2554
The diagnostic performance of time-dependent diffusion technique in differentiating benign and malignant breast tumors
Jie Ding1,2,3, Zhen Zhang3, Yajia Gu1,2, Yishi Wang4, Xiuzheng Yue4, Dazhi Chen3, Rongrong Zhu3, and Ruoshui Ha3
1Department of Radiology, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China, 2Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai, China, 3People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan, China, 4Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
1Department of Radiology, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China, 2Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai, China, 3People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan, China, 4Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Breast, Cancer
Some novel biomarkers have emerged from the fact that the ADC depends strongly on the diffusion time, such as the rate of ADC change using two diffusion times for the differentiation of breast tumor types and cell size modeling. In this study, we propose to use Multiband (MB) SENSE to accelerate the data acquisition of OGSE and PGSE sequences and compare the diagnostic value of ADC at different diffusion times as well as cell size imaging parameters using IMPULSED model for breast tumor. Our data showed vin and cellularity and the rate of ADC change have superior diagnostic performance.Introduction
Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) has been widely established as a diagnostic biomarker. Some novel biomarkers have emerged from the fact that ADC depends strongly on the diffusion time, such as the rate of ADC change using two diffusion times for the differentiation of breast tumor types and a cell size modeling technique called IMPULSED using three diffusion times. These novel techniques typically use a combination of oscillating gradient spin echo (OGSE) and pulsed gradient spin echo (PGSE) sequences for data acquisition, which usually requires a long TR, hence long scan time for the acquisition of multiple b values, diffusion times and large spatial coverage. In this study, we propose to use Multiband (MB) SENSE to accelerate the data acquisition and compare the diagnostic value of IMPULSED quantitative parameters and derived ADC from different diffusion times for breast tumor.Methods
Data acquisitionBoth OGSE and PGSE sequences were implemented and data were acquired on a Philips 3T scanner (Ingenia CX, Best, The Netherlands). 45 female patients (mean age, 50.18 years) suspected of breast tumor/cancer were recruited between Feb 2021 to Aug 2022 and 51 lesions were analyzed (33 benign and 18 malignant). The study was approved by the IRB of People's Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region and written informed consent was obtained from all the patients. The breast imaging protocol consisted of routine sequences (T1w, T2w, DCE) and an IMPULSED protocol, using MB=2. The sequence parameters for the IMPULSED protocol were listed in Table 1. Two OGSE sequences of 50Hz and 25 Hz and one PGSE sequence were used as reported in a previous study(2) (the corresponding diffusion time = 5 ms, 10 ms and 74 ms respectively). FOV =340×255mm2, in-plane resolution = 3*3 mm2, 16 slices with 5 mm slice thickness and 1 mm gap.
Data analysis
The IMPULSED quantitative parameters and derivative ADC values were calculated using in-house software based on MATLAB. Regions of interest (ROIs) were drawn on each lesion by a radiologist with 5 years of experience, referring to the DCE images, with necrosis, hemorrhage and cyst excluded. The diagnostic performances to differentiate malignant and benign breast tumors for IMPULSED quantitative parameters (Vin, Diameter, Dex and Cellularity)and ADC (ADC-N1, ADC-N2, ADC-PG, ADC-PG1000, ADC%N1-PG, ADC%N2-PG) were investigated using the receiver operating characteristic curves (ROCs). The cutoff values were determined using Youden index. Formula of ADC value change rate were ADC%N1-PG=(ADCOGSEN1-ADCPGSEN1)/ADCOGSEN1,ADC%N2-PG=(ADCOGSEN2-ADCPGSEN2)/ADCOGSEN2.
Results
The AUCs of the Vin, Diameter, Dex and Cellularity were 0.80, 0.59, 0.60, and 0.79 respectively. The AUC of the six compound ADC (ADC-N1,ADC-N2,ADC-PG,ADC-PG1000,ADC%N1-PG,ADC%N2-PG ) were 0.71, 0.59, 0.75, 0.75,0.69 and 0.80 respectively. The sensitivity and specificity and the cutoff values were listed in Table 2-3.Discussion and conclusion
In malignant lesions, the cell density is larger and the diffusion restriction of intracellular water molecules is more obvious than that in benign lesions, so intracellular volume fraction and cellularity in the cancerous tissues were higher, and extracellular diffusion coefficient was lower with malignant lesions than in benign lesions. In this study, intracellular volume fraction and cellularity had the best diagnostic performance than Dex and Diameter. The ADC value of malignant lesions was lower than that of benign lesions, but the change rate of ADC value of malignant lesions was higher than that of benign lesions, which was consistent with reports in the literature. The AUC of ADC%N2-PG was the largest. In this study, the specificity and sensitivity of ADCPG-1000 and ADC%N2-PG in the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions were higher than other ADC and derived parameters.Acknowledgements
Ningxia Natural Science Foundation, Project No.2022A0194
Science and Technology Development Project of Ningxia People's Hospital,Project No.201924
References
1. Iima M, Kataoka M, Honda M, et al. The Rate of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Change With Diffusion Time on Breast Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Depends on Breast Tumor Types and Molecular Prognostic Biomarker Expression. Investigative radiology 2021;56(8):501-508.
2. Xu J, Jiang X, Li H, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of mean cell size in human breast tumors. Magnetic resonance in medicine 2020;83(6):2002-2014.
Figures
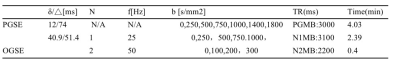
Table1,The detailed parameters and scan time for the TDS protocols

Table2,The AUC,sensitivity,specificity and the cutoff values of Impulsed quantitative parameters
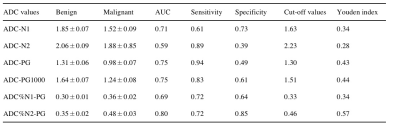
Table3,The AUC,sensitivity,specificity and the cutoff values of compound ADC values
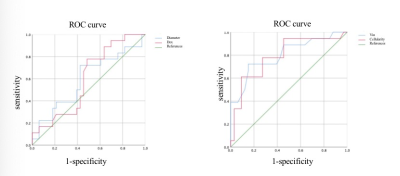
Figure1,The ROC curve of IMPULSED quantitative parameters
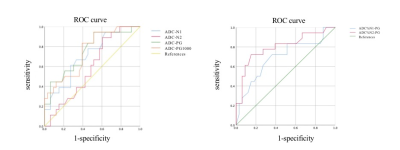
Figure2,The ROC curve of compound ADC values
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2554