2478
Feasibility of pointwise encoding time reduction with radial acquisition (PETRA) MR angiography for assessment of intracranial arteries at 7T1Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, United States, 2Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc., Jacksonville, FL, United States
Synopsis
Keywords: Blood vessels, High-Field MRI, PETRA-MRA, 7T
PETRA-MRA is a non-contrast subtraction-based MRA technique for intracranial-vasculature assessment. Compared to TOF, PETRA-MRA is robust to turbulent-flow-related signal voids and metallic-susceptibility artifacts. 7T MRI should further improve the performance of PETRA-MRA due to higher SNR allowing improved spatial-resolution. Here we demonstrate the feasibility and performance of PETRA-MRA at 7T in evaluating intracranial-vasculature. 7T 3D-TOF and PETRA-MRA were performed on volunteers. The blood-to-background contrast ratio for PETRA-MRA was significantly higher than TOF. PETRA-MRA also has better cerebral-artery-visualization with more uniform artery blood signal and comparable sharpness. Overall, PETRA-MRA is a promising technique for evaluating cerebral-arteries at 7T.Introduction
Pointwise encoding time reduction with radial acquisition magnetic resonance angiography (PETRA-MRA) is a non-contrast subtraction-based MRA technique for intracranial vasculature assessment. As a zero-TE technique, PETRA-MRA is inherently robust to metallic susceptibility artifacts and has better performance than time-of-flight (TOF) MRA in follow-up imaging of stent-assisted coil embolization1. Furthermore, unlike TOF, PETRA-MRA is not subject to turbulent-flow-related dephasing artifacts and therefore has better performance in depicting saccular unruptured intracranial aneurysms2. Lastly, PETRA-MRA produces much lower acoustic noise. 7T MRI should further improve the performance of PETRA-MRA due to higher SNR allowing improved spatial resolution. On the other hand, PETRA-MRA at 7T presents challenges such as increased SAR and limited B1 coverage in the labeling regions. To our knowledge, no previous PETRA-MRA study has been reported at 7T for imaging intracranial arteries. We aim to demonstrate the feasibility and performance of PETRA-MRA at 7T in evaluating intracranial vasculature.Purpose
To investigate the feasibility of PETRA-MRA and compare its performance to TOF on evaluating intracranial vasculature at 7T.Methods
In compliance with institutional regulations, 3D TOF and PETRA-MRA scans, which were both prototype sequences, were performed on volunteers on the investigational pTx part of a Siemens 7T MAGNETOM Terra (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with an investigational Nova 8Tx/32Rx head coil (Nova Medical Inc., Wilmington, MA, USA). The 3D TOF was performed in an axial orientation with the following parameters: FOV = 200 ×148 mm2, voxel size = 0.4 × 0.4 × 0.4 mm3, TR/TE = 17.00/3.57 ms, flip angle = 20°, GRAPPA acceleration factor of PE = 3, bandwidth = 206 Hz/Px, and acquisition time (TA) = 8 min 38 s. For PETRA-MRA, the isotropic 3D acquisitions were performed with axial orientation and the following imaging parameters: FOV = 218 ×218 mm2, TR/TE = 5.72/0.07 ms, flip angle = 6°, imaging matrix = 544 × 544, voxel size = 0.4 × 0.4 × 0.4 mm3, bandwidth = 204 Hz/Px, and radial view number = 40,000. Two imaging datasets were acquired for PETRA MRA: TAG, a slice-selective saturation slice was placed at the skull base; Control, the same slice-selective saturation slice was placed on top of the head to achieve comparable MT effects on the imaging volume. The segmentation number of saturation pulse was set to 15 and the saturation slice thickness was set to 80 mm to achieve desired black blood effects on the TAG images. The acquisition time for each TAG and CONTROL is 4 min 39s. We also acquired additional TAG and CONTROL pair with higher resolution (0.3x0.3x0.3 mm3) and the acquisition time is 6 min 37s each. The PETRA MRA images were obtained by subtracting the TAG image from the CONTROL image. The MIP images of PETRA-MRA and TOF were reviewed by two MRI scientists. Visualization of Circle of Willis and lenticulostriate arteries were independently evaluated, focusing on artery blood signal homogeneities and sharpness using a 4-point scale: 4, excellent; 3, good; 2, poor; 1, not assessable. For raw images before MIP, the contrast ratio between the middle cerebral arteries and background tissue were calculated and compared between PETRA-MRA and TOF.Results
The contrast ratio between the middle cerebral arteries and background tissue for PETRA MRA was significantly higher than TOF (12.66+/- 1.45 vs 5.85+/-1.67, p< 0.001). The subjective image scores regarding artery blood signal homogeneities were higher in PETRA-MRA than in TOF, and sharpness was comparable between PETRA-MRA and TOF.Discussion
Sensitivity of PETRA-MRA in the detection of residual flow, turbulent flow, and saturation effects is superior to that of TOF because zero-TE MRA is known to decrease susceptibility artifacts and is insensitive to slow blood flow. Our results indicate that at 7T, PETRA-MRA showed a higher blood-to-background contrast ratio compared to TOF. In addition, PETRA-MRA can cover the whole cerebral vasculature, while TOF is not able to image the top part of the brain due to placement of venous saturation band. Another advantage of PETRA-MRA is its greatly reduced acoustic noise compared to TOF, which is ideal for noise sensitive patients. One limitation of PETRA MRA is the subtraction-based method that is sensitive to motion, but this could be further addressed by rigid 3D registration to reduce the motion induced discrepancy between TAG and CONTROL images.Conclusions
PETRA-MRA, with better visualization of cerebral arteries including lenticulostriate arteries and higher contrast-to-background ratio than TOF, is a promising technique for evaluating cerebral arteries at 7T.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Heo YJ, Jeong HW, Baek JW, et al. Pointwise Encoding Time Reduction with Radial Acquisition with Subtraction-Based MRA during the Follow-Up of Stent-Assisted Coil Embolization of Anterior Circulation Aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2019;40(5):815-819.
2. Fu Q, Liu DX, Zhang XY, Deng XB, Zheng CS. Pointwise encoding time reduction with radial acquisition in subtraction-based magnetic resonance angiography to assess saccular unruptured intracranial aneurysms at 3 Tesla. Neuroradiology 2021;63(2):189-199.
Figures
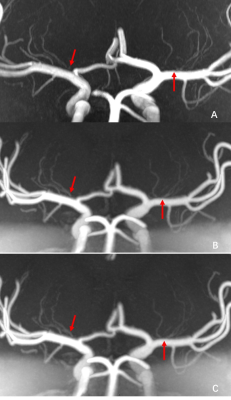
Figure 1:
A: 7T TOF MRA with 0.4mm isotropic resolution shows poor visualization of the origin of several lenticulostriate arteries (red arrows).
B: PETRA-MRA with 0.4mm isotropic resolution can visualize continuity of the small vessels at the origin of the lenticulostriate arteries (red arrows).
C: PETRA-MRA with 0.3mm isotropic resolution can visualize continuity of the small vessels at the origin of the lenticulostriate arteries (red arrows).