2606
Association of Lumbar Trabecular Bone Ultrashort Echo Time Magnetization Transfer Ratio (UTE-MTR) with Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
Jian-Bang Zhang1, Jin Liu1, Jia-Xin Feng1, Jianwei Liao1, Wei Li1, Xiao-Jun Chen1, Long Qian2, Ya-Jun Ma3, and Shao-Lin Li1
1Department of Radiology, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Zhuhai, China, 2GE Healthcare, Beijing, China, 3Department of Radiology, University of California San Diego, San Diego, CA, United States
1Department of Radiology, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University, Zhuhai, China, 2GE Healthcare, Beijing, China, 3Department of Radiology, University of California San Diego, San Diego, CA, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Bone, Skeletal
Ultrashort echo time magnetization transfer (UTE-MT) technique can non-invasively quantify the macromolecular component changes. It has great potential to assess intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD). In this study, we utilized the UTE-MT sequence to investigate the relationship between UTE-MT ratio (UTE-MTR) measurements of lumbar trabecular bone and IVDD. We found that the lumbar trabecular bone UTE-MTR negatively correlated with the IVDD grading. It demonstrates that the UTE-MTR of lumbar trabecular bone may serve as a useful biomarker to assess IVDD.Introduction
The intervertebral disc (IVD) is supplied by capillaries that largely arise in the vertebral bodies. Vertebral body structural or compositional changes may play an important role in intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) [1]. Magnetization transfer (MT) is able to assess collagenous matrix non-invasively [2]. UTE sequence is able to detect both bound and free water signals in trabecular bone, thus providing more accurate MT measurements [3]. In this study, we utilized the combination of UTE and MT technique (i.e., UTE-MT) to investigate the relationship between UTE-MT ratio (UTE-MTR) measurements of lumbar trabecular bone and IVDD.Methods
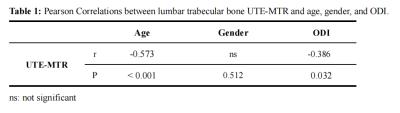
A total of 120 patients with IVDD (age 47 ± 9 years, age range 35-66) were recruited and scanned with UTE-MT sequence in lumbar on a 3T MRI scanner (Signa, Pioneer, GE Healthcare). Informed consent was obtained from all participants in accordance with the Institutional Review Board. A Fermi pulse was employed to generate the MT contrast in the UTE-MT sequence with a duration of 8 ms and bandwidth of 160 Hz. The frequency offset of this MT pulse was 1500 Hz. The UTE-MT sequence was scanned twice with flip angle of 750° for MT-On and 0° for MT-Off. Other UTE-MT sequence parameters were as follows: TR = 100 ms, TE = 0.032 ms, excitation flip angle = 5°, number of spokes per-TR = 5, FOV = 28cm × 28cm, matrix = 140 × 140, slice thickness = 3.6mm, and slice number = 16, oversampling factor = 1.2, and scan time = 3min. The UTE-MTR is calculated by the signal ratio of the difference between UTE-MT-OFF and UTE-MT-ON to the UTE-MT-OFF. To evaluate each disc, the UTE-MTR values of the adjacent upper and lower vertebral bones were calculated and averaged. The grade of IVDD was assessed using the Pfirrmann scoring system. Pearson correlation analysis was performed to calculate the correlations between lumbar trabecular bone UTE-MTR and age, gender, and ODI, respectively. A one-way ANOVA test was used to compare lumbar trabecular bone UTE-MTR between different grades of disc degeneration. A value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.Results
Figure 1 shows the representative UTE-MTR maps from two subjects (a 36‐year‐old male and a 50‐year‐old male). The lumbar trabecular bone UTE-MTR showed a negative correlation with the grade of IVDD (r= 0.263, P < 0.001) (Figure 2). Moreover, it is also shown that the lumbar trabecular bone UTE-MTR was negatively correlated with both age (r = -0.573, P < 0.001) and ODI (r = -0.386, P = 0.032), while had no association with gender. The results were summarized in Table 1.Discussion and Conclusion
To our best knowledge, this is the first prospective study of applying UTE-MT measurement in the lumbar trabecular bone to assess IVDD. Our results showed that the patients with IVDD have significantly lower UTE-MTR values in the lumbar trabecular bone. This means that the partial loss of the integrity of the vertebral bone collagen matrix may lead to an insufficient nutrition supply for IVD and further lead to IVDD. Our study suggests that the UTE-MTR measurements of lumbar trabecular bone may be a useful biomarker to predict IVDD.Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge grant support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 82172053) and the National Institutes of Health (R21AR075851 and R01AR079484).References
[1] Jung M, Rospleszcz S, Löffler MT et al (2022) Association of lumbar vertebral bone marrow and paraspinal muscle fat composition with intervertebral disc degeneration: 3T quantitative MRI findings from the population-based KORA study. Eur Radiol. 10.1007/s00330-022-09140-4
[2] Ma YJ, Chang EY, Carl M, Du J (2018) Quantitative magnetization transfer ultrashort echo time imaging using a time-efficient 3D multispoke Cones sequence. Magn Reson Med 79:692-700
[3] Ma YJ, Jerban S, Jang H, Chang D, Chang EY, Du J (2020) Quantitative Ultrashort Echo Time (UTE) Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Bone: An Update. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 11:567417
Figures

Figure 1:
Representative ultrashort echo time magnetization transfer ratio (UTE-MTR) maps in
lumbar spine. Figure a: a 36‐year‐old male volunteer
without intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD); Figure b:
a 50‐year‐old male volunteer with IVDD.
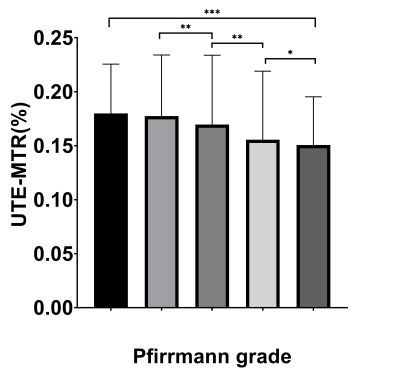
Figure 2: Correlation between lumbar trabecular bone ultrashort
echo time magnetization transfer ratio (UTE-MTR) and Pfirrmann grade of intervertebral
disc degeneration (IVDD) for a total of 120 subjects. Lumbar trabecular bone
UTE-MTR showed a negative correlation with the Pfirrmann grade of IVDD.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2606