils and the other with 90 degree phase difference. These are referred to as circularly polarized (CP) or elliptical modes [2]. Images were reconstructed using the standard vendor provided pipelines and then processed offline using MRTrix3 and FSL. This offline processing included, rigid alignment, determining the maximum value at each voxel between the two modes, distortion correction, denoising, removal of Gibbs artefact, constrained spherical deconvolution and probabilistic tractography.Results
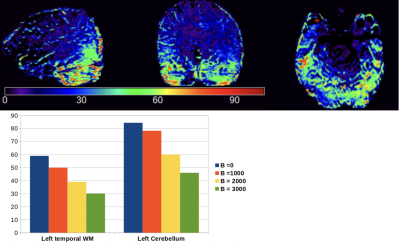
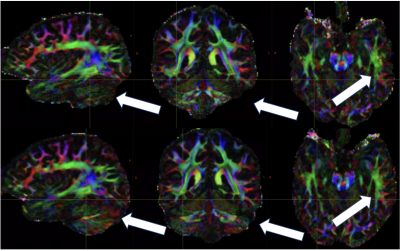
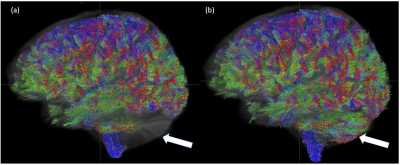
Figure 1 shows an example of the mean DWI images from CP mode and the SAMO correction. In CP mode, the characteristic high field B1 dropout in the temporal and cerebellum regions can be observed. In the elliptical mode signal is recovered in these regions despite having overall increased B1 inhomogeneity. Figure 2, shows the SNR increase between the corrected and quadrature mode acquisitions. This is upwards of 80% in cerebella brain region and 50% in the temporal white matter. The SAMO B1+ corrections then allowed for superior diffusion tensor analysis (Fig.3) and tractography (Fig.4) in particular recovering those tracks running from the cortico-spinal tracts into the cerebellum.Discussion and Conclusion
This study shows the results of a simple yet pragmatic technique for acquiring B1 homogeneous, high spatial and angular DWI on 7T MRI systems. While two total DWI sets are required, the acquisition time (26 mins) is still less than the 40 mins required for a spokes pulse pTx protocol [4] with only 2 DWI shells. For a protocol requiring only diffusion tensor imaging the SAMO acquisition would take less than 3 mins. Currently 7T imaging can only really be used as an adjunct to lower field MRI images for multi-centre clinical trials and clinical imaging of neuropathology. This SAMO correction allows for whole brain clinical quality DWIs to be acquired as well other specialised quantitative 7T MRI biomarkers in one session.Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support of the MBCIU, The University of Melbourne Node of the Australian National Imaging Facility, and funding from the Department of Defence (USA)References
1. Gallichan, D., Diffusion MRI of the human brain at ultra-high field (UHF): A review. NeuroImage, 2018. 168: p. 172-180.
2. Orzada, S., et al., RF excitation using time interleaved acquisition of modes (TIAMO) to address B1 inhomogeneity in high-field MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2010. 64(2): p. 327-333.
3. Ding, B., et al. Dynamic parallel transmission for diffusion MRI at 7T. in Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. . 2021.
4. Wu, X., et al., High-resolution whole-brain diffusion MRI at 7T using radiofrequency parallel transmission. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2018. 80(5): p. 1857-1870.
5. Vu, A.T., et al., High resolution whole brain diffusion imaging at 7T for the Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage, 2015. 122: p. 318-331.
Figures