2490
The effect of different expressions of Delta-catenin on the properties of small world brain network in breast cancer patients before chemotherapy1The department of radiology, the first Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Tumors, Cancer, BRCA patients, Delta-catenin, Resting-state fMRI
This work aimed to explore the effects of different expressions of Delta-catenin in breast cancer(BRCA) patients based on small-world brain network. The results showed that the expression status of Delta-catenin proteins had significant differences on the small-world brain network properties of patients.Background
Delta-catenin was first found in the central nervous system. Recently, several studies have shown that Delta-catenin also plays an oncoprotein role in the development of tumors[1,2].Therefore, this prospective longitudinal study aimed to investigate the effect of different expressions of Delta-catenin protein on the small-world brain network properties of BRCA patients. It was of great clinical significance to analyze whether this protein can be used as a biomarker to evaluate the prognosis of BRCA and to develop molecular targeted drugs for it.Materials and methods
In total, 113 patients with BRCA confirmed by pathology without chemotherapy were prospectively recruited into our study. According to the different expressions of Delta-catenin protein, BRCA patients were divided into high expression group ( DP group, 54 patients) and low expression group ( DN group, 59 patients ). For comparison, 41 health controls (HC group) were also included. Resting-state fMRI (rs-fMRI) sequences were scanned for all subjects with gradient echo EPI sequence using GE HDXT3.0T scanner. The clinical data of all subjects were collected, and all subjects were evaluated by detailed neuropsychological scales, including MMSE, MoCA, etc. The small-world brain network attribute indexes of all subjects were calculated and the rs-fMRI image data were preprocessed by DPABI.The brain network properties were processed by GRETNA software. Then, the SPM12 toolkit was used for group-level statistical analysis.Results
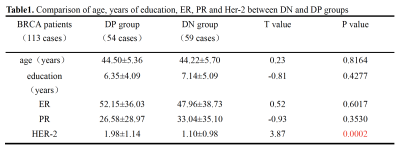
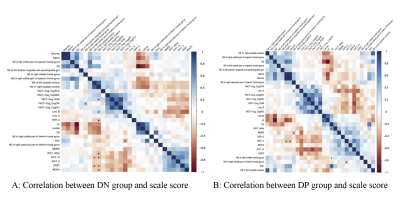
There was no significant difference in age, years of education, estrogen and progesterone between DP and DN groups. There was a statistical difference in HER-2 ( t = 3.87, P = 0.0002 ) ( see Table1). Cognitive score correlation analysis of these two groups showed that there were brain regions with statistical significance. In the DN group, NE in the bilateral caudate nucleus was negatively correlated with DSST and AVLT (short-term memory), ELOC was negatively correlated with Line-B, while NE in the right caudate nucleus was positively correlated with Line-B and FACT-Cog-SUM. In the DP group, AVLT ( long-term memory ) σ and γ were negatively correlated, and NE in the right inferior frontal gyrus was negatively correlated with MMSE. AVLT (delayed memory) was positively correlated with CP ( aggregation coefficient ), right middle frontal gyrus and ELOC ( local efficiency ) ( see Figure1).The difference in the area under the curve ( AUC ) value of sparsity between the three groups illustrated that : 1) Compared with the HC group, DN group had increased node efficiency in bilateral orbital superior frontal gyrus, right middle frontal gyrus, right orbital inferior frontal gyrus, right opercular inferior frontal gyrus and bilateral caudate nucleus. 2) In DP group, the nodal efficiency increased in bilateral orbital superior frontal gyrus, right orbital inferior frontal gyrus, right opercular inferior frontal gyrus and bilateral caudate nucleus. Left anterior cingulate and lateral cingulate node efficiency decreased. (Figure2)
Discussion
In recent years, more and more scholars believe that Delta-catenin as an important target of tumor biological therapy provides a feasible experimental basis[3]. However, only a few literatures reported the increased expression of Delta-catenin associated with poor prognosis of BRCA[4,5].The difference of node efficiency of AUC value between the three groups showed that there were some brain regions with increased node efficiency in both DN and DP groups, and some brain regions were negatively correlated with cognitive score, which may be explained by the increase of cerebral blood perfusion. Zou et al. [6] showed that, based on the rs-MRI, brain regions with high cerebral blood flow tended to increase ALFF and ReHo values accordingly. These increased brain regions were consistent with the brain regions of DMN (default mode network), which could explain the increase of NE in brain regions. However, in the DP group, the node efficiency of the left anterior cingulate and paracingulate decreased, indicating that Delta-catenin protein has a significant effect on the node efficiency of the brain region, and the cingulate plays a key role in cognitive functions such as memory, emotion and action[7].Due to the complexity structure of Delta-catenin, it acts on a wide range of protein interactions, and affects kinds of diseases[8,9]. The results above show that the Delta-catenin have effects on the small-world brain network, although it cannot directly indicate that the Delta-catenin with high expression plays the role of oncoprotein, this result also proves that Delta-catenin has great differences on BRCA patients, further horizontal and vertical study after chemotherapy is required.
