2504
Application of imaging omics based on DCE-MRI,DWI, and APT in glioma IDH-1 and Ki-67 prediction
zhenguo Yuan1, hexin Liang1, and Yuhan Wang2
1Shandong Provincial Hospital, Shandong, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
1Shandong Provincial Hospital, Shandong, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Tumors, Brain
We developed and validated radiomic models based on DWI, DCE, and APTw sequences to evaluate Ki-67 proliferation and IDH-1 mutation in gliomaIntroduction
To investigate the application value of support vector machine model based on diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) and amide proton transfer weighted (APTW) imaging in predicting isocitrate dehydrogenase 1(IDH-1) mutation and Ki-67 expression in glioma.Methods
The DWI, DCE and APTw images of 81 patients with glioma confirmed by pathology were retrospectively analyzed and divided into IDH-1 group and Ki-67 group according to the purpose of the study. IDH-1 group was divided into IDH-1(+) group and IDH-1(-) group according to IDH-1 mutation status, and Ki-67 group was divided into positive group (Ki-67≤25%) and strong positive group (Ki-67 > 25) according to Ki-67 expression level. The volume of interest (VOI) was manually delineated on the obtained images and radiomics features were extracted. All cases were divided into training group and validation group according to 70%∶30%. The training group was used to screen features and establish machine learning models. Mann-Whitney U test and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) have been completed. The support vector machine (SVM) model was established with the data after feature screening. Four single sequence models and one combined model were established in IDH-1 group and Ki-67 group. The receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the diagnostic performance of the model, and the results were expressed as the area under the curve (AUC), accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative prediction rates. Validation group data is used for further validation.Results
Both IDH-1 mutation and Ki-67 expression status were predicted by the single sequence model, but the combined model had the best performance, which was superior to the single sequence model. In the Ki-67 group, the combined model was built from six selected radiomics features, yielding AUC values of 0.965 and 0.931 in the training and validation sets, respectively. In the IDH-1 group, the combined model was built from four selected radiomics features, yielding AUC values of 0.997 and 0.967 in the training and validation sets, respectively.Discussion
DWI sequence reflects tumor cell density, DCE sequence reflects tumor capillary formation and permeability, and APTw sequence reflects the content of free protein in tumor. These FMRI sequences can provide us with a lot of useful information. The diagnostic performance of our combined model with the addition of FMRI sequences is better than that of previous studies, which is consistent with our hypothesis.Conclusion
The radiomics model established by DWI, DCE and APTw images can be used to detect IDH1 mutation status and Ki-67 expression in glioma patients before surgery. The radiomics model constructed with combined sequences performs better than the single sequence model.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.Figures
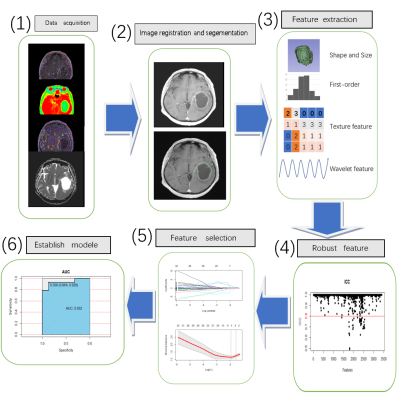
Figure 1 shows that (1) ADC, Ktrans, Ve and APTw maps are registered together with corresponding CE-T1WI images using 3D-Slicer. (2) Manually delineate. (3) Extract radiomic features. (4) Features with intra-group correlation coefficient (ICC) > 0.8 were retained, and (5) features were screened using the minimum absolute contraction and selection operator (LASSO). (6) Construct single and multi-sequence image omics models and compare the AUC, sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of different models.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2504