2501
A Novel Biomimetic Nanodrug with High Reactive Oxygen Species Production for Precision Combination Therapy of Glioblastoma
Haiyan Gao1 and Meiyun Wang1,2
1Henan provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2Laboratory of Brain Science and Brain-Like Intelligence Technology, Institute for Integrated Medical Science and Engineering, Henan Academy of Sciences, Zhengzhou, China
1Henan provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2Laboratory of Brain Science and Brain-Like Intelligence Technology, Institute for Integrated Medical Science and Engineering, Henan Academy of Sciences, Zhengzhou, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Tumors, Brain
This project intends to innovatively design and synthesize novel radiotherapy sensitization and enhanced CDT dual-effect sensitization nanodrugs, further wrap them with engineered red blood cell membrane vesicles, and construct a high-performance biomimetic nanomedicine synergistic treatment system with high targeting, high specificity and high yield of reactive oxygen species, in order to achieve the specificity and high efficiency accumulation of nanomedicines in the GBM, while reducing toxicity to normal tissues. Magnetic resonance and other imaging methods are used to guide the efficient treatment of drugs and monitor the effect of tumor ablation.Background and Purpose
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common primary tumor in the brain, accounting for 82% of malignant gliomas in the brain, with a 5-year survival rate of 5.5%, seriously endangering social health [1]. Radiation therapy (RT) combined with chemotherapy is the main treatment for unresected GBM, but its clinical treatment results are unsatisfactory [2]. With the penetration of nanotechnology into the medical field, combination therapy has entered the public’s eye, providing new ideas for the development of a new generation of radiotherapy synergistic systems [3]. Chemodynamic therapy (CDT) is a new type of tumor treatment technique based on the transformation reaction of endogenous chemical products in tumors using Fenton or Fenton-like reactions [4]. However, CDT alone is limited by the low efficiency of the Fenton catalytic reaction and the low reactive oxygen species (ROS) yield. Studies have shown that the external energy field X-ray can improve the catalytic activity of Fenton reagent, accelerate its redox cycle, promote the regeneration of Fenton reaction materials, and continuously lead to high ROS yield, which will provide a new way to achieve high-efficiency treatment of GBM [5]. Based on the above analysis, the combination of radiotherapy sensitization and CDT to prepare a novel and high-yield ROS dual-effect sensitization system will provide a new idea for the treatment of GBM.Methods
As shown in Figure 1, we explored a sensitizer based on high atomic number (high-Z) metal nanoparticles and magnetic nanoparticles for dual sensitization of both RT and CDT (referred as RCT sensitizer), the sensitizer was triggered by X-ray to produce high yield of ROS. Meanwhile, through in vivo genetic engineering strategy, NGR tripeptide, an effective tumor targeting ligand, was displayed outside the red-blood-cell membranes-derived nanovesicles to produce a large number of bioengineered cell membrane nanovesicles (BCMNs) for tumor targeted delivery of RCT. At the in vitro, the high-yield of ROS induced by RCT as well as its mechanisms will be investigated. Subsequently, the characteristics and mechanisms of dual sensitization therapy induced by biomimetic nanomedicines are thoroughly analyzed in glioblastoma cell lines that are very resistant to radiotherapy. Furthermore, fluorescence imaging (FL)/magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)/computed tomography (CT) imaging and therapeutic study are performed in subcutaneous and orthotopic tumor bearing mice to demonstrate the biomimetic nanomedicine precision combination therapy in vivo application.Results and Discussions
