2728
Diagnostic value of APT, DWI, and DCE-MRI in molecular classification and prognosis of breast cancer
Xiaoyan Liu1,2, Baojian Wang2, Litao Zhang1, Zhenbo Ma1, Yanlei Wang2, Yishi Wang3, Xiujuan Li1, and Yuanzhong Xie1
1Taian City Central Hospital, Taian, China, 2Shandong First Medical University, Taian, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
1Taian City Central Hospital, Taian, China, 2Shandong First Medical University, Taian, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Breast, CEST & MT, Tumor;Amide proton transfer imaging;
According to the molecular classification of breast cancer, the clinical therapeutic strategy is formulated. Currently, the diagnostic value of amide proton transfer (APT) imaging in breast cancer is still unclear. This study aims to explore the diagnostic value of APT, DWI, and DCE-MRI in the molecular classification and prognosis of breast cancer. Our results showed that there were differences in TTP and BE values between luminal and non-luminal subtypes of breast cancer. The combination of APT, DWI, and DCE-MRI had the highest diagnostic efficiency. APT, DWI, and DCE-MRI parameters were correlated with different prognostic factors of breast cancer.Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common malignant tumor with high heterogeneity in women. Its different histological grades, molecular typing and gene expression make it possible to formulate various clinical treatment plans. At present, conventional scanning sequences of breast MRI include T1WI, T2WI, DWI and dynamic contrast enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI), but their application in breast diseases has certain limitations [1]. Amide proton transfer imaging(APT), as an imaging technique based on chemical exchange saturation transfer, indirectly reflects the content of free protein in vivo by detecting the exchange rate of amide protons on polypeptide chains and hydrogen protons in water and has been increasingly applied to the characterization of tumors. However, the value of APT in the diagnosis of breast cancer is still unclear, and there are relatively few reports about the application of APT in breast diseases. The purpose of this study is to explore the diagnostic value of APT, DWI and DCE-MRI in molecular classification and prognosis of breast cancer.Method
This prospective study was approved by the ethics committee of our hospital, and each patient signed an informed consent form. 48 cases of breast cancer treated in our hospital from November 2021 to September 2022 were selected and divided into Luminal subtype group (n=39) and non-Luminal subtype group (n=9) according to their molecular classification. T1WI, T2WI, DWI, APT and DCE-MRI scans were performed for all patients. The ADCb=800 value, asymmetric magnetization transfer rate with an offset of 3.5ppm[MTRasym (3.5 ppm)], maximum enhancement(ME), wash-in rate (WIR), time to peak(TTP), Brevity of Enhancement (BE) of the lesion were measured and compared. Then the diagnostic efficiency of MRI-related parameters in molecular typing of breast cancer was evaluated by using the ROC curve. Finally, the correlation between MRI parameters and different prognostic factors of breast cancer was analyzed by Spearman and Pearson correlation.Results and discussion
1. comparison of APT, DWI, and DCE-MRI parameters between luminal and non-luminal breast cancer patients.The TTP value and BE value of non-luminal subtype(Fig.2) were higher than those of luminal type, and the differences were statistically significant (P=0.017, 0.001, respectively), but the differences of ME, WIR, MTRasym and ADCb=800 values between the two groups were not statistically significant (P>0.05) (Table 1, Figure 1). The enhanced features of DCE-MRI could reflect breast cancer's blood supply and micro-vessel density. The results of this study suggest that the TTP and BE values of non-Luminal breast cancer are higher due to the strong proliferation of tumor cells and more micro-vessels.