Conclusion
Different expression levels of Delta-catenin protein altered the small-world brain networks of BRCA patients, resulting in a series of clinical symptoms including cognitive impairment and memory loss. It is expected that the investigation of molecular targeted drugs for Delta-catenin has important clinical significance to BRCA.Acknowledgements
Thanks to all my colleaguesReferences
[1]Mi jin Lee,Isa Tas,Rui Zhou,et al.Development of a Multiplex Bead-Based Method for the Microquantitation of δ-Catenin[J].Journal of nanoscience and nanotechnology,2020,20(9): 5819-5822.
[2]Fei Huang,Junying Chen,Zeng Wang,et al.δ-Catenin promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma[J].Oncology reports,2018,39(2):809-817.
[3]Zhang JY, Wang Y, Zhang D, et al. δ-catenin promotes malignant phenotype of non-small cell lung cancer by non-competitive binding to E-cadherin with p120ctn in cytoplasm[J].J Pathol,2010,222:76–88.
[4]Di Zhang,JunYi Zhang,En-Hua Wang et al.δ-catenin promotes the malignant phenotype in breast cancer[J].Tumour biology: the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine,2015,36(2):569-75
[5]Chenfei Huang,Steven,Verhulst,Yi Shen et al.AKR1B10 promotes breast cancer metastasis through integrinδ-catenin mediated FAK/Src/Rac1 signaling pathway[J].Oncotarget,2016,7(28): 43779-43791
[6]Zou Q, Wu CW, Stein EA, et al. Static and dynamic characteristics of cerebral blood flow during the resting state. Neuroimage, 2009, 48(3): 515-524.
[7]Rolls ET. The cingulate cortex and limbic systems for emotion,action,and memory[J]. Brain Struct Funct, 2019, 224(9): 3001-3018.
[8]Taeyong Ryu,Hyung Joon,Park Hangun,et al.Improved memory and reduced anxiety in δ-catenin transgenic mice.[J].Experimental neurology,2019,318:22-31.
[9]Adegbola Abidemi,Lutz Richard,Nikkola Elina,et al.Disruption of CTNND2,encoding delta-catenin causes a penetrant attention deficit disorder and myopia[J].HGG advances, 2020, 1(1).
Figures
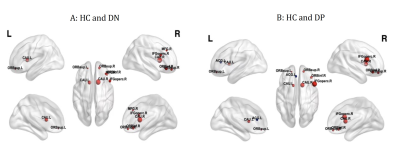
Between-group differences in the nodal efficiency over AUC values
Figure A: DN increased AUC in bilateral orbital part of superior frontal gyrus, right middle frontal gyrus, right opercular part inferior frontal gyrus, right orbital part inferior frontal gyrus and bilateral caudate nucleus, compared with HC
Figure B: DP increased AUC in bilateral orbital part of superior frontal gyrus, right opercular part inferior frontal gyrus, , right orbital part inferior frontal gyrus, bilateral caudate nucleus, and decreased in anterior cingulate and paracingulate gyri, compared with HC