2739
A novel nomogram built from mDixon-Quant MRI-based radiomics features and clinical characteristics for grading invasive ductal breast cancer1First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Clinical and Technical Support, Philips Healthcare, WuHan, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Breast, MR Value
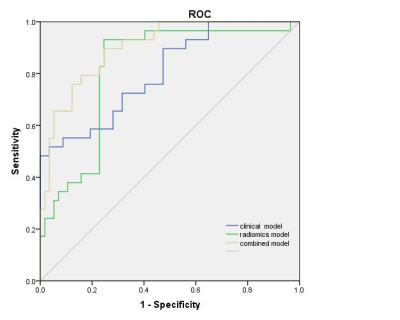
The histological grade of invasive breast cancer should be obtained by invasive needle biopsy , and the extracted tissue might not represent the heterogeneity of the whole tumor. Therefore, a novel nomogram was built from mDixon-Quant MRI-based radiomics features and traditional clinical image characteristics for grading invasive ductal breast cancer. The AUC of the combined model reached 0.907, which was significantly higher than that of the model only using traditional clinical image characteristics (0.782) or radiomics features (0.834). The proposed method can be an effective supplement to conventional breast MRI in predicting the histological grade of invasive ductal breast cancer.Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common malignancy in women and the leading cause of cancer-related death in women, and the most common histological type is invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), which accounts for about 80 percent of all breast cancers[1]. The histological grade of IDC can reflect the clinical behavior or prognosis of breast cancer and is an independent prognostic indicator of breast cancer[2]. However, the histological grade of invasive breast cancer should be obtained by invasive needle biopsy or surgery, and the extracted tissue might not represent the heterogeneity of the whole tumor. Radiomics is a high-throughput quantitative imaging analysis method that uses advanced mathematical algorithms to extract a large number of features from medical images, revealing tumor features that may not be discernible to the naked eye, and these features can reveal potential information related to structural heterogeneity of the whole breast tumor[3]. MRI-based radiomics has revealed an increasing number of quantitative imaging biomarkers that can be cleaved and have been applied to breast cancer diagnosis, molecular subtype classification, treatment evaluation, early prognosis prediction, and recurrence risk prediction, thus providing valuable information for individualized clinical treatment[4-6]. In this study, we established a novel nomogram built from mDixon-Quant MRI-based radiomics features and traditional clinical image characteristics for differentiating pathological grades of IDC.Materials and Methods
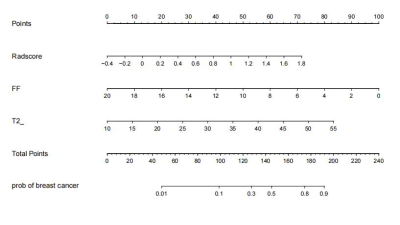
A prospective analysis was performed for 88 female patients with pathologically confirmed IDC who underwent breast 3.0T MRI examination using a 16-channel breast array coil (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Netherlands) in our hospital from December 2019 to September 2022, including 31 cases of high-grade (grade III.) and 57cases of low-grade (grade I-II). The clinical data and routine radiology characteristics of patients were collected (Table 1). The univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to screen the independent risk factors of clinical radiology of breast cancer histological grade, and a clinical radiology model was established based on independent risk factors. According to the dynamic contrast-enhanced image, the 3D slicer open-source software (https://www.slicer.org/) was used to manually delineate the region of interest (ROI) in the enhanced region of the FF image of mDixon-Quant sequence and extract the radiomics features. SPSS 21.0, python3.7 and R4.2.1 software packages were used for statistical analysis.The Mann-Whitney U test, intra-group correlation coefficient (ICC), and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression were used to screen radiomics features and establish the radiomics model. Radiomics scores (RadScore) were calculated by weighting and summing the selected features according to the corresponding coefficients in the LASSO regression. The logistic regression was used to combine the independent risk factors of clinical radiology with the RadScore to establish the combined model of clinical radiology and radiomics. An intuitive and visual nomogram was generated using R4.2.1 package .The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) and the calibration curve were used to evaluate the model performance. The Delong test was used to evaluate the difference in the area under the ROC curve (AUC) between different models. And the decision curve analysis (DCA) was used to evaluate the clinical value of the proposed model.Results
