2476
The value of high resolution black blood 3D T1-VISTA-MSDE in the detection of cerebral venous sinus1Xijing Hospital, Air Force Medical University, Xi 'an, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Keywords: Blood vessels, Blood vessels, black blood, venous sinus thrombosis
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST) is one of ischemic cerebrovascular diseases with low morbidity and high mortality. Three-dimensional volumetric isotropic turbo spin echo acquisition(3D-VISTA)can be adopted, which has high resolution and most blood signals will be suppressed. In addition, a motion-sensitized and fault-driven equilibrium(MSDE) technology were applied for more thorough blood suppression. 3D-VISTA showed SNR and CNR were significantly higher than when compared with enhanced three-dimensional TFE sequence, which could more accurately identify CVST. 3D-VISTA sequence can be used to improve the recognition rate of craniocerebral veins, which could provide valuable evidence for accurate identification of clinical craniocerebral venous thrombosis.
Introduction
Craniocerebral venous thrombosis is a disease that tend to be easily misdiagnosed and mistreated in clinical practice. Digital subtraction cerebral angiography (DSA) is the gold standard for the diagnosis of CVST, but invasive operation and risk of increased intracranial pressure limit its widespread application . The enhanced magnetization preparation rapid gradient echo sequence is commonly used to diagnose cerebral venous thrombosis. But there is some interference in the recognition of thrombus due to the contrast agent filling the venous blood tube after enhancement. The traditional 3D-TFE enhanced sequence cannot be completely relied upon by the radiologist due to the risk of missed diagnosis in some small venous thrombi and the volumetric effect of contrast enhancement [1][2].Three-dimensional volumetric isotropic turbo spin echo acquisition with motion-sensitized and fault-driven equilibrium (3D-VISTA-MSDE) sequence can suppress blood signals. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate whether 3D-VISTA-MSDE could improve the accurate identification of cerebral venous thrombosis.Methods
14 patients who had been clinically suspected to have craniocerebral venous thrombosis were recruited from May to October 2022. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were performed on a 3.0T Philips scanner (Ingenia CX, Best, the Netherlands) with a 32-channel head coil. Patients underwent contrast enhanced with 3D-TFE and 3D-VISTA sequences, Detailed sequence parameters are shown in Table 1. Two senior radiologists (LY, 13 years with experience and WMQ 15 years with experience) evaluated the images of patients with cerebral thrombosis. Signal to noise ratio (SNR) and contrast noise ratio (CNR) were calculated for evaluating image quality[3]. For each patient, the frequency of the two groups with definite cerebral venous thrombosis was calculated according to the upper arachnoid sinus, lower arachnoid sinus, straight sinus, sinuses, left and right transverse sinus, and left and right sigmoid sinus. Paired Chi-square test was performed on the statistical data with SPSS statistical software (IBM SPSS Statistics 21 ). P<0.05 was regarded as significantly difference.Results
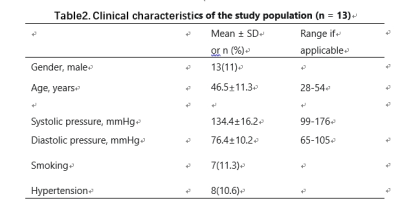
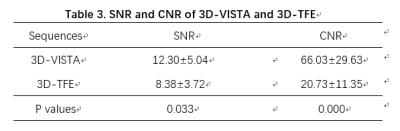
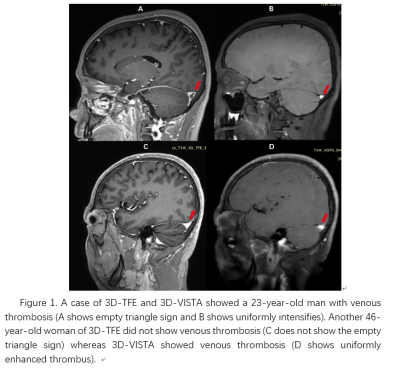
13 patients (54.6 ±8.2 years old, 10 males) were enrolled while one patient was excluded because obvious motion artifacts affect image observation in this study. Detailed information of patients was shown in Table 2. SNR and CNR of 3D-VISTA sequence were significantly higher than that of 3D-TFE (P=0.033, P<0.001) in Table 3 . The kappa value of κ was 0.373 (p <0.001)between 3D-VISTA and 3D-TFE in Table4.The representative case showed in figure 1.Discussion
The current study revealed that 3D-VISTA sequence can significantly improve the detection of cerebral venous thrombosis, which had better performance of SNR and CNR when compared with traditional sequence. The diagnostic significance of 3D-VISTA sequence for cerebral venous thrombosis was higher than that of 3D-TFE sequence. 3D-VISTA sequence had complete blood inhibition due to blood empty-flow effect and the pair of motion sensitive gradients (similar to the bipolar gradients of diffusion sequence) [4]. Through motion sensitive gradients, tissue signals of flow (movement) are attenuated for further inhibit blood [5]. The limitations was the small number of cases and the lack of multi-sequence joint contrast diagnosis.Conclusion
Enhanced 3D-VISTA sequence can significantly improve clinical recognition of craniocerebral venous thrombosis.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement.References
[1] Niu, PP, Yu, Y, Guo, ZN, et al. Diagnosis of non-acute cerebral venous thrombosis with 3D T1-weighted black blood sequence at 3T. J NEUROL SCI. 2016; 367 46-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2016.05.052 [2]Yang, X, Wu, F, Liu, Y, et al. Diagnostic performance of MR black-blood thrombus imaging for cerebral venous thrombosis in real-world clinical practice. EUR RADIOL. 2021; 32 (3): 2041-2049. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08286-x [3] Wintersperger, BJ, Runge, VM, Biswas, J, et al. Brain tumor enhancement in MR imaging at 3 Tesla: comparison of SNR and CNR gain using TSE and GRE techniques. INVEST RADIOL. 2007; 42 (8): 558-63. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e31803e8b3f [4]Yang, Q, Fan, Z, Bi, X, et al. Early detection and quantification of cerebral venous thrombosis by Magnetic Resonance Black Blood Thrombus Imaging (MRBTI) J CARDIOVASC MAGN R. 2016; 18 (S1): doi: 10.1186/1532-429x-18-s1-p16 [5]Hakim, A, Kurmann, C, Pospieszny, K, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of High-Resolution 3D T2-SPACE in Detecting Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. AM J NEURORADIOL. 2022; 43 (6): 881-886. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7530Figures