2723
Reliability and sensitivity of fMRI at 3T and 1.5 T: metrics toward fMRI guided individualized precise TMS treatment1Center for Cognition and Brain Disorders, The Affiliated Hospital of Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou, China, 2Zhejiang Key Laboratory for Research in Assessment of Cognitive Impairments, HangZhou, China, 3Institute of Psychological Sciences, Hangzhou Normal University, HangZhou, China, 4Hangzhou Normal University Affiliated Deqing Hospital, HangZhou, China, 5Yong Zhang, GE Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Data Acquisition, fMRI
FDA cleared a TMS treatment protocol with fMRI-guided individualized targeting for major depressive disorder. This protocol was based on 3T scanner. However, 1.5 T MRI is more widely available in hospitals. We comprehensively tested the reliability and sensitivity of fMRI metrics related to TMS treatment on 1.5T and 3T scanners. In general, the sensitivity of 3T is larger than 1.5T. However, the reproducibility of peak FC location and the activation location, the reliability of RS-fMRI local metrics, are similar for 1.5T and 3T. In conclusion, 1.5 fMRI meets the needs for guiding individualized precise rTMS treatment.Introduction
On September 1, 2022, FDA cleared a transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) system with fMRI-guided individualized treatment protocol for major depressive1 , emphasizing the importance of individualized TMS therapy in clinical routine. Most fMRI-guided TMS treatment studies have used 3T scanners2, however, 1.5 T MRI scanner is more widely available in hospitals. To ascertain whether fMRI data on 1.5T field strength scanners are practical for fMRI-guided rTMS, we evaluate the reliability and sensitivity of fMRI metrics at 3T and 1.5T scanners.Methods
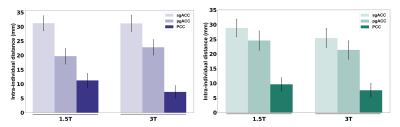
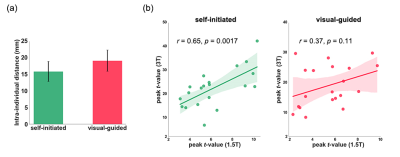
Twenty subjects were scanned with both resting-state fMRI (RS-fMRI) and task fMRI at 1.5T and 3T. The RS-fMRI included two eyes open (EO) runs and one eyes closed (EC) run in a counterbalanced order across participants and scanners. Finger-tapping task fMRI included self-initiated (SI) and visual-guided (VG) finger movement tasks. A systematic evaluation of test-retest reliability and sensitivity of the RS-fMRI local metrics including the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF), percent amplitude of fluctuation (PerAF), Wavelet based amplitude of low frequency fluctuations (Wavelet-ALFF), degree centrality (DC), regional homogeneity (ReHo) was conducted in a voxel-wise whole-brain analysis. Furthermore, to assess the reproducibility of fMRI-guided potential target, we examined the intra-individual distance between the peak locations of seed-based FC (with three seed regions (subgenual cingulate cortex anterior (sgACC), pregenual ACC (pgACC), posterior cingulate cortex (PCC)) of two RS-fMRI scans. In addition, the consistency of peak activation location and intensity of finger tapping task on 1.5T and 3T scanners was estimated by intra-individual distance and Pearson correlation coefficient for SI and VG condition, respectively.Results
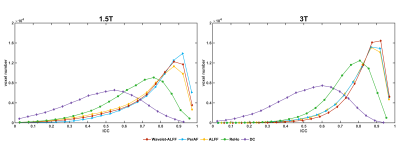
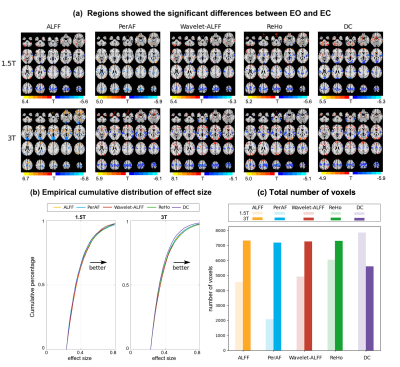
The test-retest reliability of the RS-fMRI local metrics was higher in 3T than 1.5T, with similar trends: PerAF ≈ Wavelet-ALFF ≈ALFF > ReHo > DC (Figure1). In addition, Wavelet-ALFF showed a relatively larger effect size and number of voxels for detecting the differences between EO and EC in all five RS-fMRI local metrics (Figure2). The intra-individual distance for the individualized FC peak location at 1.5T was 9.6 – 31.2mm, comparable to that of 3T (7.6 – 31.1mm) (Figure3). For the consistency of finger tapping task fMRI on 1.5T and 3T, the mean intra-individual distance between 1.5T and 3T data for the peak activation location of SI condition and VG condition was 15.8mm and 19mm, respectively. A strong correlation of the peak activation intensity was observed between 1.5T and 3T for the SI condition than the VG condition (r = 0.65 and 0.37, respectively) (Figure4).Discussion and conclusion
The reliability and sensitivity of fMRI metrics exhibited a similar trend at 1.5T and 3T. The intra-individual reproducibility of fMRI-guided potential target defined by peak FC location and activation location is comparable between 1.5T and 3T, which is in line with studies completed at 3T3,4.These findings provide an important reference for individualized rTMS target definition on 1.5T and 3T scanners. These results indicate that the 1.5T scanner could be applied to fMRI-guided individualized rTMS treatment.Acknowledgements
Work supported by Key Realm R&D Program of Guangdong Province (2019B030335001), Key Medical Discipline of Hangzhou.References
1 Devices@FDA 501k approval: K220177, Magnus Neuromodulation System (MNS) with SAINT Technology, Model Number 1001K, Premarket Notification 510(k). accessdata.fda.gov. Published September 1, 2022. Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/pmn.cfm?ID=K220177. [Accessed 01 Sep 2022].
2 Cole, E. J. et al. Stanford accelerated intelligent neuromodulation therapy for treatment-resistant depression. American Journal of Psychiatry 177, 716-726 (2020).
3 Cash, R. F. H. et al. Personalized connectivity-guided DLPFC-TMS for depression: Advancing computational feasibility, precision and reproducibility. Human Brain Mapping 42, 4155-4172, doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.25330 (2021).
4 Zhao, N. et al. The Location Reliability of the Resting-State fMRI FC of Emotional Regions Towards rTMS Therapy. Neuroinformatics, doi:10.1007/s12021-022-09585-4 (2022).
Figures