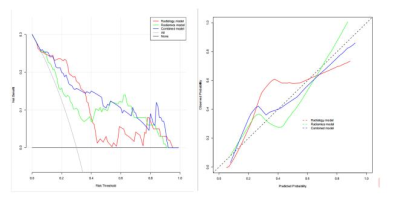
FF and T2* were statistically different between the two groups (p<0.001). Further multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that FF and T2* were still independent predictors of histological grade(p=0.014 and 0.008 respectively). The AUC of the clinical radiological model constructed by these two features was 0.782(0.678-0.885 95% CI) . A total of 851 radiomics features were extracted from each ROI, of which 10 radiomics features were associated with the histological grade of IDC. The AUC of the radiomics model was 0.834(0.742-0.925 95% CI). The AUC value of the combined model was 0.907 (Figure 1). The Delong test showed that the AUC value of the combined model was significantly higher than that of the clinical radiology model and radiomics model (p=0.028 and 0.012) . DCA showed that the clinical value of the combined model was higher than the radiomics model or the clinical radiology model (Figure 2), and the nomogram from the combined model was shown in Figure 3.Discussion
Based on the selected optimal radiomics features, a nomogram based on tumor radiomics features and traditional clinical image characteristics was constructed for predicting the histological grade of breast IDC, with an AUC of 0.907, higher than that of the model only using traditional clinical image characteristics (0.782) or radiomics features (0.834). This is similar to the results of Demircioglu et al.[7], who predicted histological grade based on MRI-radiomics model, but obtained relatively moderate results with an AUC of 0.75 (the sensitivity and specificity were both 0.72). The addition of mDixon-Quant MRI-based radiomics could improve the diagnostic performance with sensitivity and specificity of 0.933 and 0.768, respectively. The proposed method should be an effective supplement to conventional breast MRI for preoperative grading of breast IDC. However, the sample size of this study is relatively small, and more and more data should be included to enhance the model further.Conclusion
We have built a novel nomogram for grading breast IDC using mDixon-Quant MRI-based radiomics features and standard clinical imaging parameters, which showed a quite clinical potential because of the good performance.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018 ,68(6):394-424. DOI:10.3322/caac.21492.
[2] Zhang S, Huang S, Zhang H,et al. Histo- and clinico-pathological analysis of a large series of triple-negative breast cancer in a single center in China: Evidences on necessity of histological subtyping and grading.CHINESE J CANCER RES, 2020, 32(5):580-595.DOI:10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2020.05.03.[3] Granzier RWY, Ibrahim A, Primakov S, et al.Test–Retest Data for the Assessment of Breast MRI Radiomic Feature Repeatability[J]. J MAGN RESON IMAGING, 2022, 56(2):592-604.DOI:10.1002/jmri.28027.
[4] Kayadibi Y, Kocak B, Ucar N, et al. MRI Radiomics of Breast Cancer: Machine Learning-Based Prediction of Lymphovascular Invasion Status.ACAD RADIOL. 2022,29 (1):S126-S134.DOI:10.1016/j.acra.2021.10.026.
[5] Yin XX, Hadjiloucas S, Zhang Y.et al. MRI radiogenomics for intelligent diagnosis of breast tumors and accurate prediction of neoadjuvant chemotherapy responses-a review. COMPUT METH PROG BIO. 2022, 214:106510.DOI:10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106510.
[6] Lee JY, Lee KS, Seo BK, et al. Radiomic machine learning for predicting prognostic biomarkers and molecular subtypes of breast cancer using tumor heterogeneity and angiogenesis properties on MRI. EUR RADIOL. 2022,32(1):650-660.DOI:10.1007/s00330-021-08146-8.
[7] Demircioglu A, Grueneisen J, Ingenwerth M, et al. A rapid volume of interest-based approach of radiomics analysis of breast MRI for tumor decoding and phenotyping of breast cancer. PLoS One. 2020,15(6):e0234871.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0234871.