2. Analysis of the diagnostic efficiency of APT, DWI, and DCE-MRI parameters in luminal and non-luminal breast cancer According to the results of binary logistic regression analysis, ME, TTP and WIR values in DCE-MRI model were independent predicting factors in the differentiation of luminal and non-luminal breast cancer (P = 0.030, 0.013, 0.031, respectively), among which TTP value had diagnostic efficacy, and there was a statistical difference between BE and WIR value (Z= 2.145, P = 0.032). The diagnostic efficiency of APT + DWI + DCE-MRI was the highest (Z = 1.351-3.820, P = 0.001-0.009). The AUC of the combination was 0.973, the sensitivity was 88.9%, and the specificity was 89.7%. The diagnostic efficiency of DCE-MRI had an AUC of 0.89 with a sensitivity of 77.8%, and a specificity of 74.4% (Fig. 3).
3. Correlation analysis of APT, DWI, DCE-MRI parameters, and different prognostic factors of breast cancer MTRasym value was positively correlated with T stage and WHO classification; MTRasym value was associated with PR expression; MTRasym value was positively correlated with Ki-67 index, while ADC value and ME value were negatively associated with Ki-67 index. TTP and BE values were correlated with molecular typing; BE was correlated with ER and PR expression (Fig. 4). The higher the tumor grade and stage, the stronger the proliferation ability and the more malignant degree. APT value reflects the protein proliferation ability in cells, so it is positively correlated with some prognostic factors of breast cancer.
Conclusion
APT, DWI and DCE-MRI can be used in the differential diagnosis of luminal classification of breast cancer and the evaluation of the prognosis of breast cancer.Acknowledgements
Youth Science Foundation Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81903010)References
Wang Ruhua, Zhang Yan, Cheng Jingliang, Huang Huiyu, Jin Yanan, Li Xiaoming, Zhang YongThree dimensional amide proton transfer weighted imaging and its combined diffusion weighted imaging in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Radiology, 2022,56 (03): 266-272Figures
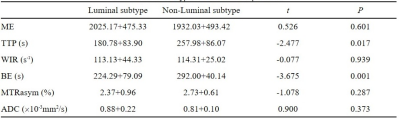
Tab.1 Comparison of APT, DWI and DCE-MRI parameters between luminal and non-luminal subtype breast cancer patients.
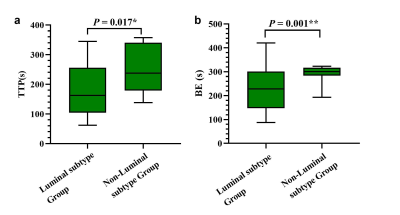
Fig.1 Box plots of TTP-value(a) and BE-value (b) between luminal and non-luminal subtype groups.
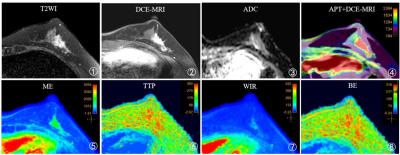
Fig. 2 A 52-year-old woman with non-special type invasive carcinoma of left breast, which molecular subtyping was HER-2 overexpression type. Averaged ADCb=800 value, APT value, ME value, TTP value, WIR value and BE value of the lesion were 2.12%, 0.390%, 0.88×10-3 mm2/s, 1668.16, 323.37s, 99.49s-1, 293.97s respectively.
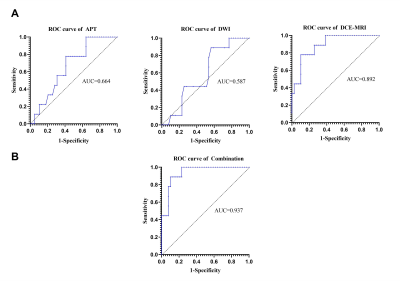
Fig. 3 ROC curves of APT, DWI, DCE-MRI models and APT+DWI+DCE-MRI models for differentiating luminal and non-luminal breast cancer.
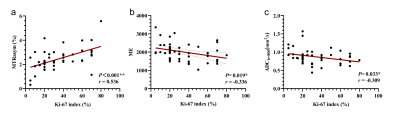
Fig. 4 Correlation between APT signal value(a), ME value(b), ADCb=800 value(c) and Ki-67 proliferation index.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2728