2721
Spin-echo-based generalized Slice Dithered Enhanced Resolution (gSLIDER) for mesoscale fMRI at 3 Tesla1Radiology, SF VA Medical Center, San Francisco, CA, United States, 2Northern California Institute of Research and Education, San Francisco, CA, United States, 3Radiology, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, United States, 4Division of Radiological Sciences Laboratory, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Pulse Sequence Design, Contrast Mechanisms, Neuro
We demonstrate sub-millimeter generalized Slice Dithered Enhanced Resolution (gSLIDER) for high-resolution spin-echo (SE) fMRI at 3T. Activations were significantly greater than standard SE fMRI, demonstrating the suitability of this method for high-resolution, mesoscale fMRI.Synopsis
We demonstrate sub-millimeter generalized Slice Dithered Enhanced Resolution (gSLIDER) for high-resolution spin-echo (SE) fMRI at 3T. Activations were significantly greater than standard SE fMRI, demonstrating the suitability of this method for high-resolution, mesoscale fMRI.Introduction
Submillimeter spin-echo based functional MRI (fMRI) at ultra-high-field can resolve neural architecture at the level of columns and layers1,2. Such scanners are limited in number so there is strong incentive to develop techniques for sub-millimeter functional imaging at lower field strengths, despite limitations in sensitivity and specificity to microvascular sources of BOLD activations. Slice Dithered Enhanced Resolution (SLIDER) methods can increase SNR efficiency using thicker slices that overlap spatially. Initial approaches used thick slices with a dithered spatial offset to achieve twice the SNR for fMRI3,4. In contrast, generalized SLIDER (gSLIDER) uses RF encoding instead of spatial offsets for an orthogonal basis set which allows for maintaining higher SNR after deblurring/thin-slice reconstruction5,6. Although originally designed for sub-millimeter diffusion MRI, gSLIDER’s SE-based contrast should also reduce large vein bias to facilitate mesoscale fMRI. To evaluate the suitability of gSLIDER for fMRI, we compared gSLIDER against standard SE using a visual stimulation paradigm at 1mm and 0.8mm isotropic resolutions.Methods
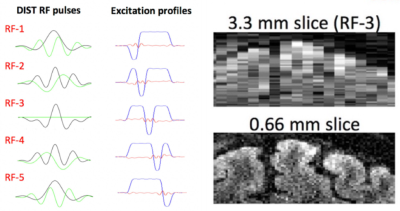
Data was acquired on 2 healthy volunteers in a Siemens 3T Prisma using a 64ch head/neck coil. Subjects viewed a visual hemifield localizer stimulus (35s blocks and 9 repetitions per hemifield) presented with PsychoPy v2021. Trigger pulses were added per slice to the pulse sequence to facilitate syncing between sequence and stimulus delivery. Data collection: 1mm iso whole brain gSLIDER/SE scans: In plane FOV = 220x220 mm; PF = 6/8; GRAPPA 3; MB=2, TE = 69 ms; TR = 17.5s (3.5s per dithered volume); Slice Thickness = 1mm (Slab Thickness = 5mm); PE direction = AP. 0.8mm isotropic whole brain gSLIDER/SE scans were also collected: Matrix = 270x270; PF = 6/8; GRAPPA 3; TE = 79 ms; TR = 17.5s (3.5s per dithered volume); Slice Thickness = 0.8mm (Slab Thickness = 4mm); PE direction = AP. gSLIDER reconstruction: 5 thick-slab volumes were acquired, each with slabs 5x the thickness of the final slice resolution and with a different slice phase (Figure 1). Custom MATLAB code incorporating magnitude, phase data and B1 maps processed the reconstruction into time series for analysis. The slab combination used Tikhonov regularization, wherein a larger regularization parameter (λ) results in greater residual blurring but reduced noise7 and λ = 0.1 was used in the current study. fMRI analyses: gSLIDER and SE functional analyses used identical GLM-based AFNI pipelines. A T-test was performed for a right versus left hemifield contrast. Results were cluster thresholded at p<0.1, k=30. Extent of activation (voxel counts after thresholding) were calculated within skull-stripped brain masks.Results
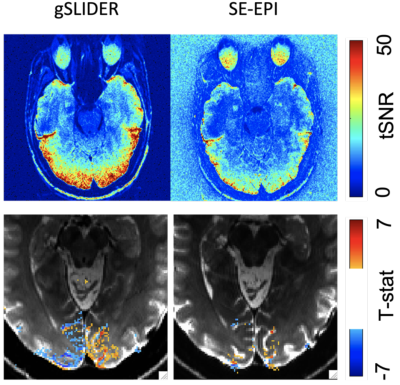
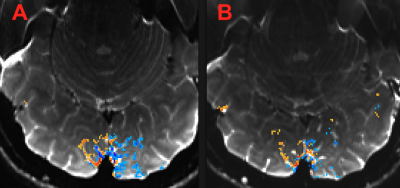
Figure 2 demonstrates in a representative slice ~2x high tSNR and greater activation extent with gSLIDER vs traditional SE whole brain data at 1mm isotropic resolution. This slice demonstrates an almost 300% increase in activation extent from gSLIDER over standard SE. Figure 3 demonstrates the same pattern with 0.8mm isotropic whole brain data. This slice demonstrates an 82% increase in activation extent from gSLIDER over standard SE. Head motion was comparable between subjects.Conclusion
This work demonstrates that gSLIDER is a strong alternative to traditional SE in ways that make mesoscale functional imaging possible at 3T. With ~2x the tSNR of SE fMRI, gSLIDER at 3T approaches a specificity and sensitivity combination typically seen at higher field strengths like 7T. A limitation of the spin-echo-based gSLIDER sequence is the slow temporal resolution due to the need for T1 relaxation between each RF encoding. Future work will include more tissue-based quantitative comparisons and will additionally be aimed at improving the temporal resolution of gSLIDER with sliding window reconstruction approaches or Stimulus Locked approaches8.Acknowledgements
Grants R01EB028670, UCSF RAP REAC AwardReferences
1: Yacoub, et al Robust detection of ocular dominance columns in humans using Hahn Spin Echo BOLD functional MRI at 7 Tesla. Neuroimage, 2007; 37(4):1161-77
2: Huber, et al. High-Resolution CBV-fMRI Allows Mapping of Laminar Activity and Connectivity of Cortical Input and Output in Human M1. Neuron vol. 96,6 (2017)
3: Vu, et al. Evaluation of SLIce Dithered Enhanced Resolution Simultaneous MultiSlice (SLIDER-SMS) for human fMRI. NeuroImage, 2018; 164: 164–171
4: Feinberg, Vu, Beckett. Pushing the limits of ultra-high resolution human brain imaging with SMS-EPI demonstrated for columnar level fMRI. Neuroimage, 2018, 164:155-163
5: Setsompop et al, High-resolution in vivo diffusion imaging of the human brain with generalized slice dithered enhanced resolution: Simultaneous multislice (gSlider-SMS). 2017, MRM, 79(1)
6: Liao, et al High-fidelity, high-isotropic-resolution diffusion imaging through gSlider acquisition with B1+ and T1 corrections and integrated ΔB0/Rx shim array. MRM, 2020, 83(1)
7: Beckett, et al Evaluation of spin-echo generalized Slice Dithered Enhanced Resolution (gSLIDER) for high-resolution fMRI at 3T. Proc. ISMRM 2021
8: Vu AT, Beckett A, Feinberg DA, Mukherjee P. StImulus Locked K-space shuffling (SILK) for ultra-high resolution fMRI. Proc. ISMRM 2018.
Figures