We successfully synthesized RCT nanosensitizing drugs formed byand characterized them by modern materials science technology, Using cell membrane encapsulation technology, we successfully encapsulated RCT nanosensitizing drugs to obtain targeted NGR-BCMNs@RCT nanomedicines, we studied its performance, preliminary studies found that the RCT nanoparticles have good X-ray radiotherapy sensitizing activity and promote Fenton response activity, producing a large number of hydroxyl radicals under the condition of pH 5.4 and hydrogen peroxide, This is because the RCT nanoparticles with this heterostructure have higher stability and superior performance. And at the same time, the photodynamic activity of RCT nanoparticles and NGR-BCMNs@RCT nanomedicines is excited, producing a large amount of singlet oxygen. These properties give NGR-BCMNs@RCT nanomedicine significant anti-glioblastoma activity. Next, subcutaneous and in situ models of glioblastoma were established using U87 cells, and the pre-experimental results further verified the high targeting, specificity, and diagnostic performance of NGR-BCMNs@RCT biomimetic nanomedicine. FL results showed that NGR-BCMNs@RCT nanomedicine group was efficiently enriched in tumor regions compared to the NGR blocking group after 12 hours (Figure 2a, 2b), due to the enhanced blood-brain barrier penetration and targeting effect of the nanomedicine. And the strong signal emitted by the nanomedicine at the tumor site can be clearly observed from the CT image (Figure 2c, 2d), suggesting that the NGR-BCMNs@RCT biomimetic nanodrug had in vivo CT imaging contrast agent performance. T2-weighted MRI was also performed on glioblastoma mice in situ, the results showed that the nanomedicines were an effective magnetic resonance contrast agent that could be used to guide glioblastoma treatment (Figure 2e, 2f).Conclusion
The biomimetic chemoradiotherapy sensitization system with high yield of reactive oxygen species developed in this project is an important supplement to the combination of traditional radiotherapy and chemotherapy drugs, and is crucial to improve the survival rate and disease control of glioblastoma.Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province, China (222300420354, 212300410240), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81720108021, 81601466, 82001783), Medical Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province (SBGJ202101002).References
[1]. Ostrom QT, Patil N, Cioffi G, Waite K, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2013–2017. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, iv1–iv96.[2]. Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD, Rich JN, Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006, 444(7120):756–760.[3]. Song G, Cheng L, Chao Y, Yang K, Liu Z. Emerging Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials for Cancer Radiation Therapy. Adv. Mater 2017, 29(32):1-26.[4]. Tang Z, Zhao P, Wang H, Liu Y, Bu W. Biomedicine Meets Fenton Chemistry. Chem Rev 2021,121(4):1981-2019.[5]. Zhang C, Wang X, Dong X, Mei L, Wu X, Gu Z, Zhao Y. X-ray-facilitated redox cycling of nanozyme possessing peroxidase-mimicking activity for reactive oxygen species-enhanced cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 276:1-11.Figures
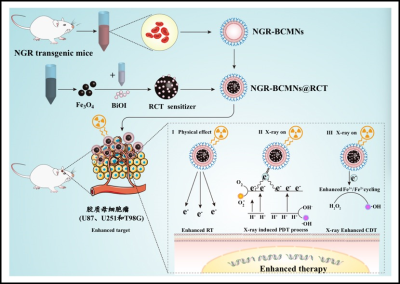
Figure 1. Construction of NGR-BCMNs@RCT nanomedicine and their effects on targeting and efficient treatment of glioblastoma cell lines
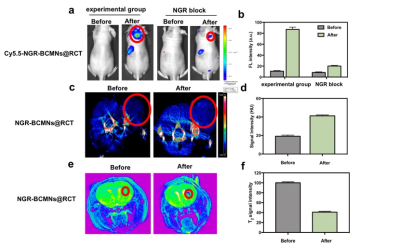
Figure 2. (a) fluorescence images of U87 tumor-bearing mice and NGR-blocked mice before and after intravenous administration of nanomedicine; (b) The corresponding quantification analysis of fluorescence intensity of tumor region; (c) CT images of U87 subcutaneous tumor-bearing mice injected with nanomedicine; (d) Before and after comparison of CT signal intensity in tumor; (e) T2-weighted MRI of U87 in situ tumor-bearing mice injected with nanomedicine; (f) Before and after comparison of T2 signal intensity in tumor. Red dots mark the tumor area.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.58530/2023/2501