2498
Histogram analysis of APT Combined with DTI and DSC MRI for Predicting IDH Mutation and MGMT promotor methylation Status in Glioma1Department of Radiology, Union hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430022, China., Wuhan, China, 2Department of Neurosurgery, Union hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430022, China., Wuhan, China, 3People's Hospital of Dongxihu District, Wuhan, Hubei, China., Wuhan, China, 4Department of Pathology, Union hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430022, China., Wuhan, China, 5Clinical & Technical Solutions, Philips Healthcare, Beijing 100600, China., Wuhan, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Tumors, Multi-Contrast
In this study, the diagnostic performance of histogram features of APT, DTI and DSC in predicting IDH mutation and MGMT promoter methylation status of gliomas was compared. Secondly, the histogram parameters from the signal-time intensity curve of DSC significantly improved the predictive performance of DSC model. Most importantly, the combined logistic regression model combined with APT, DTI and DSC can evaluate the tumor nature of glioma more comprehensively and obtain better diagnostic performance, which is expected to become an imaging molecular marker for the prediction of glioma genotyping in the future.Introduction
The overall survival and response to treatment of glioma are highly related to both WHO grade and molecular characteristics. Molecular markers are more consistent with the tumor entity and better predictive of its clinical behavior. Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutations are considered as early driver mutations in gliomas and are now the molecular basis for glioma classification. O6-methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter is described as a relevant biomarker for clinical decision making in the treatment of glioblastoma. The post-hoc analysis of phase III clinical trials showed that the importance of IDH and MGMT promoter methylation status in the choices of treatment regimens and survival rate for glioma patients(1-3). Several previous studies have explored the value of preoperative multimodal MRI in predicting IDH mutations and MGMT promoter methylation status in gliomas, including diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC), MR spectroscopy (MRS) et al. Amide proton transfer (APT), the most developed branch of chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging, that depends on the concentrations of endogenous cellular proteins, is considered effective in detecting glioma genotyping. The study purpose was to investigate the significances of histogram analysis of APT, DTI and DSC MRI metrics in non-invasively predicting IDH mutation and MGMT promoter methylation status in gliomas.Methods
173 patients with suspected brain tumors were recruited to undergo APT, DTI and DSC scan. Totally 74 patients were assessed eventually in this prospective study. T1-weighted (T1WI), fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR), contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (CE-T1WI), APT, DTI and DSC MRI sequences was performed at 3T. The fifteen associated histogram features from parameters maps of APTw, relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV), relative cerebral blood flow (rCBF), mean transit time (MTT), time-to-peak (TTP), T0, fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity (MD), axial diffusivity (AD) and radial diffusivity (RD) were analyzed in the regions of the tumor core and peritumoral edema, respectively. Eight structural imaging features were visually evaluated on structural MRI scans. Logistic regression analysis and receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis was performed to build predictive models and evaluate the predictive performances.Results
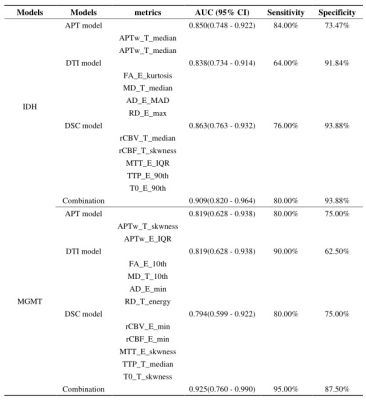
The participants’ clinical characteristics are summarized in Table 1. The median of APTw in the tumor core (APTw_T_median) yielded highest AUCs in IDH-mutation status prediction (AUC, 0.805; sensitivity, 76.0%; specificity, 79.6%) (Table 2). The skewness of APTw in the tumor core (APTw_T_skewness) achieved the best performance in MGMT promotor methylation status prediction (AUC, 0.806; sensitivity, 80.0%; specificity, 75.0%) (Table 3). The multivariate logistic regression combination models may enhance the discrimination of IDH-mutation and MGMT promotor methylation status and obtained balanced sensitivity and specificity, especially for MGMT promotor methylation(Table 4 and Figure 1).Discussion
This study investigated the abilities of APT, DTI, and DSC parameters to detect IDH mutation and MGMT promotor methylation status and demonstrated the non-invasive predictability of IDH mutation status in gliomas, with the best performance using the median of APTw from tumor core. The skewness of APTw may be an imaging marker to predict the MGMT promoter methylation status. Interestingly, the above histological imaging metrics are more feasible to predict IDH mutations than MGMT promoter methylation. The mutations in Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) facilitate the production of 2-hydroxyglutarate(2-HG), leading to competitive inhibition of α-ketoglutarate-dependent enzyme, resulting in different epigenetic histone and DNA modifications(4), and consequently changes in cellular metabolism and protein content. MGMT promotor methylation leads to reduce the expression of DNA repair protein and attenuate tumor resistance to alkylated chemotherapy(4). APT reflects changes in intracellular protein content at the molecular level. Thus, APT is sensitive to alterations in protein content of glioma caused by IDH mutations, the methylation status of the MGMT promoter. MGMT methylation may inhibit MGMT from regulating angiogenesis in GBM through key positive regulators. In our study, the minimum of rCBV in edema may be used to predict MGMT promoter status. In addition, MTT, TTP, and T0 that may be ignored in many previous studies were significantly different between mutant and wild IDH gliomas, which improved the predictive performance of IDH mutation status combined with rCBV and rCBF. The combination of multi-parametric MRI could comprehensively evaluate the internal components of the tumor, the destruction of surrounding tissue structures, tumor angiogenesis, and blood perfusion, which are important indicators of aggressivity in glioma. What’s more, histogram analysis could better reflect the heterogeneity within the region of interest compared with a simple calculation of the mean values for various metrics(5).Conclusion
APT is a promising non-invasive method for predicting IDH-mutation and MGMT promotor methylation status in glioma, especially for MGMT promotor methylation status. The combination of appropriate histogram parameters achieved a more efficient approach to predict molecular characteristics in gliomas.Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2021CFB447) and the Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan 430071, P.R. China(T152201).References
1. Bell EH, Zhang P, Shaw EG, et al. Comprehensive Genomic Analysis in NRG Oncology/RTOG 9802: A Phase III Trial of Radiation Versus Radiation Plus Procarbazine, Lomustine (CCNU), and Vincristine in High-Risk Low-Grade Glioma. J Clin Oncol 2020;38(29):3407-3417.
