2743
Deep Learning Radiomics of Preoperative Breast MRI for Prediction of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer1Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School Of Medicine, shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Breast, Radiomics, Deep Learning
This study described the application of MRI-based deep learning radiomics in patients with breast cancer, presenting a novel individualized clinical decision nomogram that could be used to predict axillary lymph node metastasis providing a noninvasive approach to assist clinicians in clinical decision-making.Objective
To develop a radiomic signatures constructed from deep learning features and a radiomic nomogram for prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis (ALNM) in breast cancer patients.Methods
Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging data from 479 breast cancer patients with 488 lesions was studied. The included patients were divided into two cohorts by time (training/testing cohort, n=366/122). Deep learning features were extracted from diffusion-weighted imaging–quantitatively measured apparent diffusion coefficient (DWI-ADC) imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI(DCE-MRI) by a pretrained Neural Networks of Densenet121. After the selection of both radiomic and clinicopathological features, deep learning signature and a nomogram were built for independent validation.Results
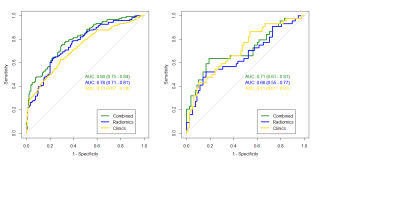
Twenty-three deep learning features were automatically selected in the training cohort to establish the deep learning signature of ALNM. Three clinicopathological factors, including LN palpability (odds ratio (OR)= 6.04; 95% confidence interval (CI)= 3.06-12.54, P=0.004), tumor size in MRI ( OR= 1.45, 95%CI= 1.18-1.80, P=0.104) and Ki-67( OR=1.01;95%CI= 1.00-1.02,P= 0.099), were selected and combined with radiomic signature to build a combined nomogram. The nomogram showed excellent predictive ability for ALNM (AUC 0.80 and 0.71 in training and testing cohorts, respectively). The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 65%, 80%, and 75%, respectively in the testing cohort.Conclusions
This study described the application of MRI-based deep learning radiomics in patients with breast cancer, presenting a novel individualized clinical decision nomogram that could be used to predict ALNM providing a noninvasive approach to assist clinicians in clinical decision-making.Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 82071870, No. 82101991), the Program of Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (No. 21S31905000,19DZ1930504). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, and preparation of the manuscript.
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed by all authors.
References
[1] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel R L, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries [J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71: 209-249.
[2] Tirada N, Aujero M, Khorjekar G, et al. Breast Cancer Tissue Markers, Genomic Profiling, and Other Prognostic Factors: A Primer for Radiologists [J]. Radiographics, 2018, 38: 1902-1920.
[3] Abass M O, Gismalla M D A, Alsheikh A A, et al. Axillary Lymph Node Dissection for Breast Cancer: Efficacy and Complication in Developing Countries [J]. J Glob Oncol, 2018, 4: 1-8.
[4] Qiu S Q, Zhang G J, Jansen L, et al. Evolution in sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer [J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2018, 123: 83-94.
[5] Choi E J, Youk J H, Choi H, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted MRI of invasive breast cancer for the prediction of sentinel lymph node status [J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2020, 51: 615-626.
[6] Zhao M, Wu Q, Guo L, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging features for predicting axillary lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer [J]. Eur J Radiol, 2020, 129: 109093.
[7] Gillies R J, Kinahan P E, Hricak H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data [J]. Radiology, 2016, 278: 563-577.
[8] Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, et al. Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis [J]. Eur J Cancer, 2012, 48: 441-446.
[9] Han L, Zhu Y, Liu Z, et al. Radiomic nomogram for prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer [J]. Eur Radiol, 2019, 29: 3820-3829.
[10] Feng B, Chen X, Chen Y, et al. Solitary solid pulmonary nodules: a CT-based deep learning nomogram helps differentiate tuberculosis granulomas from lung adenocarcinomas [J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30: 6497-6507.
[11] Wu X, Li Y, Chen X, et al. Deep Learning Features Improve the Performance of a Radiomics Signature for Predicting KRAS Status in Patients with Colorectal Cancer [J]. Acad Radiol, 2020, 27: e254-e262.
[12] Huang G, Liu Z, Laurens V, et al. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks[C]// Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. IEEE Computer Society.
[13] Yu Y, Tan Y, Xie C, et al. Development and Validation of a Preoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Radiomics-Based Signature to Predict Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis and Disease-Free Survival in Patients With Early-Stage Breast Cancer [J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2020, 3: e2028086.
[14] Zhou J, Zhang Y, Chang K T, et al. Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions on DCE-MRI by Using Radiomics and Deep Learning With Consideration of Peritumor Tissue [J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2020, 51: 798-809.
[15] Bae M S, Shin S U, Ryu H S, et al. Pretreatment MR Imaging Features of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Association with Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Recurrence-Free Survival [J]. Radiology, 2016, 281: 392-400.
[16] Cain E H, Saha A, Harowicz M R, et al. Multivariate machine learning models for prediction of pathologic response to neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer using MRI features: a study using an independent validation set [J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2019, 173: 455-463.
[17] Li H, Shi K, Reichert M, et al. Differential Diagnosis for Pancreatic Cysts in CT Scans Using Densely-Connected Convolutional Networks [J]. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc, 2019, 2019: 2095-2098.
[18] Bevilacqua J L, Kattan M W, Fey J V, et al. Doctor, what are my chances of having a positive sentinel node? A validated nomogram for risk estimation [J]. J Clin Oncol, 2007, 25: 3670-3679.
[19] Chen J Y, Chen J J, Yang B L, et al. Predicting sentinel lymph node metastasis in a Chinese breast cancer population: assessment of an existing nomogram and a new predictive nomogram [J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2012, 135: 839-848.
[20] Liu C, Ding J, Spuhler K, et al. Preoperative prediction of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer by radiomic signatures from dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI [J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 49: 131-140.
[21] Song D, Yang F, Zhang Y, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI radiomics nomogram for predicting axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer [J]. Cancer Imaging, 2022, 22: 17.
[22] Tang W J, Kong Q C, Cheng Z X, et al. Performance of radiomics models for tumour-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) prediction in breast cancer: the role of the dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI phase [J]. Eur Radiol, 2022, 32: 864-875.
[23] Guvenc I, Whitman G J, Liu P, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging increases diagnostic accuracy of breast MR imaging for predicting axillary metastases in breast cancer patients [J]. Breast J, 2019, 25: 47-55.
[24] Dong Y, Feng Q, Yang W, et al. Preoperative prediction of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer based on radiomics of T2-weighted fat-suppression and diffusion-weighted MRI [J]. Eur Radiol, 2018, 28: 582-591.
[25] Mayerhoefer M E, Materka A, Langs G, et al. Introduction to Radiomics [J]. J Nucl Med, 2020, 61: 488-495.
[26] Truhn D, Schrading S, Haarburger C, et al. Radiomic versus Convolutional Neural Networks Analysis for Classification of Contrast-enhancing Lesions at Multiparametric Breast MRI [J]. Radiology, 2019, 290: 290-297.