2. Tesileanu CMS, Sanson M, Wick W, et al. Temozolomide and Radiotherapy versus Radiotherapy Alone in Patients with Glioblastoma, IDH-wildtype: Post Hoc Analysis of the EORTC Randomized Phase III CATNON Trial. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2022;28(12):2527-2535.
3. Gorlia T, van den Bent MJ, Hegi ME, et al. Nomograms for predicting survival of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: prognostic factor analysis of EORTC and NCIC trial 26981-22981/CE.3. Lancet Oncol 2008;9(1):29-38.
4. van der Meulen M, Ramos RC, Mason WP, Von Deimling A, Maas SLN. Opinion & Special Article: Glioma Classification: How to Interpret Molecular Markers in a Diffuse Glioma Pathology Report. Neurology 2022.
5. Kamimura K, Nakajo M, Yoneyama T, et al. Histogram analysis of amide proton transfer-weighted imaging: comparison of glioblastoma and solitary brain metastasis in enhancing tumors and peritumoral regions. European radiology 2019;29(8):4133-4140.
Figures
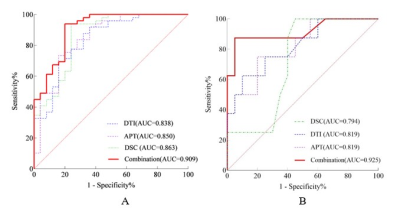
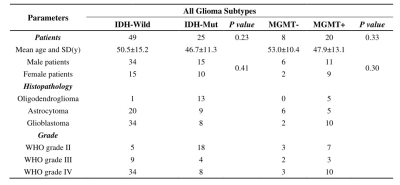
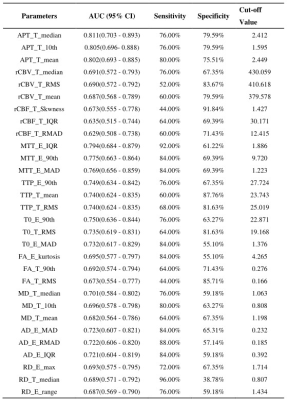
Table 2. The top-three performance of every metrics in IDH Genotyping of all Gliomas.
10th, 10 percentile; 90th: 90 percentile; IQR: interquartile range; max: maximum; MAD: mean absolute deviation; RMAD: robust mean absolute deviation; RMS: root mean squared; APT: amide proton transfer; FA: fractional anisotropy; MD: mean diffusivity; AD: axial diffusivity; RD: radial diffusivity; rCBF: relative cerebral blood flow; rCBV: relative cerebral blood volume; MTT: mean transit time; TTP: time-to-peak; T: tumor; E: edema
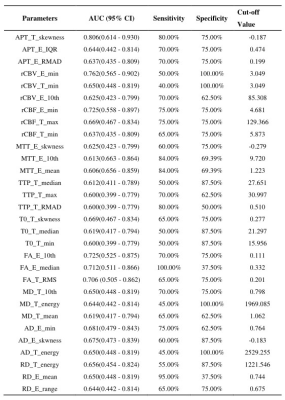
Table 3. The top-three performance of every metrics in MGMT genotyping of all gliomas.
10th, 10 percentile; 90th: 90 percentile; IQR: interquartile range; max: maximum; MAD: mean absolute deviation; RMAD: robust mean absolute deviation; RMS: root mean squared; APT: amide proton transfer; FA: fractional anisotropy; MD: mean diffusivity; AD: axial diffusivity; RD: radial diffusivity; rCBF: relative cerebral blood flow; rCBV: relative cerebral blood volume; MTT: mean transit time; TTP: time-to-peak; T: tumor; E: edema